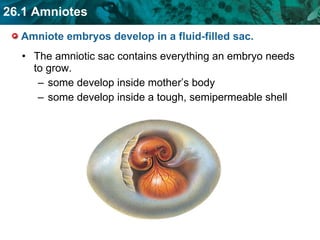
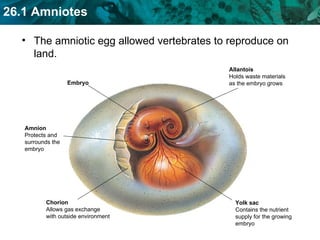
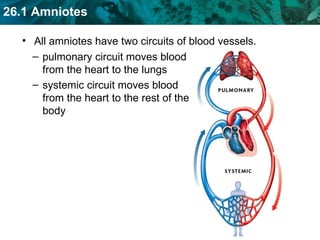
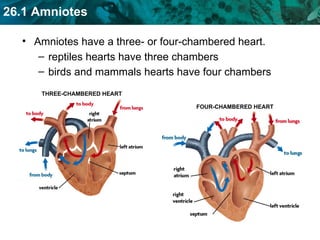
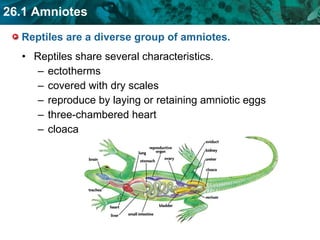
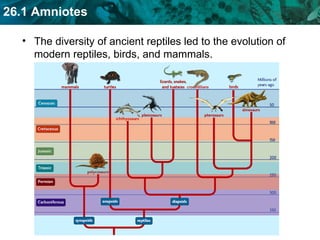
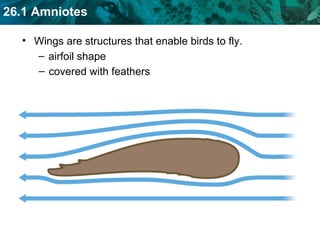
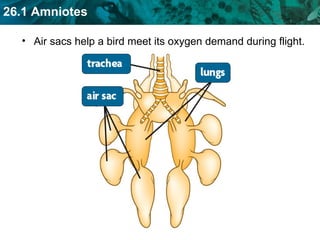
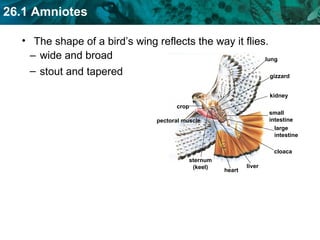
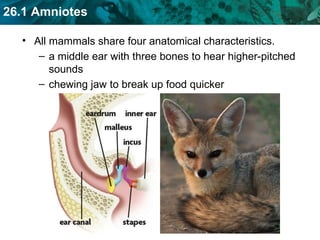
The document discusses key characteristics of amniotes such as reptiles, birds, and mammals. Amniotes develop in amniotic sacs that provide fluid and nutrients to the growing embryo. This allows for reproduction on land. Amniotes have two circulatory systems - pulmonary and systemic - as well as three- or four-chambered hearts depending on whether they are reptiles or birds and mammals. The document then covers anatomical and physiological adaptations of reptiles, birds, and mammals.