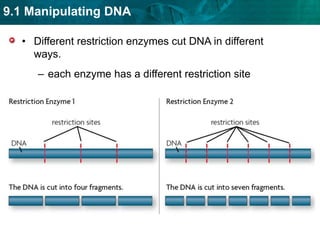
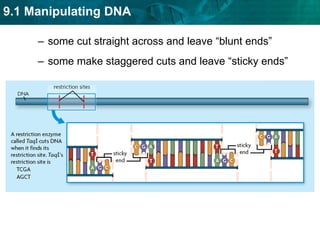
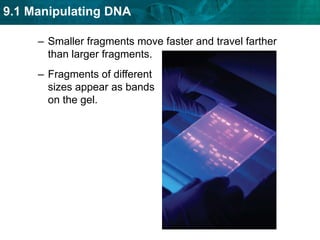
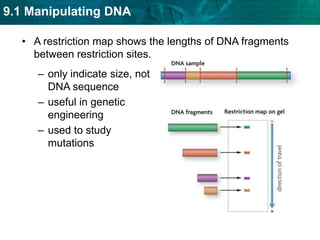
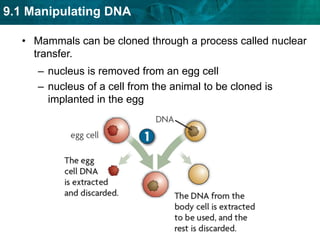
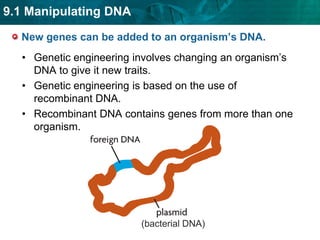
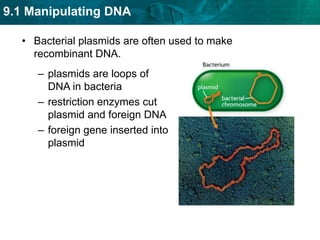
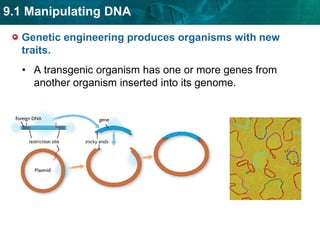
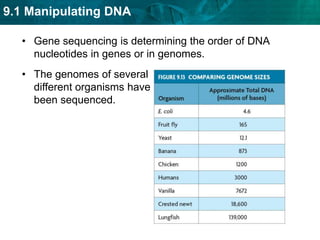
1. Biotechnology relies on restriction enzymes that cut DNA at specific nucleotide sequences. Different enzymes cut DNA in different ways, leaving either blunt or sticky ends. Restriction maps show the lengths of DNA fragments cut by these enzymes.
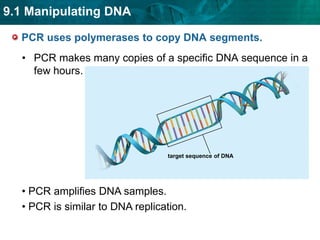
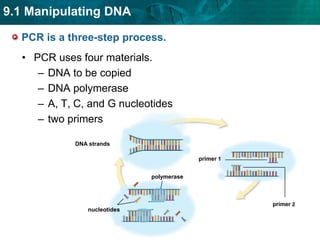
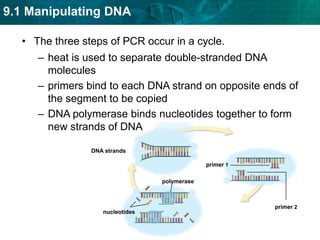
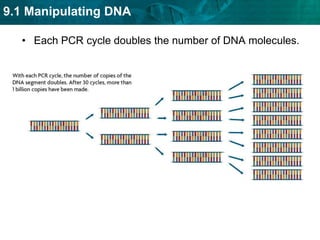
2. The polymerase chain reaction (PCR) amplifies specific DNA sequences. It uses DNA polymerase to copy short DNA segments billions of times over, by cycling between high and low temperatures.
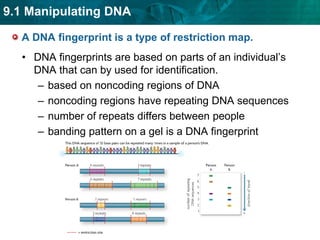
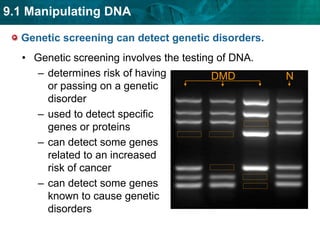
3. DNA fingerprinting identifies individuals by analyzing variations in noncoding DNA regions containing repeating sequences. The probability that any two individuals will have identical fingerprints across multiple regions is very small.