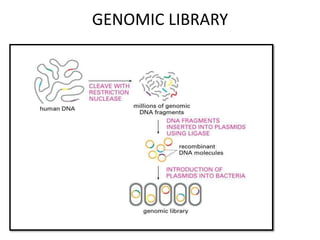
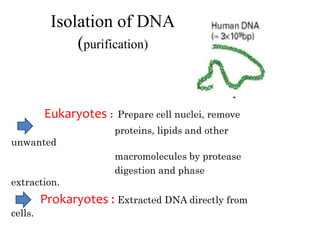
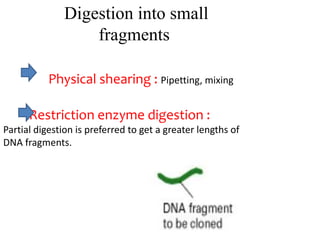
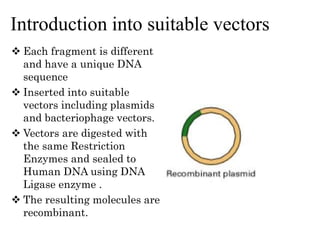
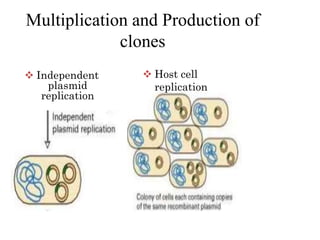
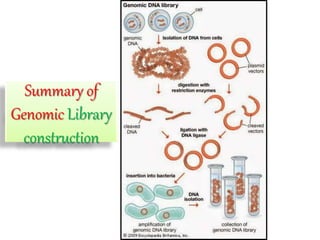
The document explains the construction of gene libraries, focusing on genomic libraries which are collections of genetically engineered bacteria or yeast containing the entire DNA of an organism. It outlines the steps involved in creating a genomic library, including DNA isolation, digestion into smaller fragments, incorporation into vectors, and replication within host bacteria. Additionally, the document describes the uses of genomic libraries for studying genome structure, developing genetic tests, and facilitating DNA sequencing projects.