This document provides an overview of curriculum components, including:
1. Definitions of curriculum, aims, goals, and objectives.
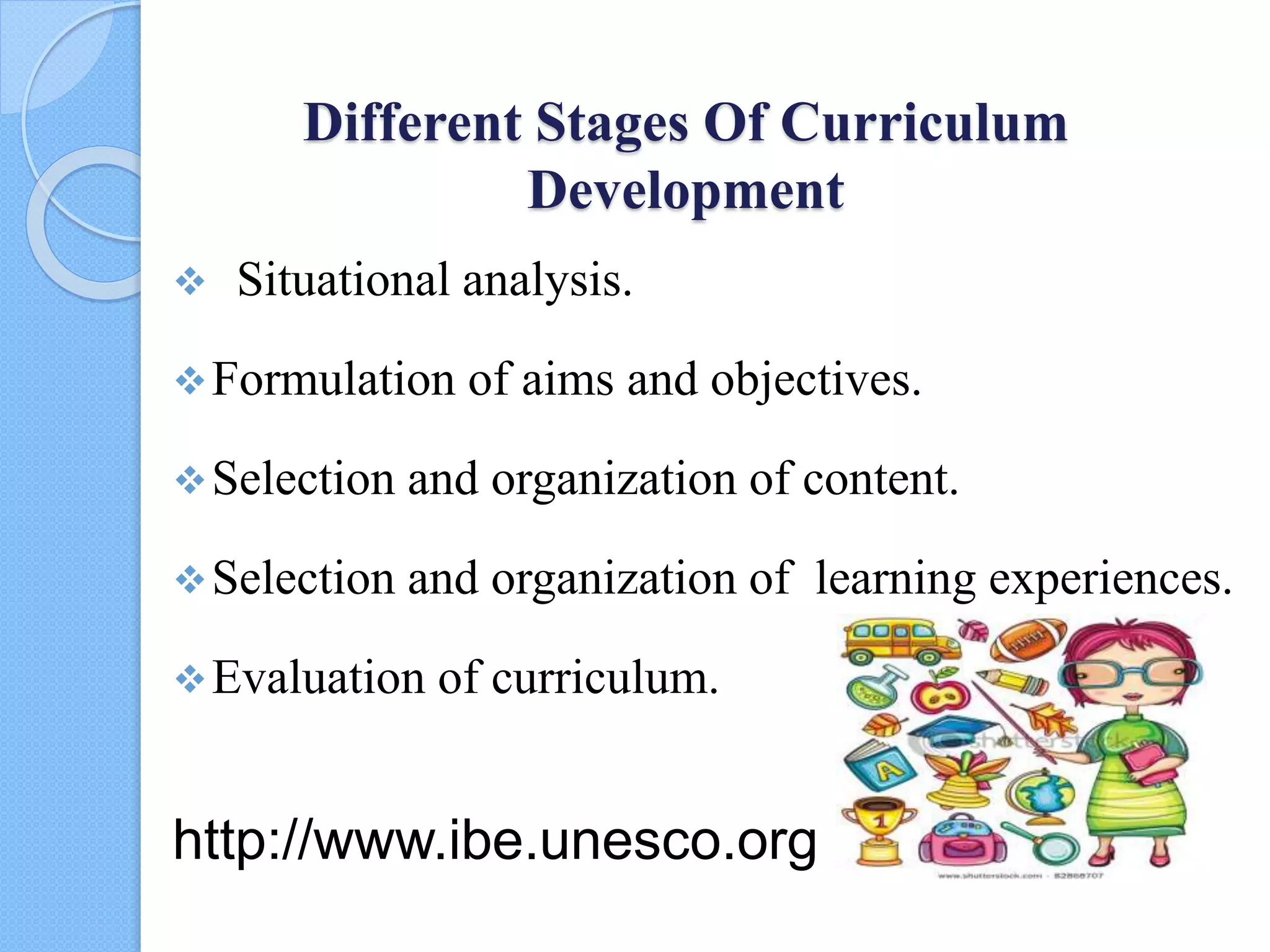
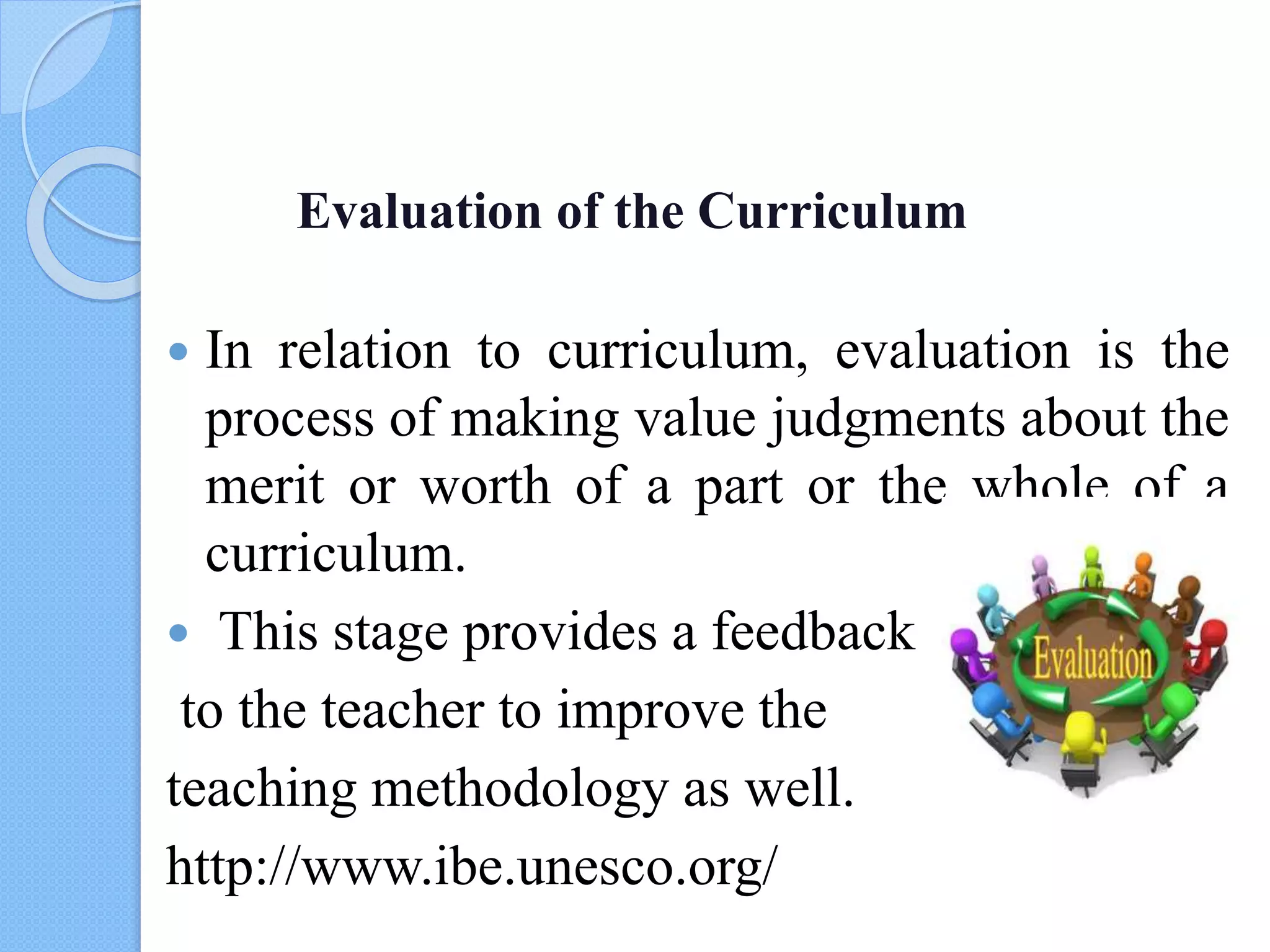
2. The stages of curriculum development, including situational analysis, formulation of aims and objectives, selection and organization of content and learning experiences, and evaluation.
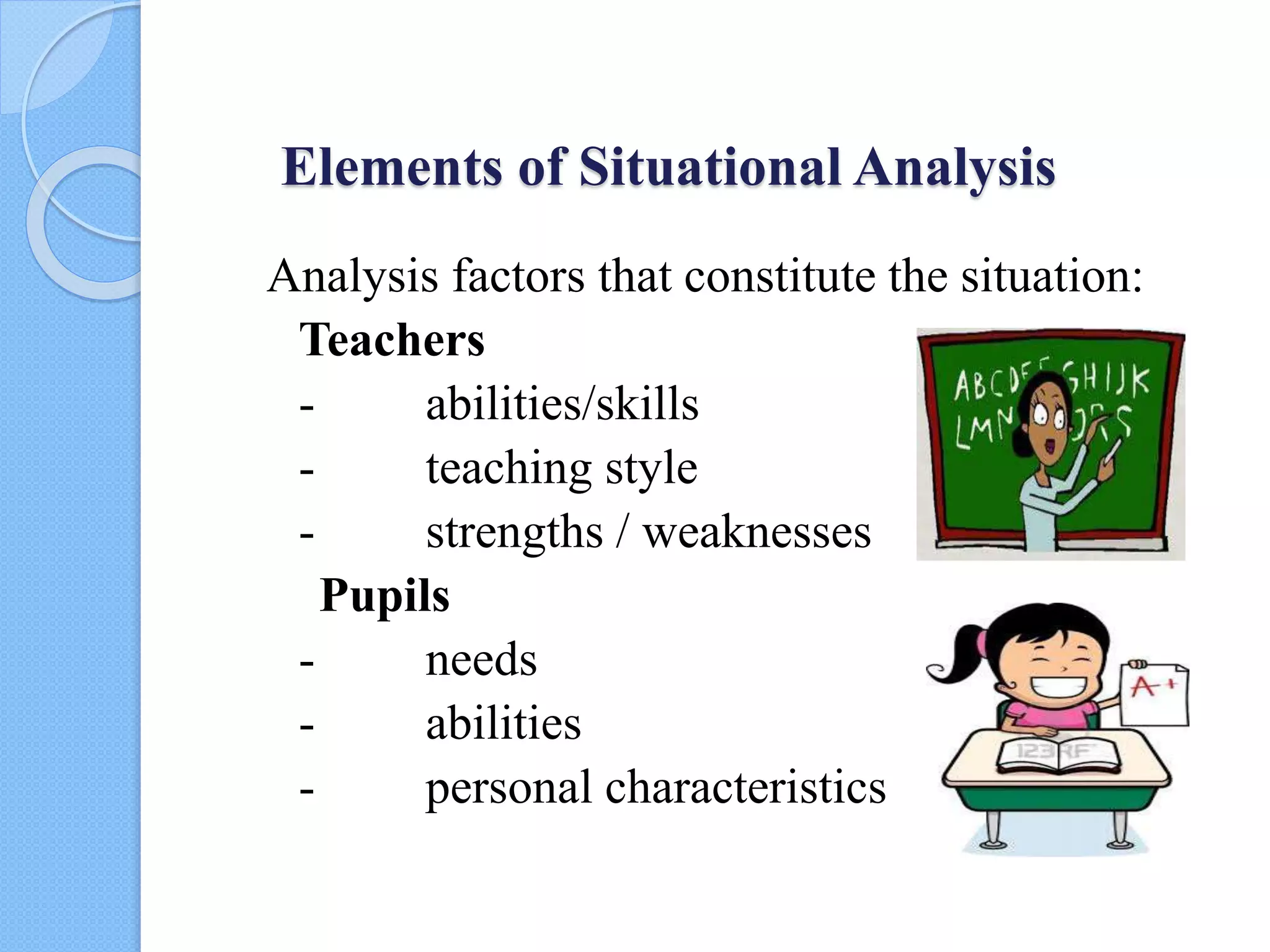
3. Descriptions of the key elements at each stage, such as analyzing student and teacher factors for situational analysis, and ensuring content selection aligns with aims and objectives.