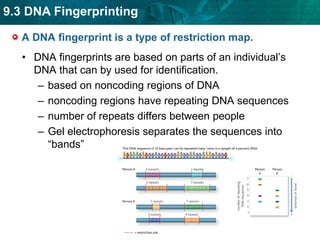
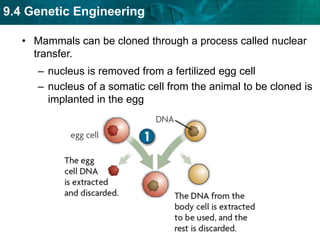
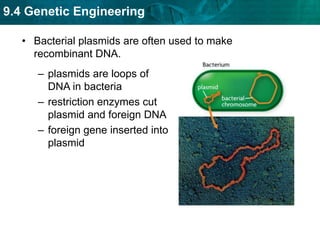
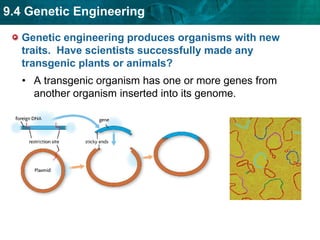
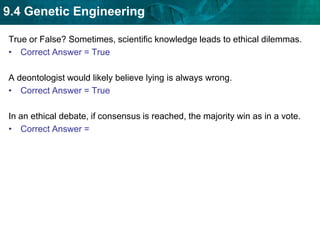
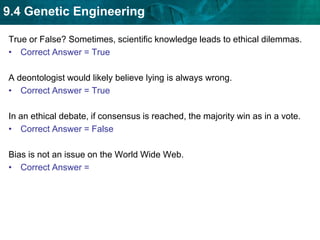
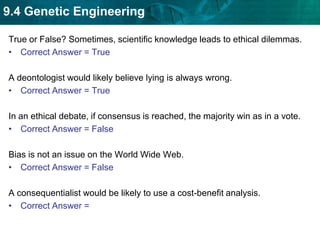
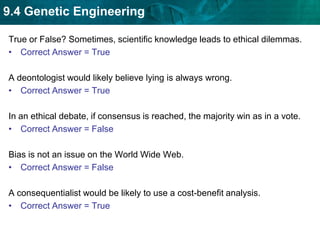
DNA fingerprinting identifies individuals at the molecular level based on noncoding regions of DNA that contain repeating sequences. The number of repeats differs between people and can be used to identify individuals or determine relationships through gel electrophoresis. DNA fingerprinting is used for evidence in criminal cases, paternity tests, immigration requests, and studying biodiversity. Cloning produces genetically identical copies of organisms through techniques like nuclear transfer in mammals. Cloning has potential benefits like organ transplants and saving endangered species but also raises concerns about health, biodiversity, and success rates. Genetic engineering modifies organisms' DNA to give them new traits using recombinant DNA techniques. Transgenic organisms with genes from other species are used in research and agriculture but also provoke concerns about