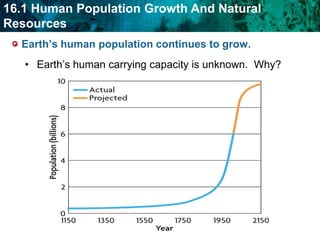
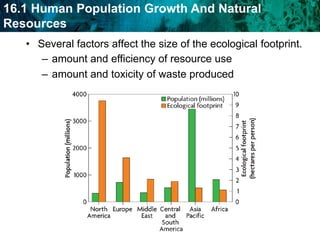
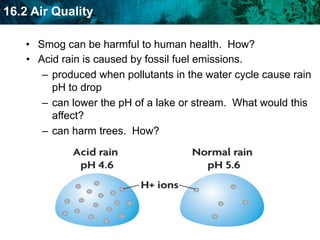
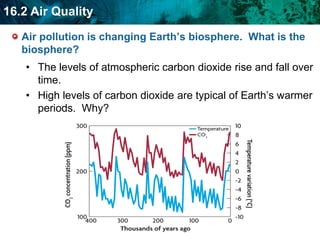
As the human population grows, demand for Earth's resources increases and puts pressure on renewable and nonrenewable resources. Technological advances have helped increase Earth's carrying capacity by supporting agriculture and medicine. However, fossil fuel emissions contribute to pollution and climate change, affecting the biosphere. Air pollution from fossil fuels can harm human health and the environment through effects like smog, acid rain, and the greenhouse effect. Pollution also threatens freshwater ecosystems and enters the food chain through biomagnification.