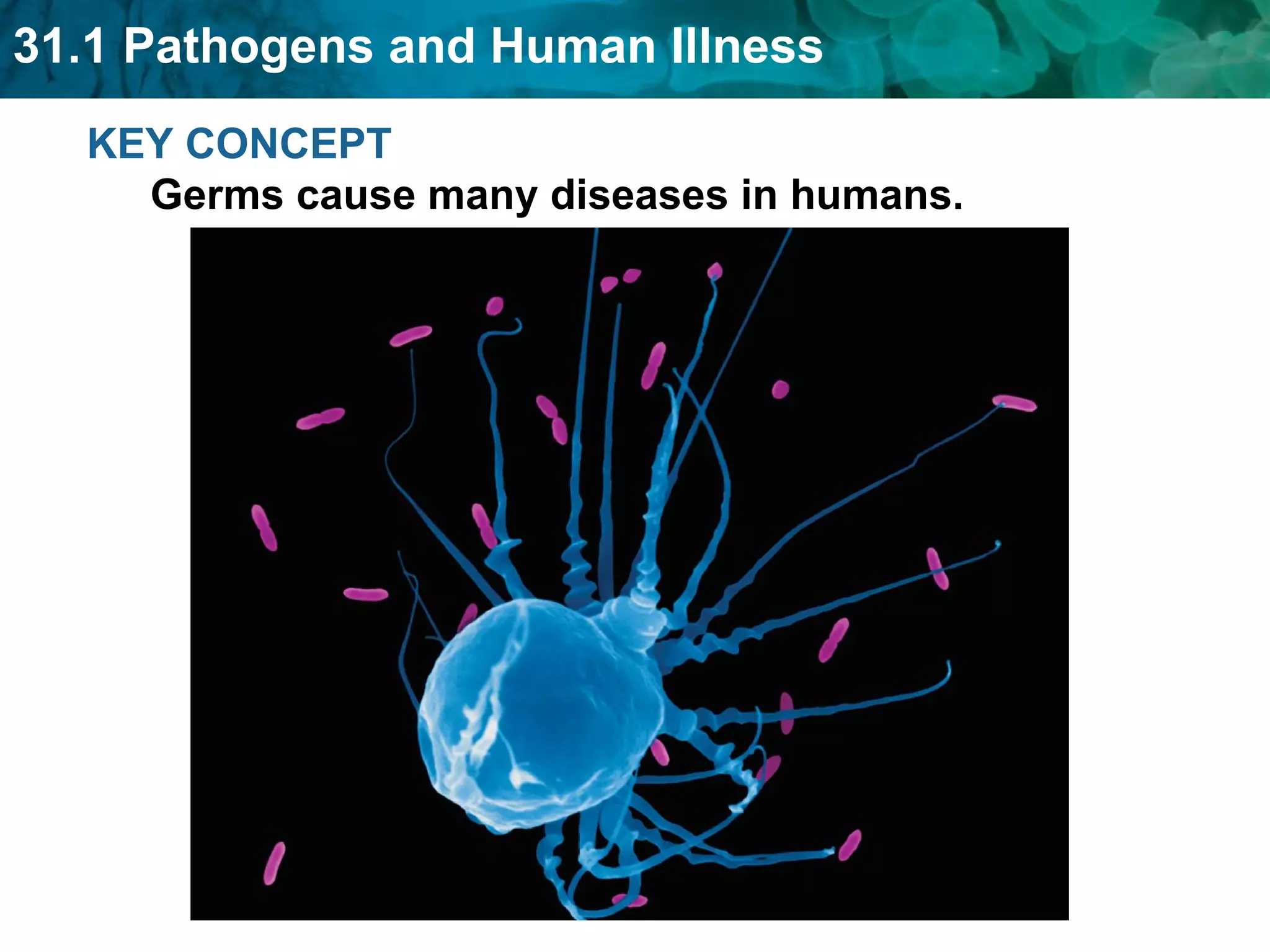
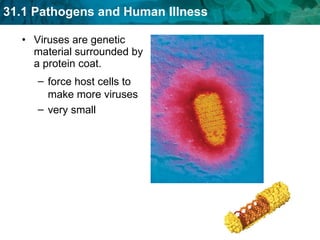
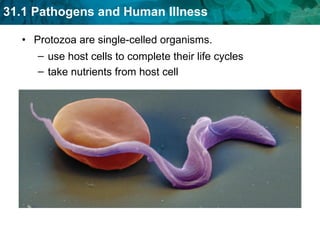
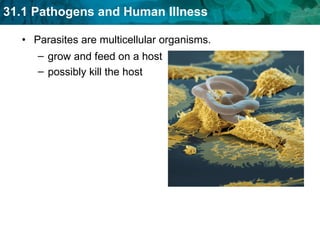
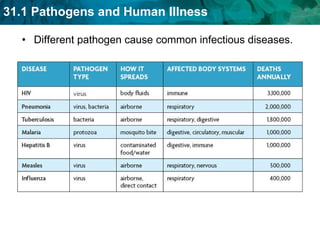
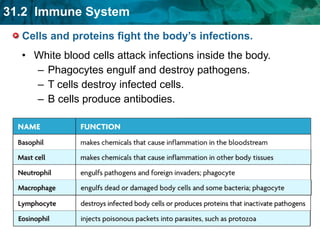
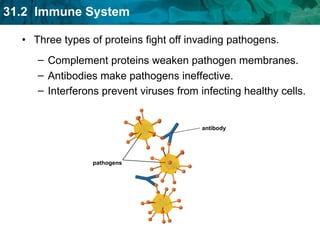
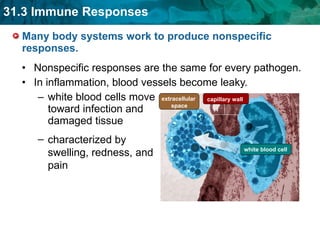
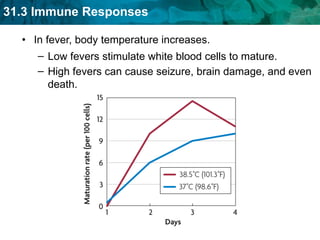
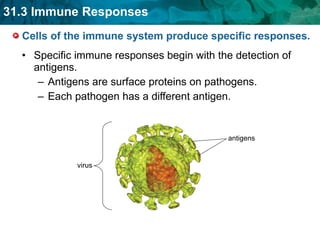
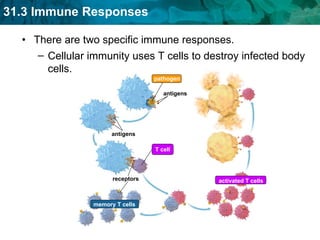
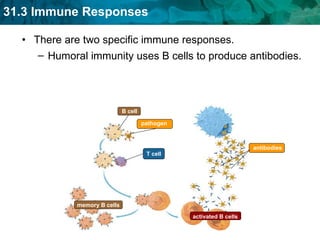
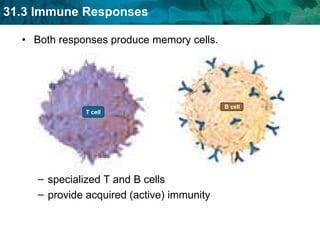
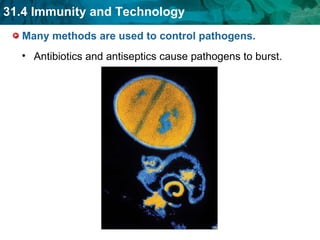
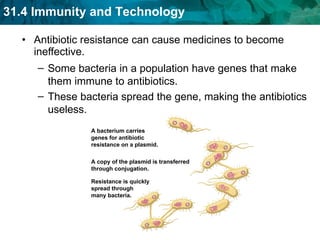
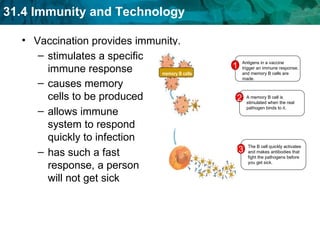
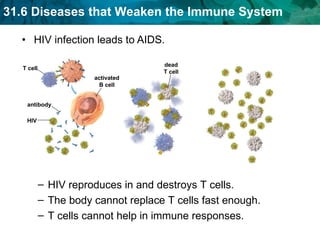
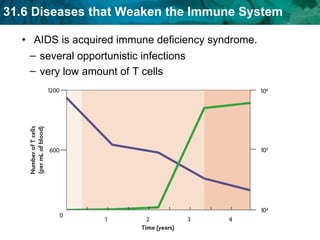
Germ theory proposes that microorganisms cause diseases. Germs such as bacteria, viruses, fungi and protozoa can enter the body through direct or indirect contact and cause illness. The immune system consists of organs, cells and molecules that fight infections through nonspecific responses like inflammation and fever, as well as specific responses that target particular pathogens. Vaccines produce immunity by artificially inducing the immune system to recognize antigens from a pathogen.