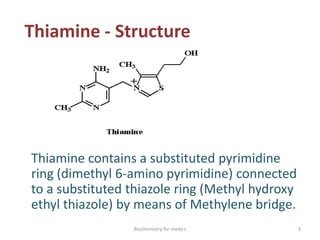
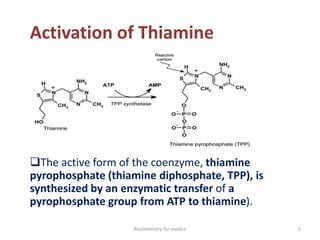
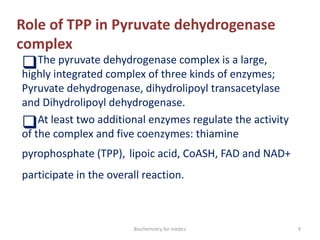
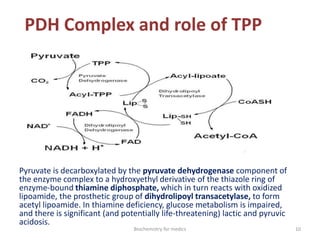
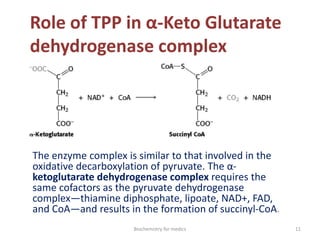
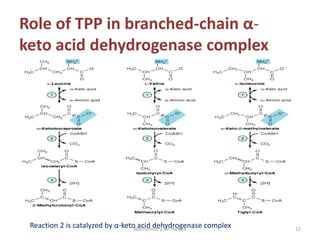
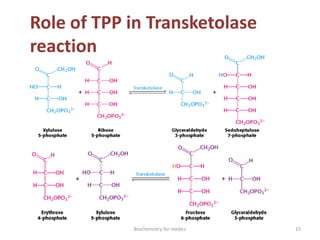
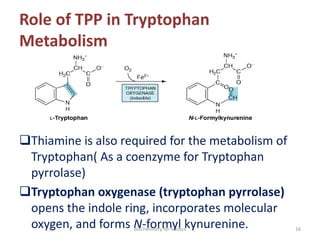
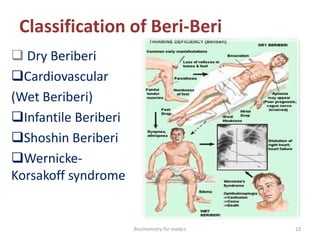
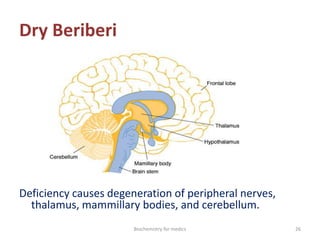
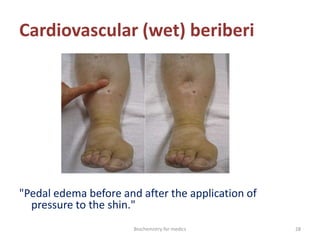
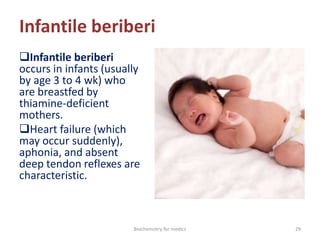
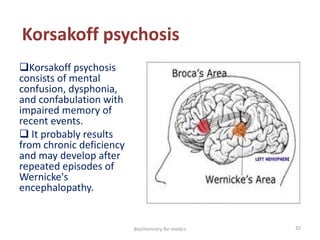
Thiamine (vitamin B1) is an essential cofactor required for several enzyme reactions involved in carbohydrate metabolism. It is present in plant and microbial sources but not synthesized by animals. A deficiency impairs the metabolism of pyruvate, α-ketoglutarate, and branched-chain amino acids, most severely affecting the nervous system and heart. Deficiency causes diseases like beriberi, characterized by peripheral neuropathy or heart failure. Treatment involves high-dose thiamine supplementation.