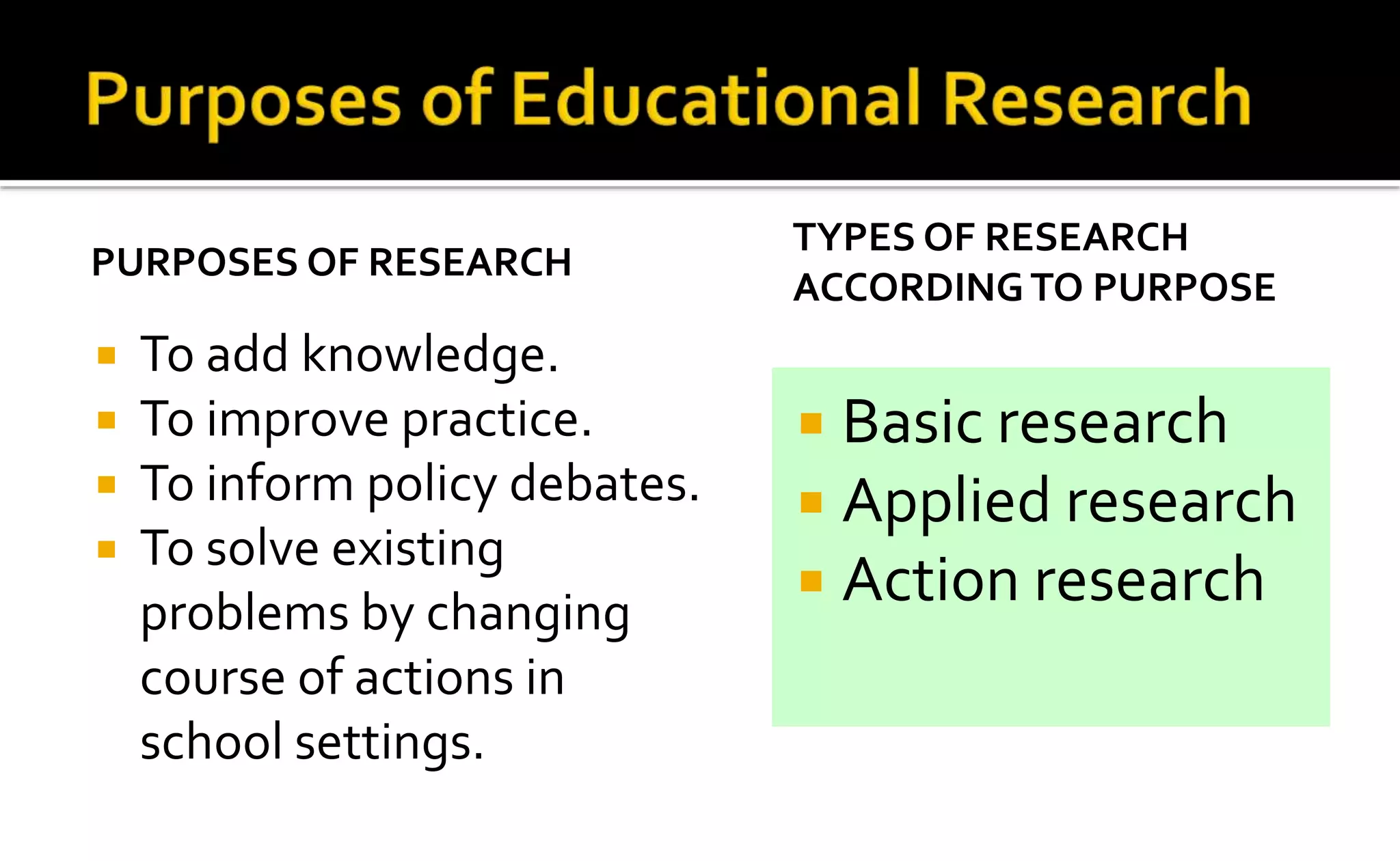
The document outlines research methods in education, emphasizing the systematic collection and analysis of data to answer questions and improve educational practices. It identifies various phases of research, including planning, empirical, analytical, dissemination, and utilization, as well as types of research such as basic, applied, and action research. The overall aim is to enhance knowledge, inform policy, and solve problems in educational settings.