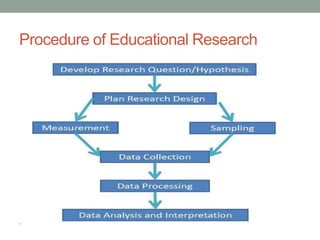
The document outlines the steps of the educational research process. It begins with identifying a research problem and reviewing relevant literature. This is followed by specifying the purpose of the study and describing the methodology for collecting and analyzing data. The final steps are interpreting the results and reporting findings to relevant audiences who can then evaluate and apply the research. The scientific method involves identifying a problem, formulating a hypothesis, deducing implications to test through evidence collection, and verifying whether the evidence supports the hypothesis.