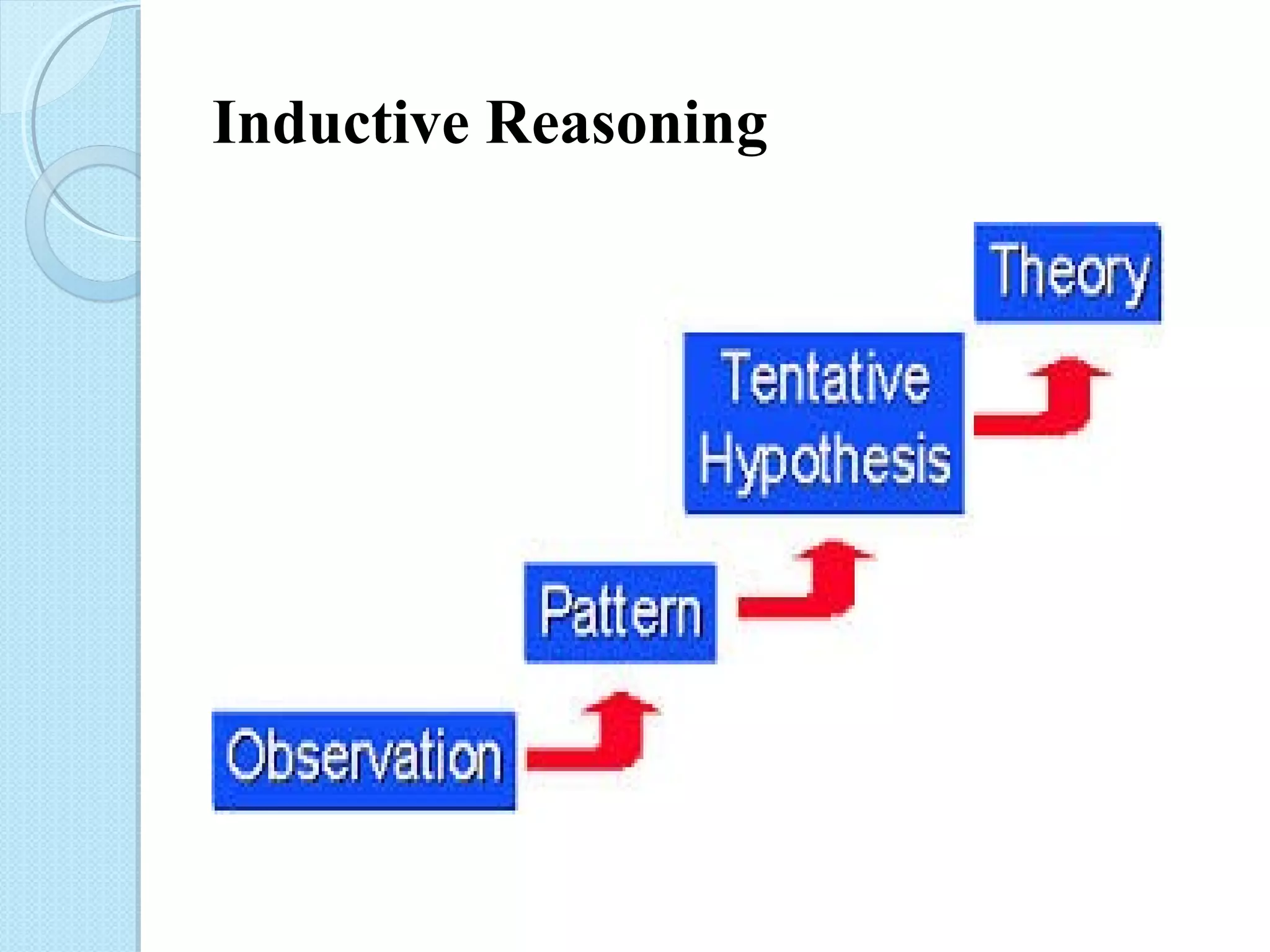
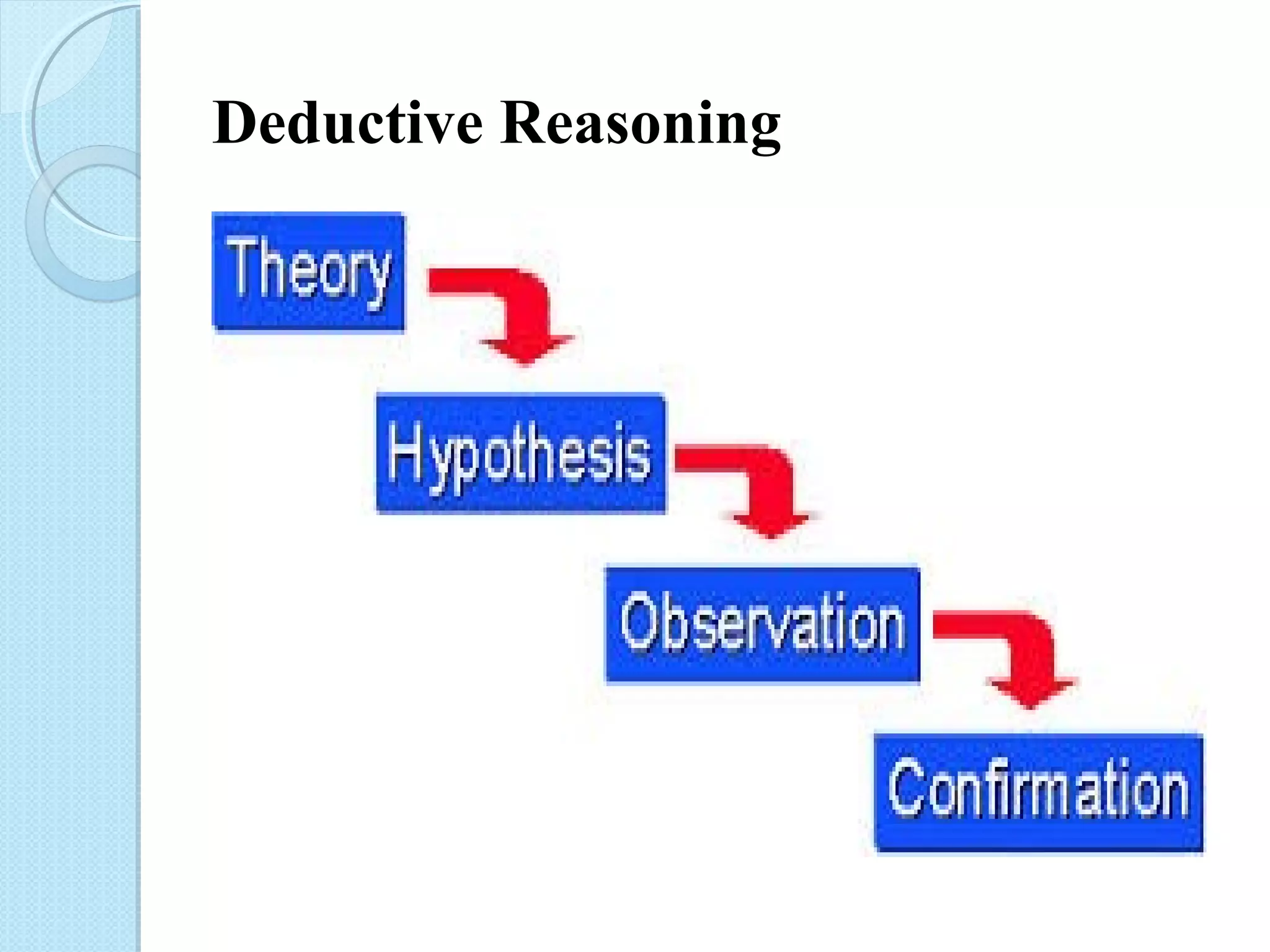
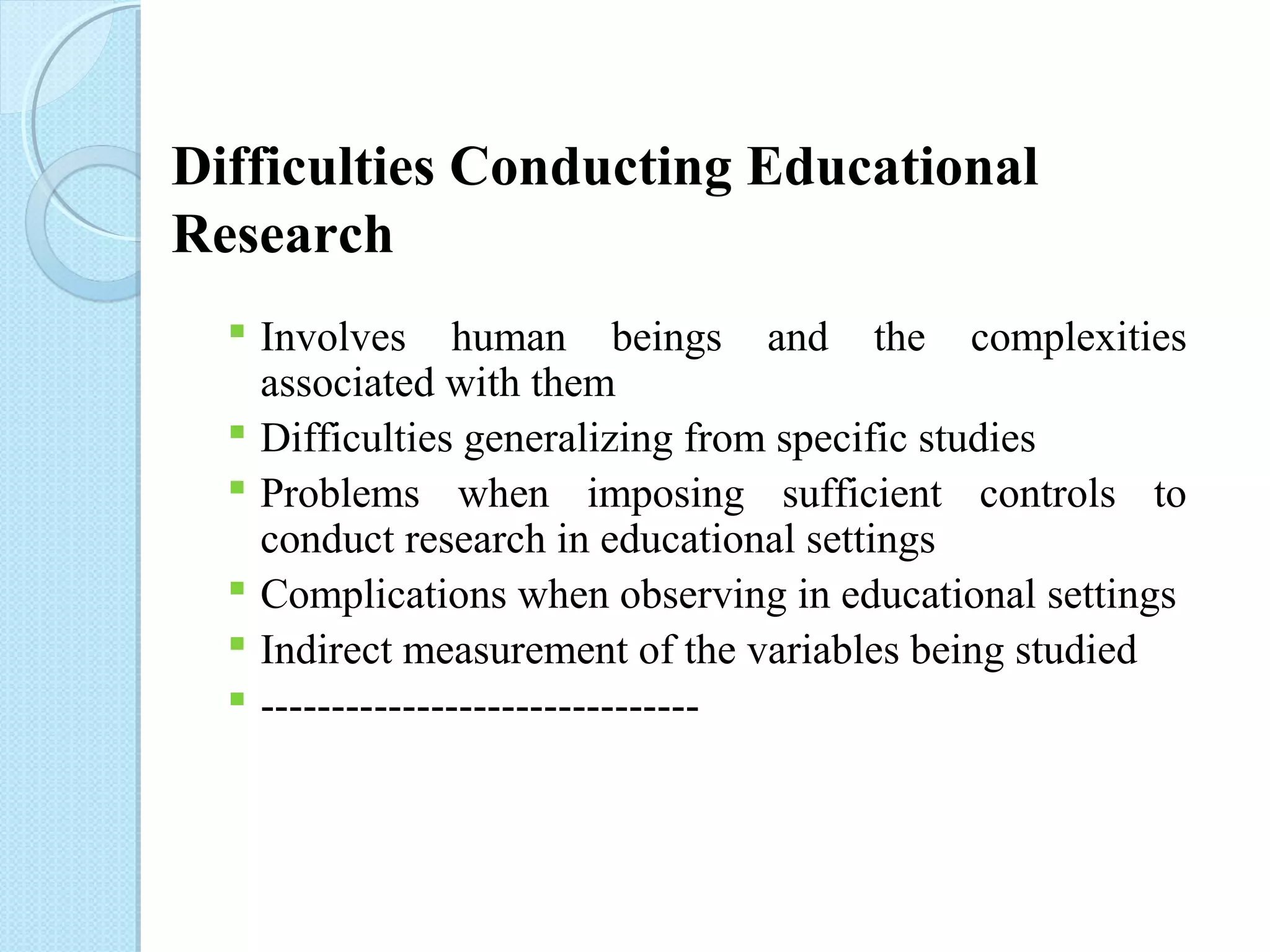
This document discusses research methodology and educational research. It covers topics like the nature of research, characteristics of research, sources of acquiring knowledge, inductive vs deductive reasoning, the scientific method, needs for research in education, steps in educational research, and characteristics of educational research. The goal of research is to explain, predict, and control phenomena through systematic study using methods like formulating hypotheses, collecting data, and analyzing results. Educational research specifically aims to solve educational problems.