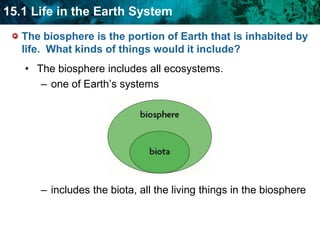
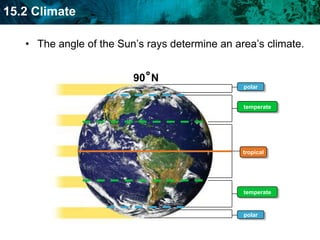
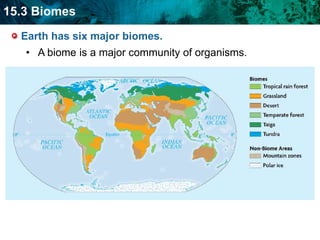
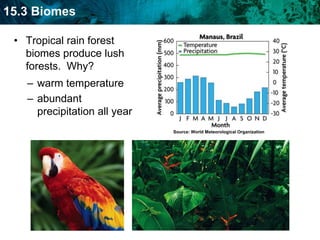
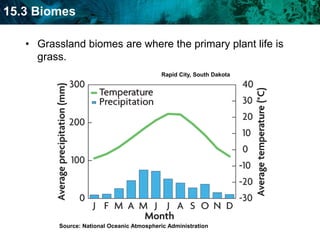
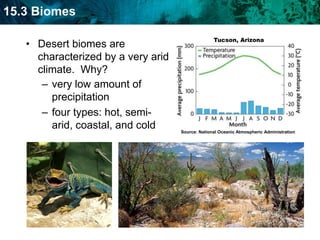
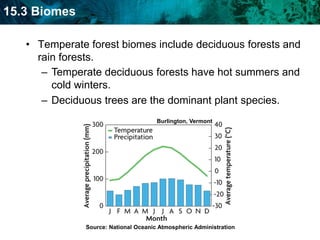
The document discusses the biosphere and climate. The biosphere includes all ecosystems and living things on Earth. Climate is the long-term weather patterns of a region, determined by factors like temperature, sunlight, and wind. Earth has six major biomes defined by climate, including tropical rainforests, grasslands, deserts, temperate forests, taiga, and tundra.