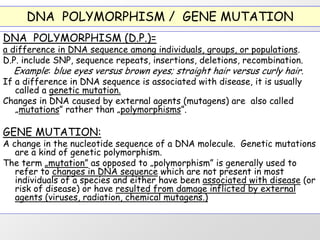
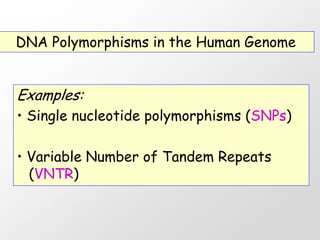
1. DNA polymorphisms, such as single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) and variable number tandem repeats (VNTRs), are natural variations in DNA sequences among individuals.
2. These polymorphisms can be used for indirect DNA diagnosis of genetic diseases through detection of restriction fragment length polymorphisms (RFLPs). DNA from family members is digested with restriction enzymes and analyzed through gel electrophoresis and Southern blotting.
3. If a polymorphism is found near a disease-causing mutation and is linked to it, its inheritance pattern can help determine which family members have inherited the mutation and are at risk for the associated genetic disease.
















![Single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) [„SNiPS”]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/l11dnapolymorphismsmutationsandgeneticdiseases4-110914061008-phpapp01/85/L11-dna__polymorphisms__mutations_and_genetic_diseases4-19-320.jpg)












