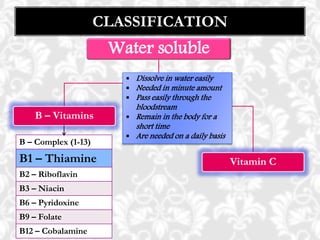
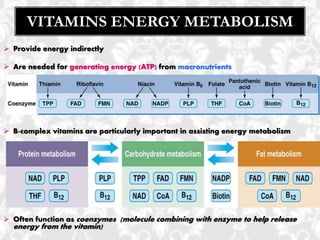
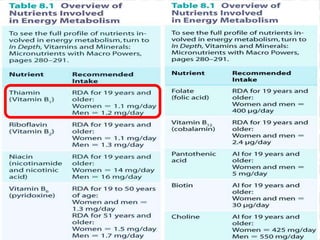
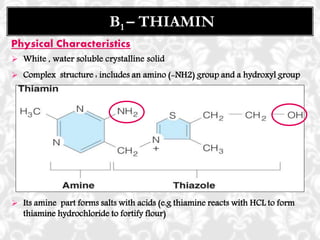
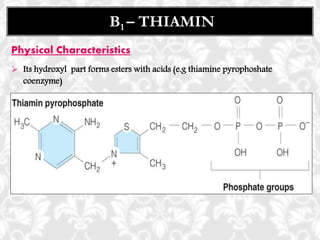
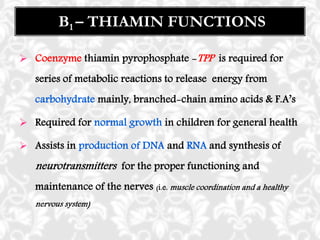
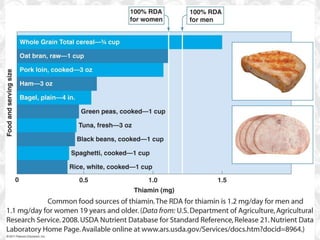
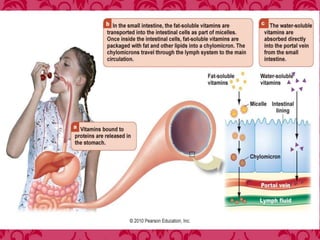
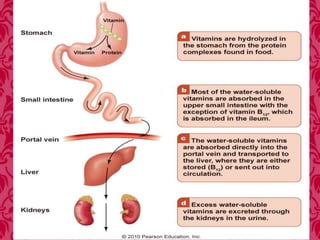
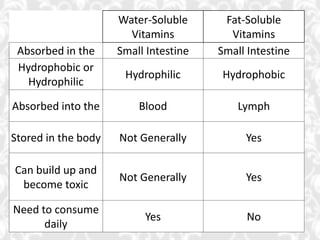
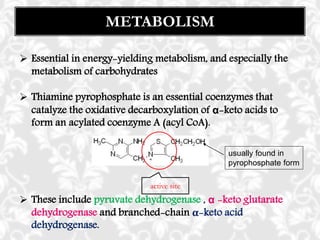
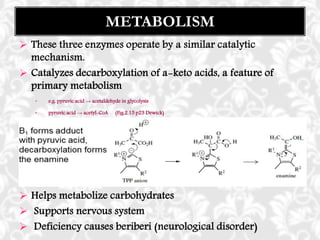
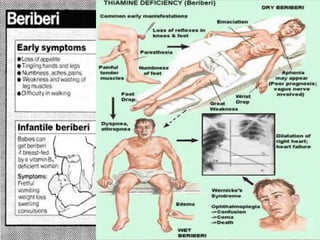
This document discusses vitamin B1 (thiamine). It begins by classifying B1 as a water-soluble vitamin that is part of the B-complex group. It then describes B1's functions in energy metabolism and as a coenzyme. Sources of B1 are also listed, including pork, liver, beans and enriched grains. The document concludes by covering absorption in the small intestine, deficiencies that can arise from inadequate intake such as beriberi, and issues related to toxicity.