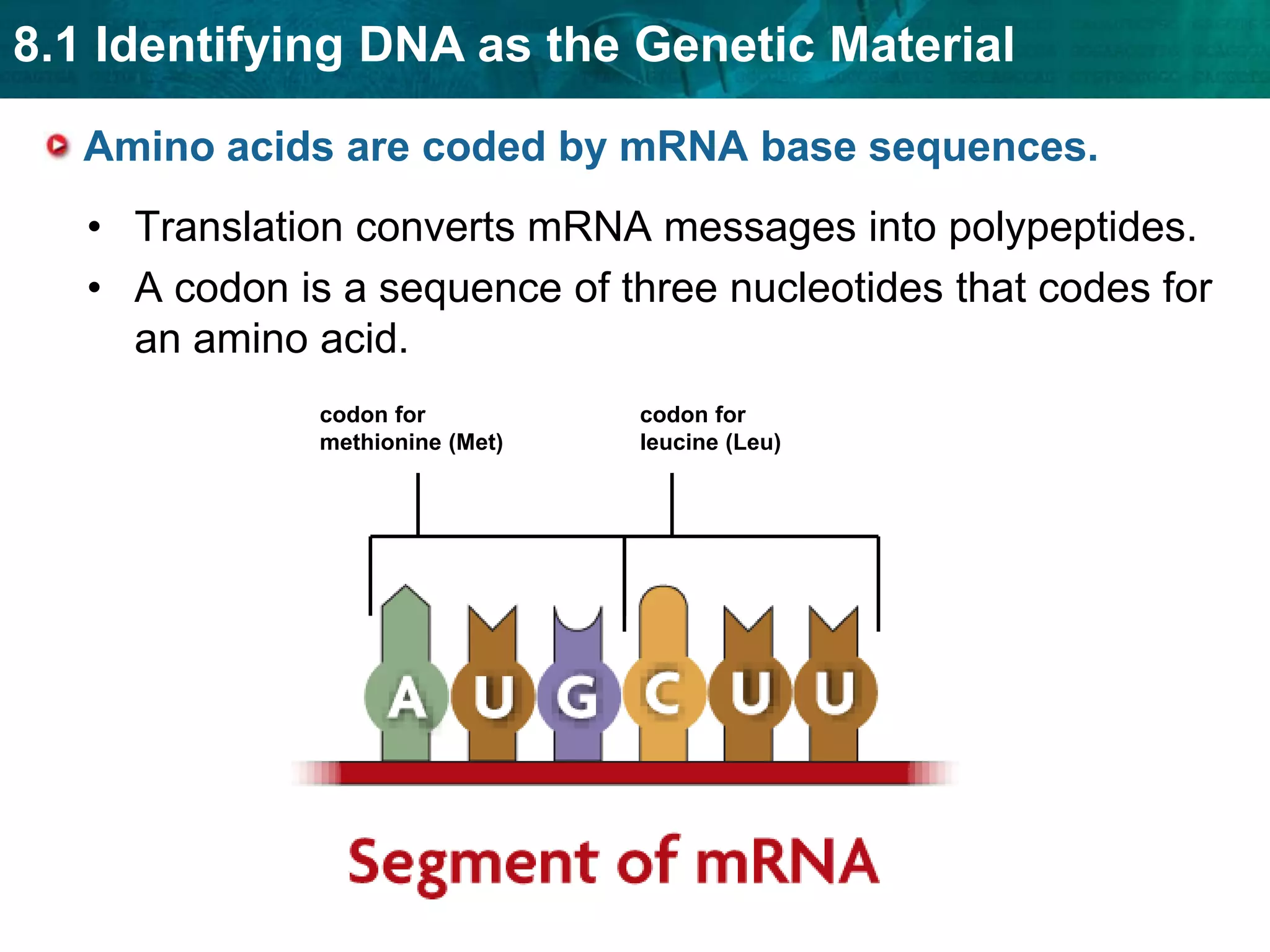
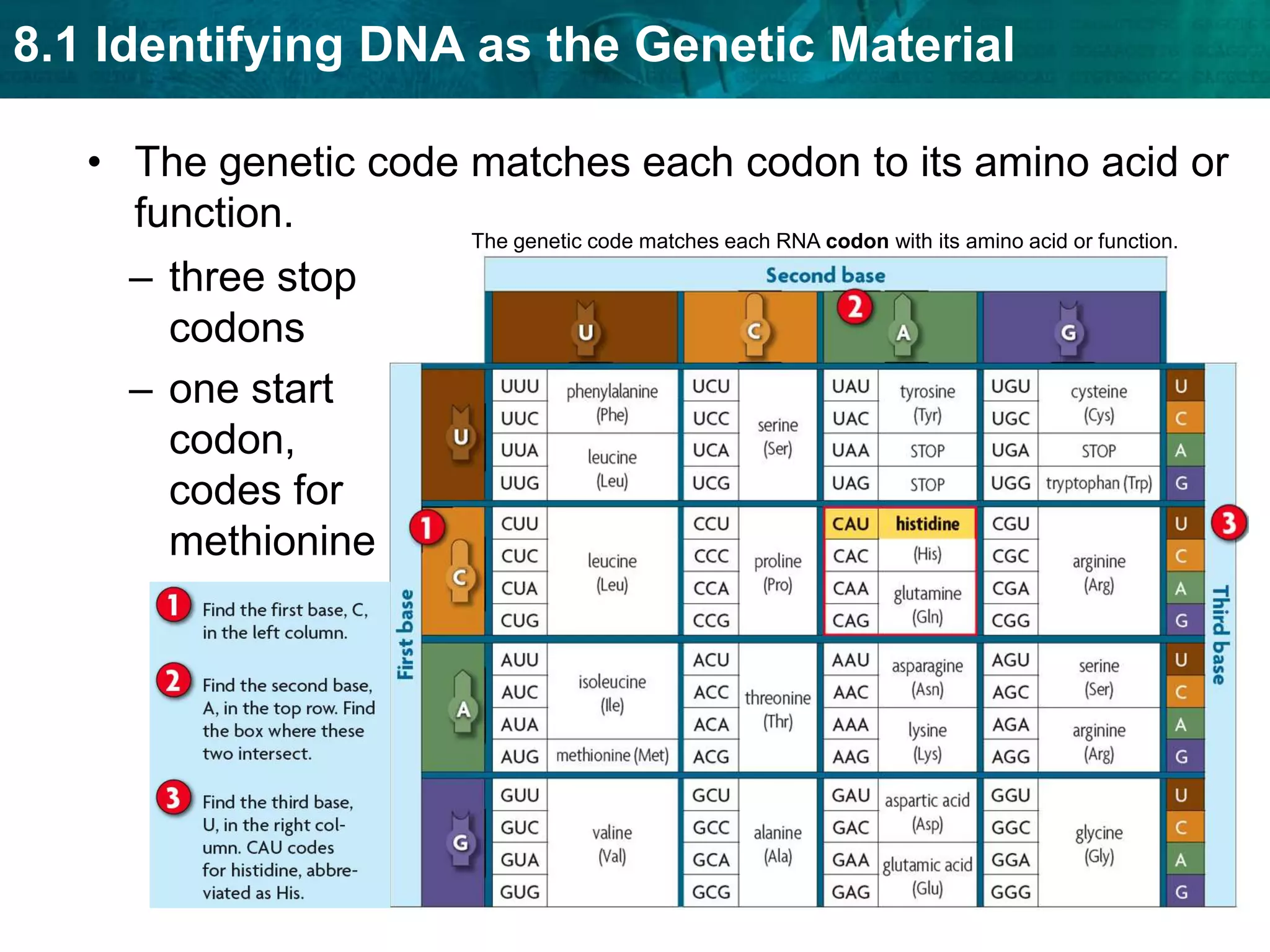
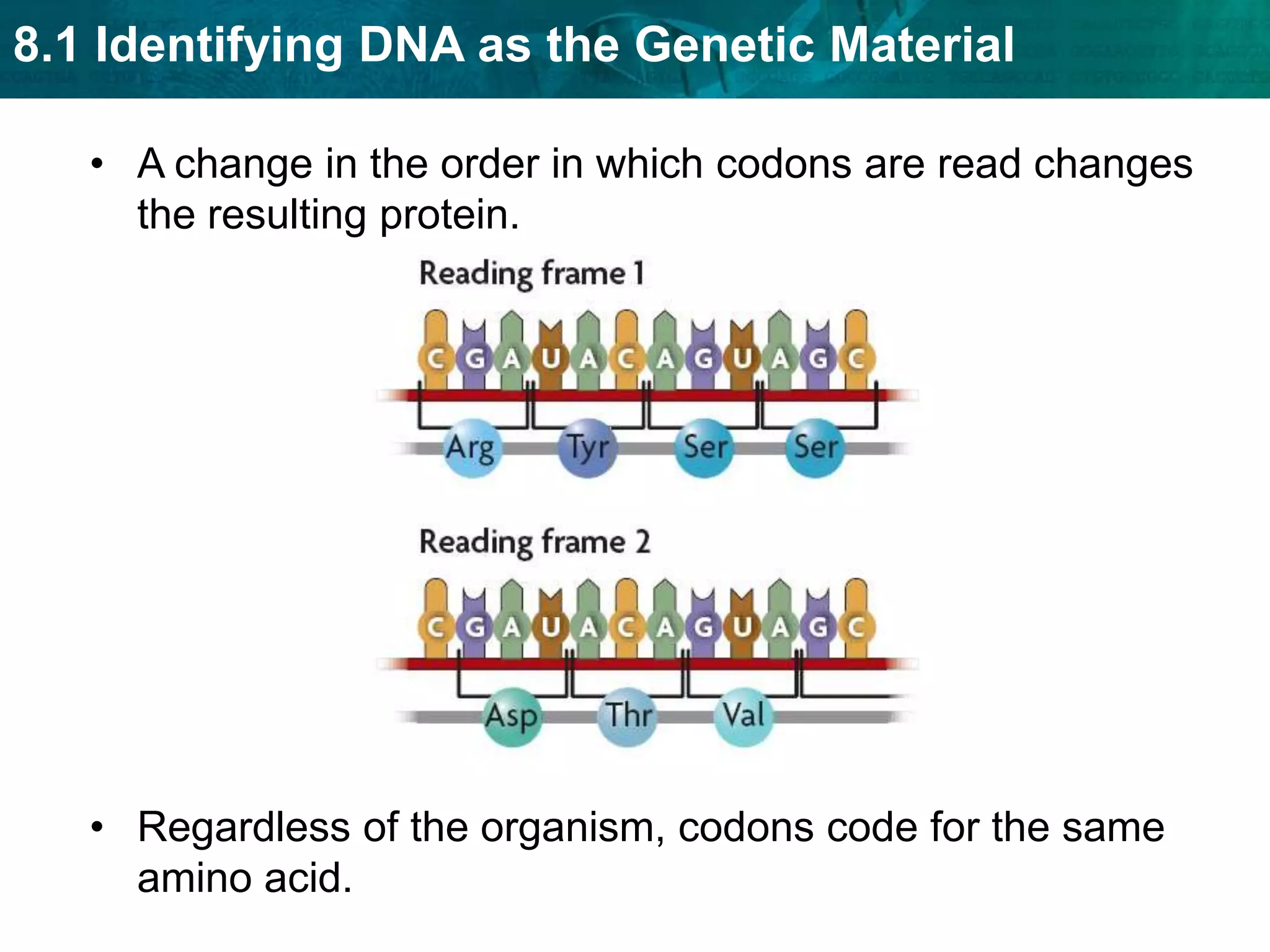
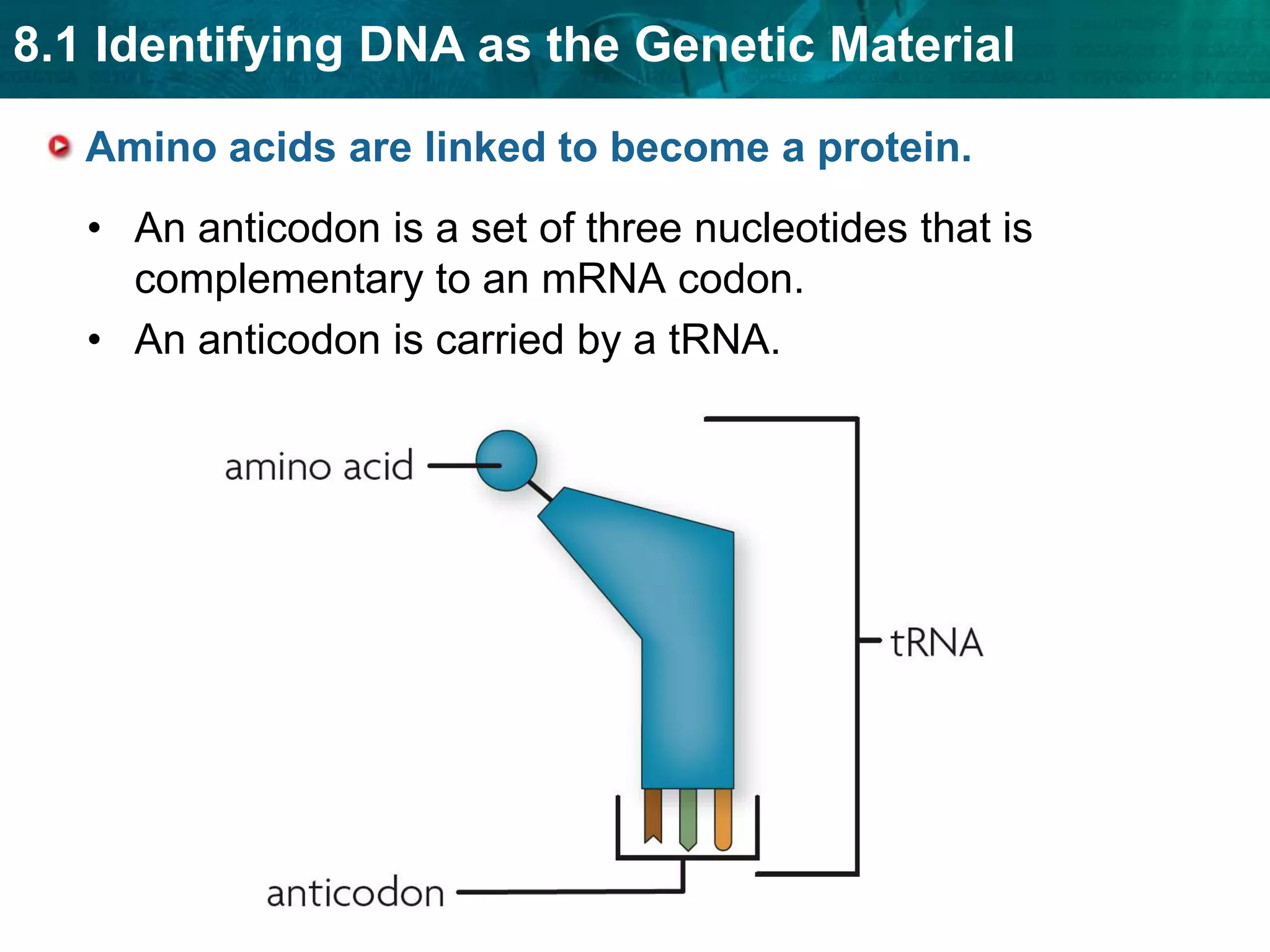
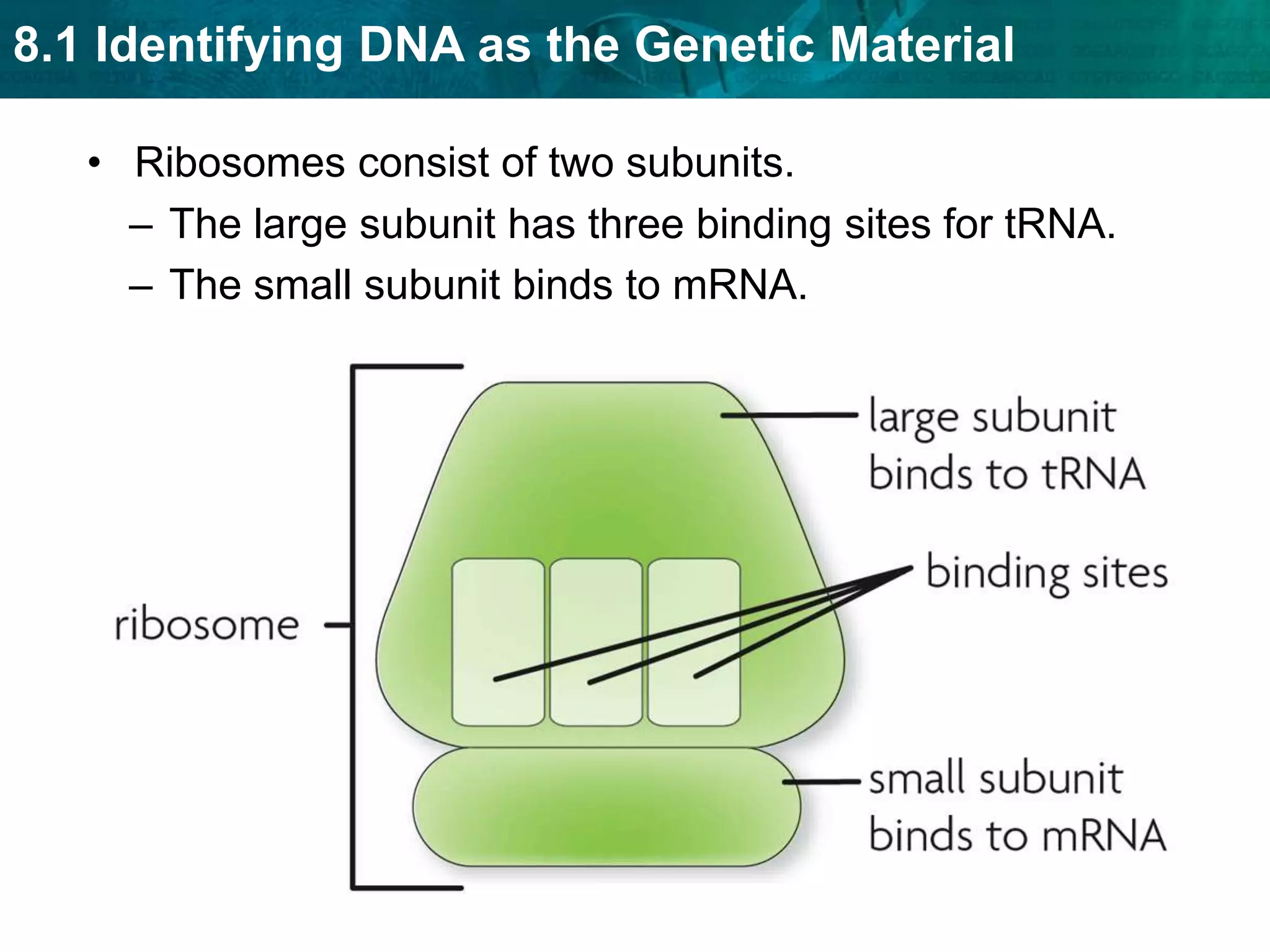
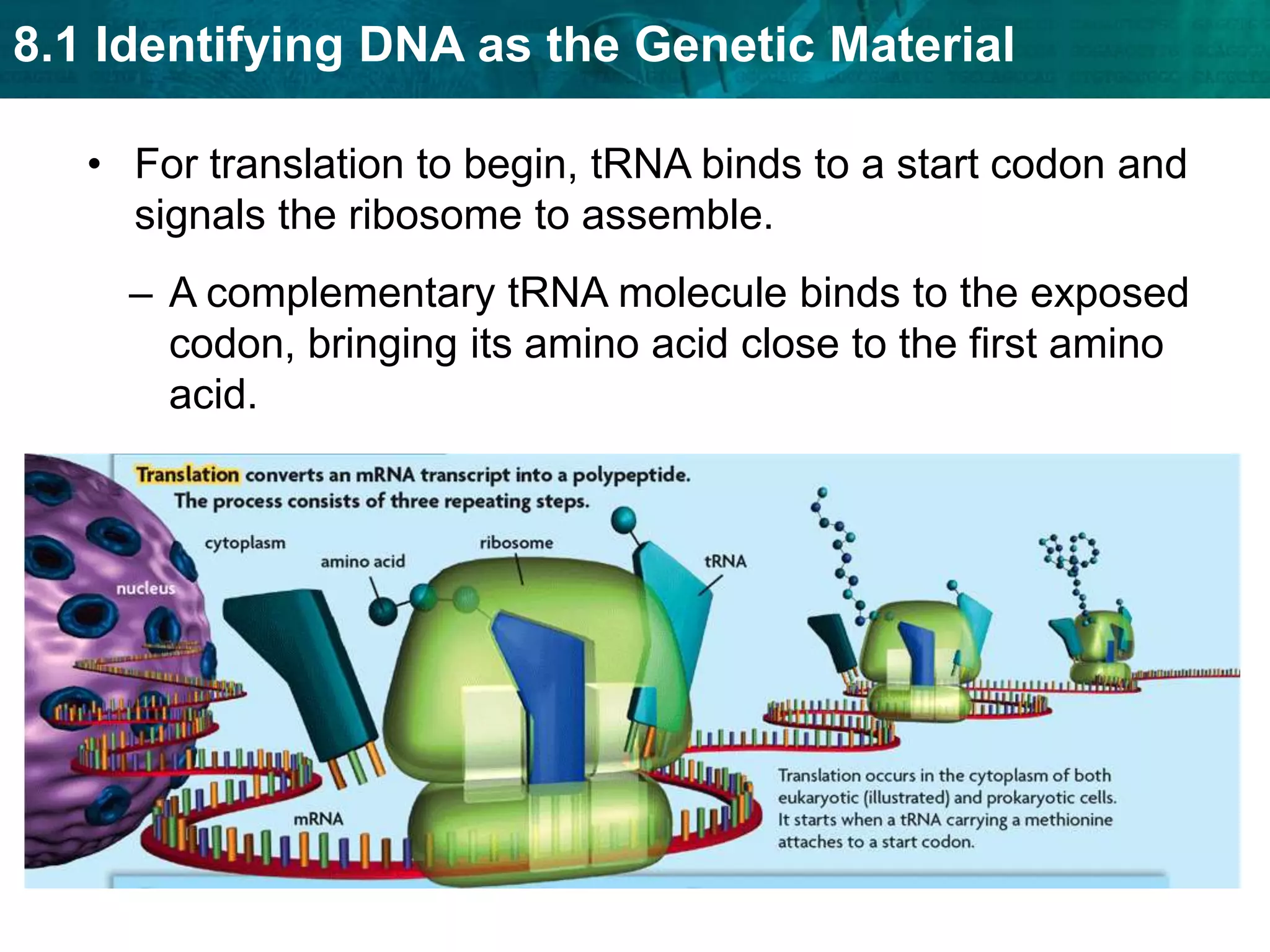
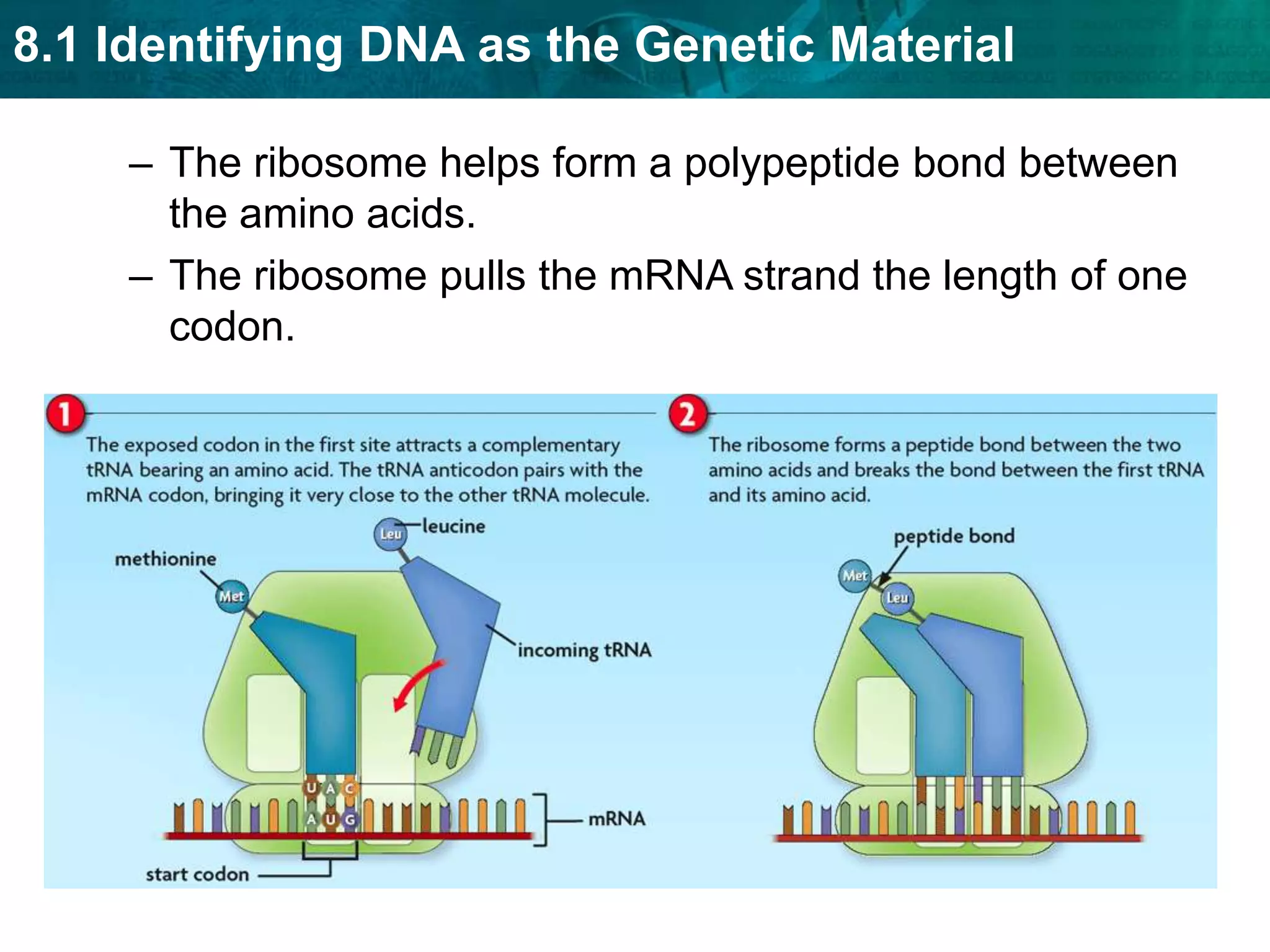
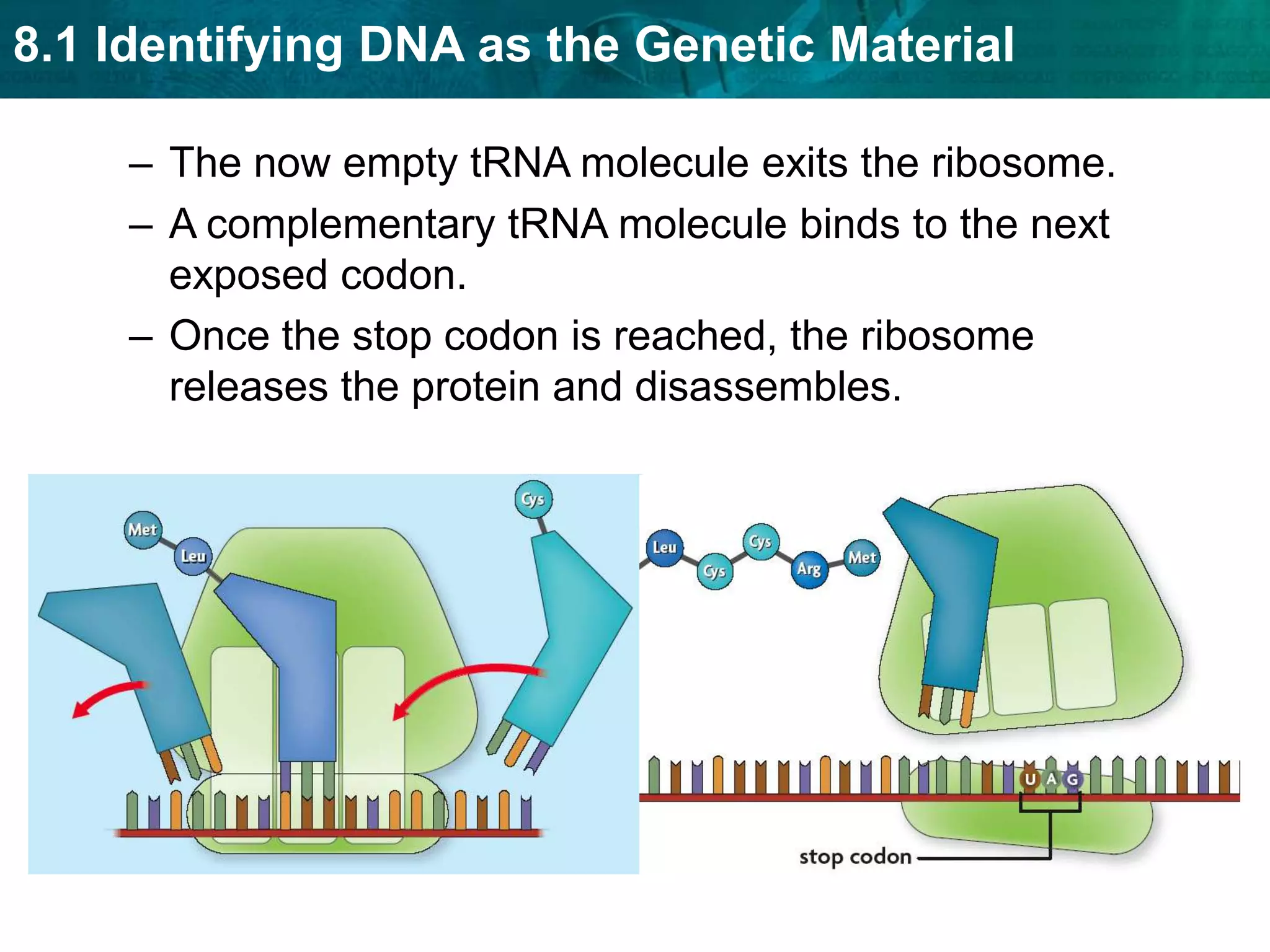
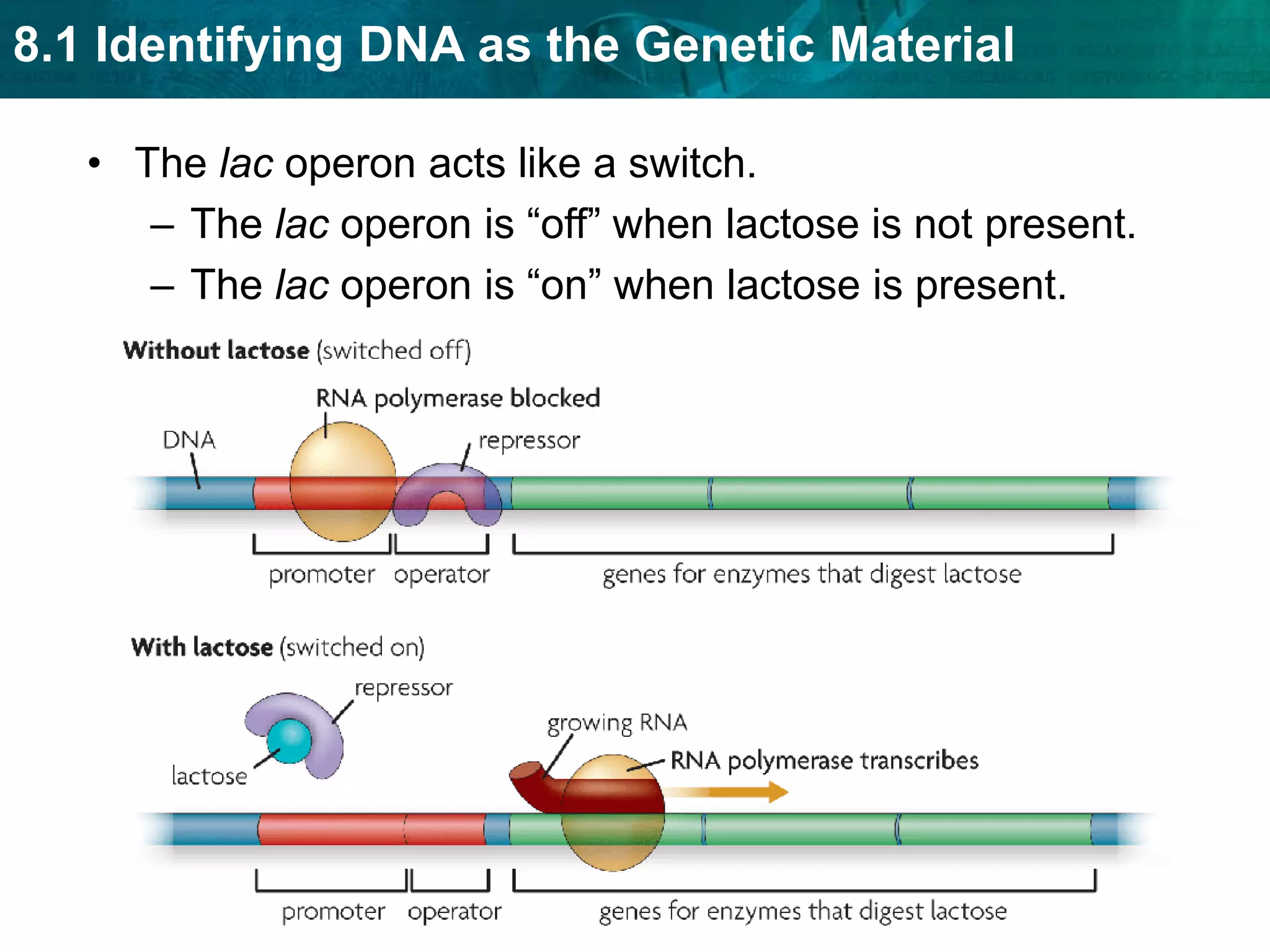
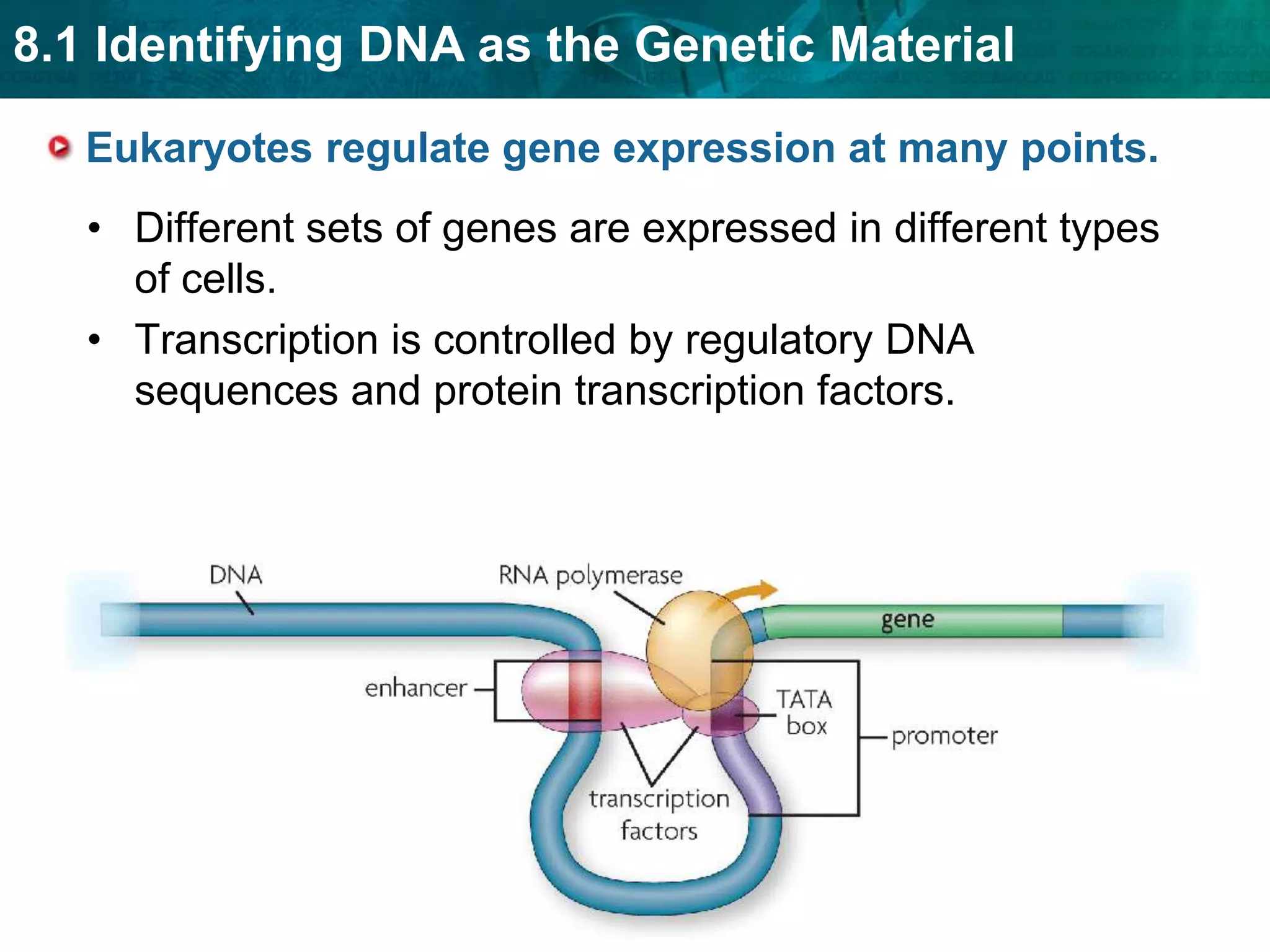
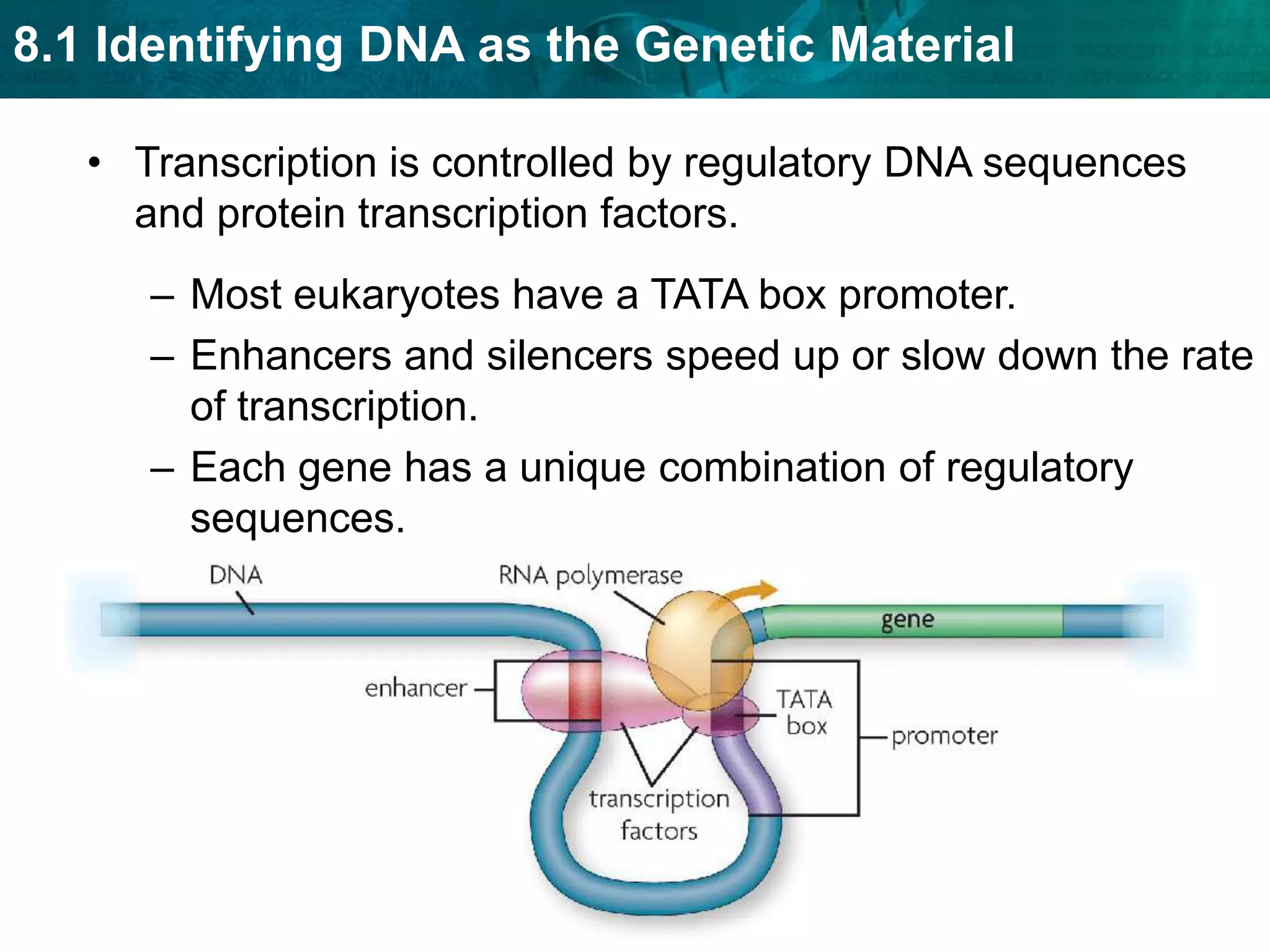
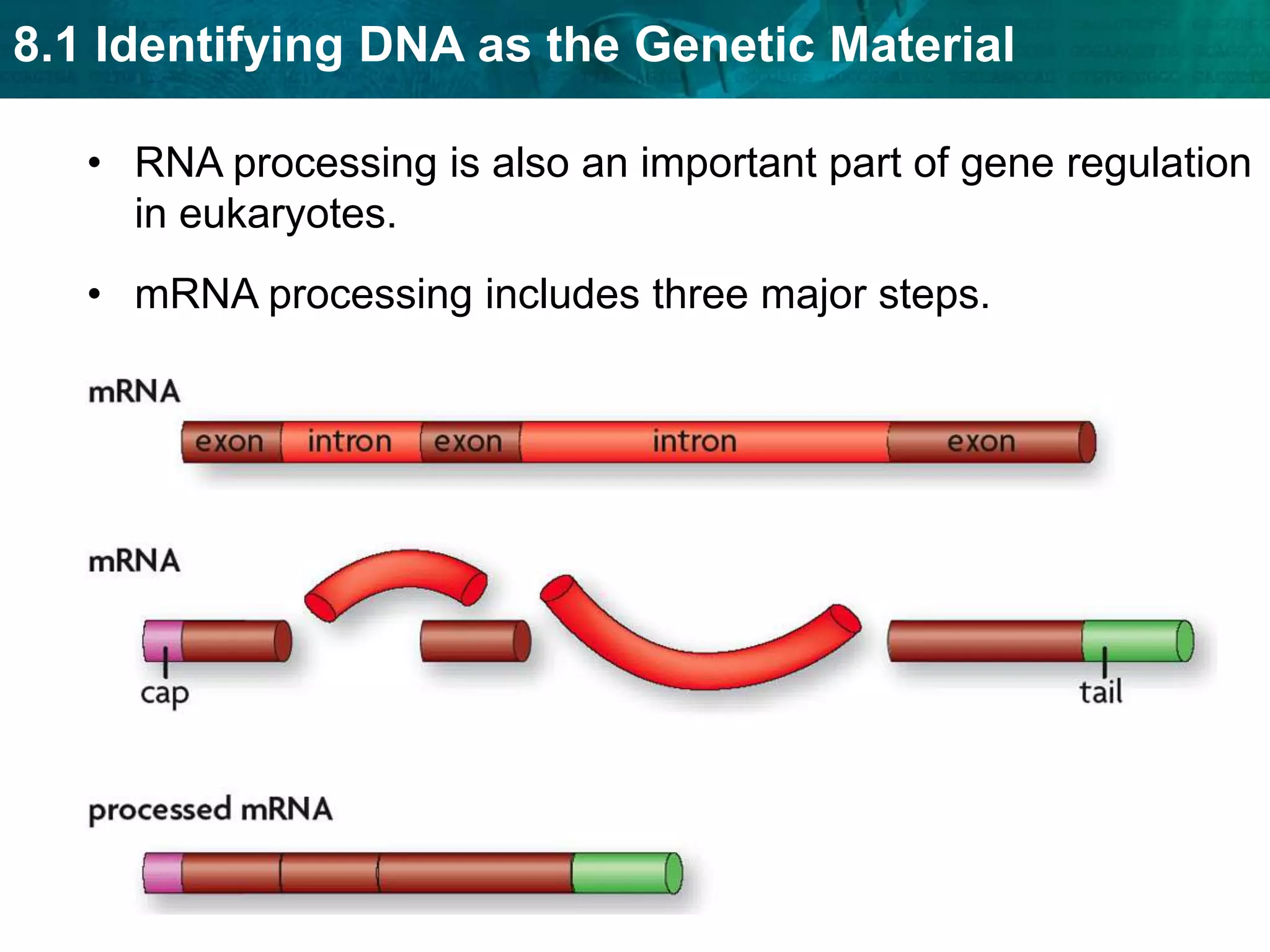
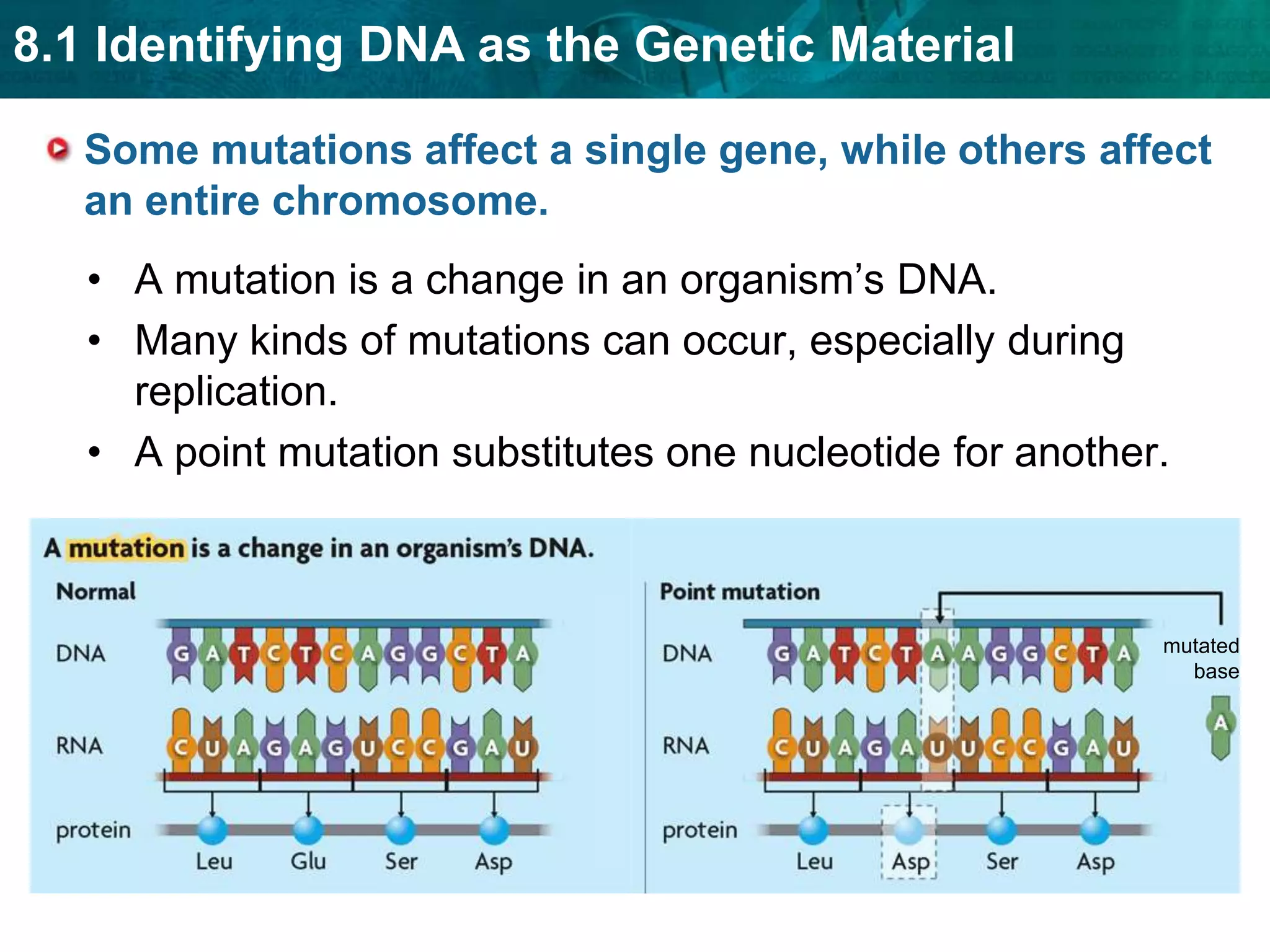
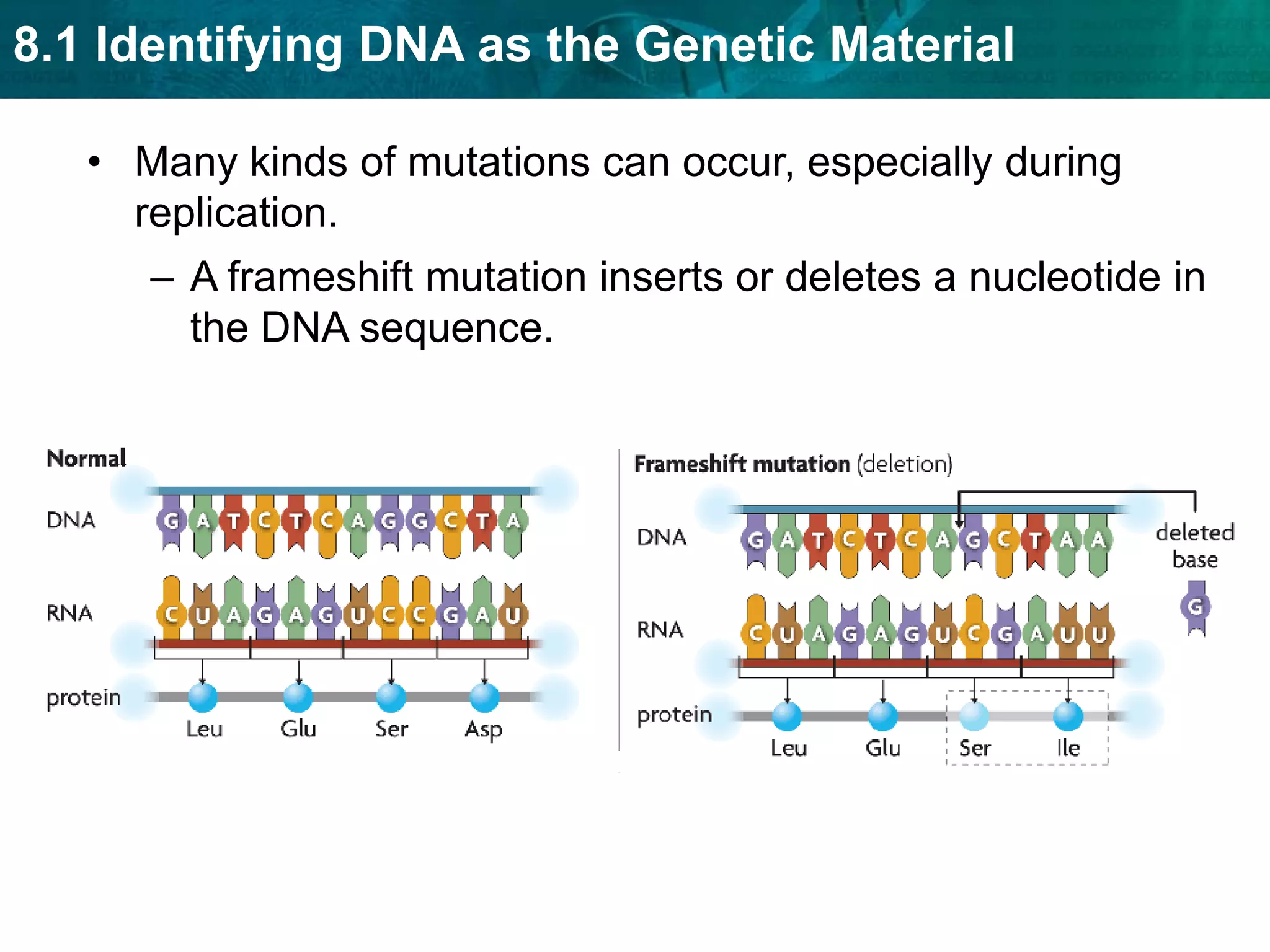
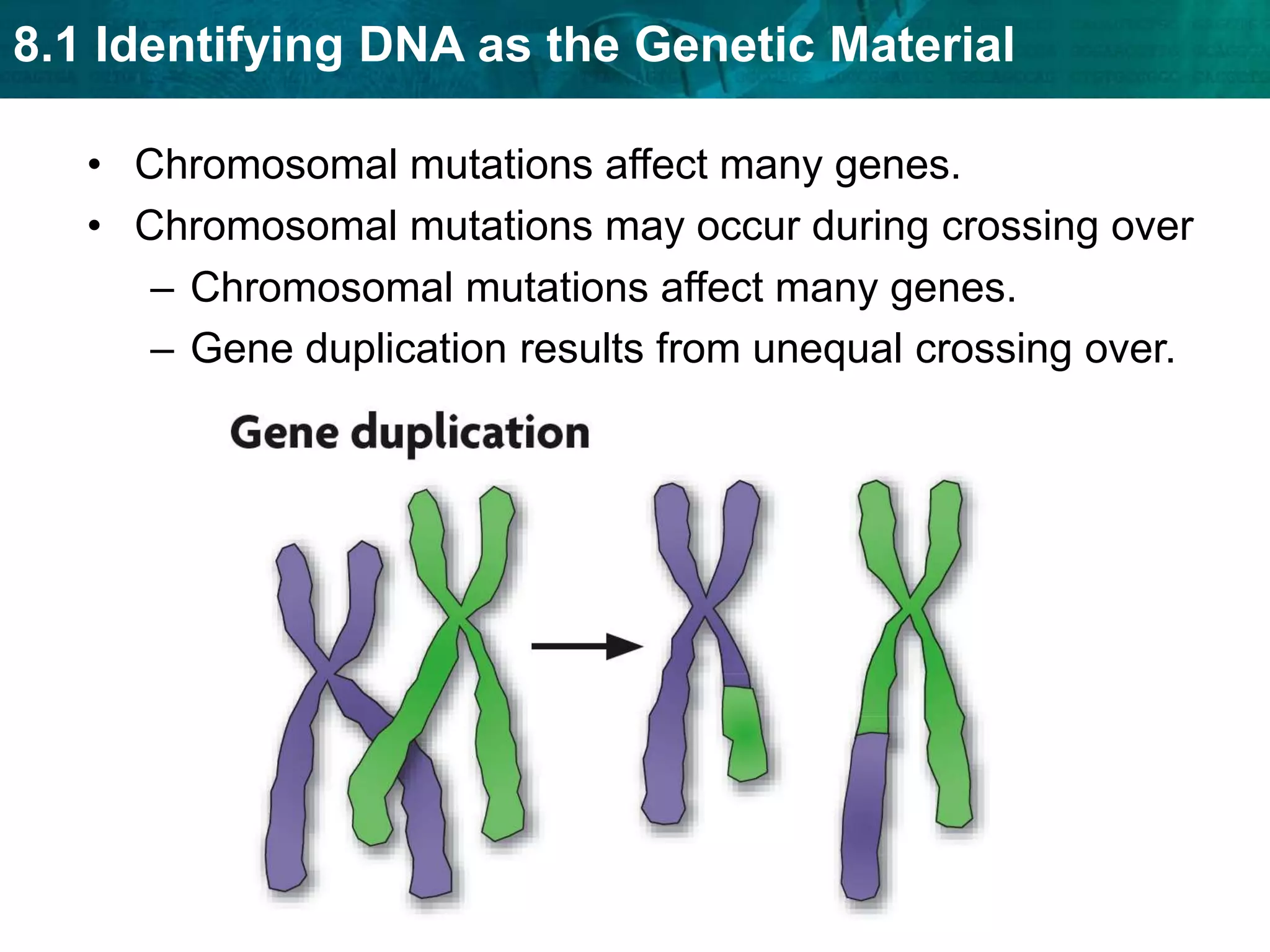
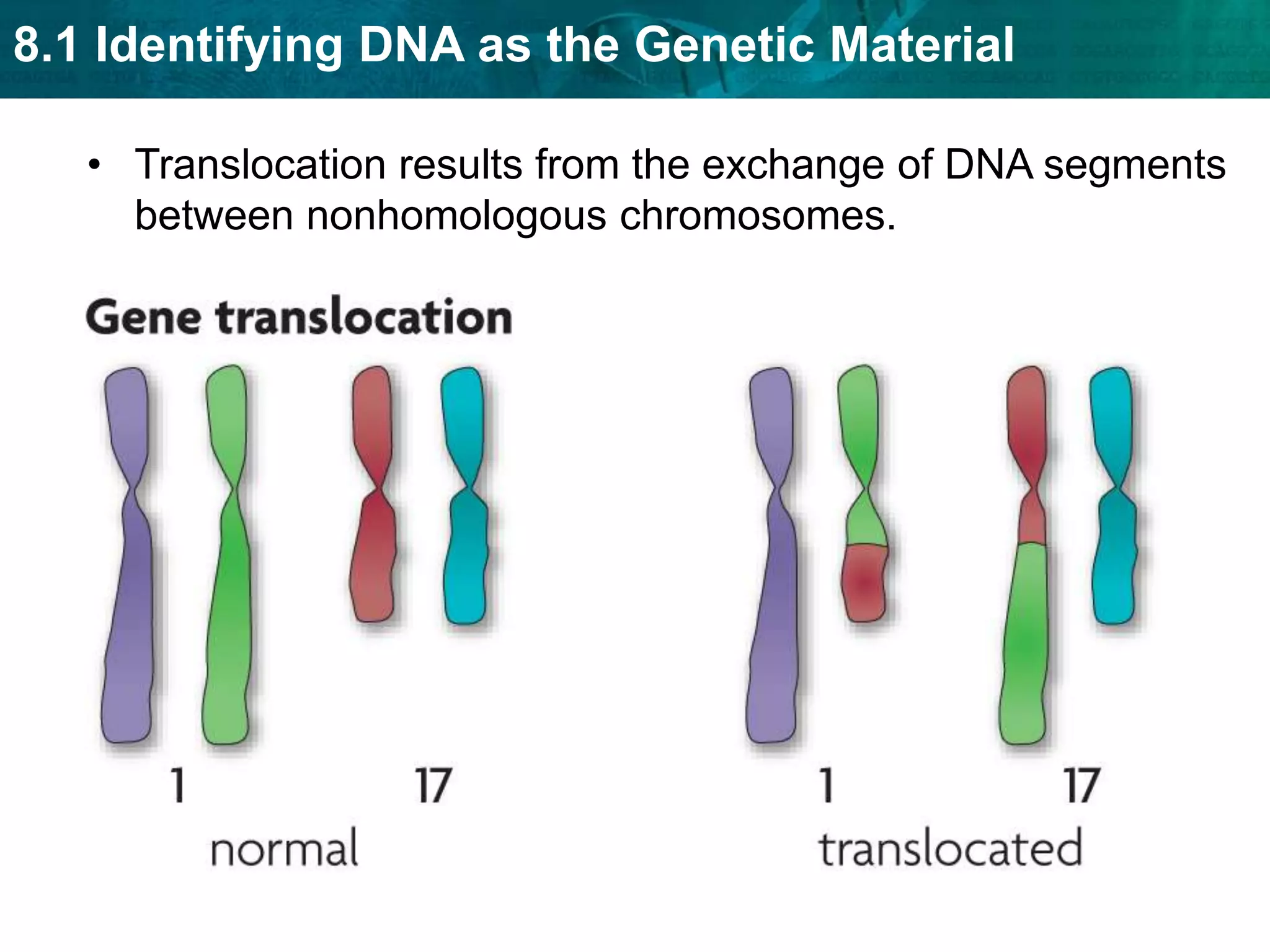
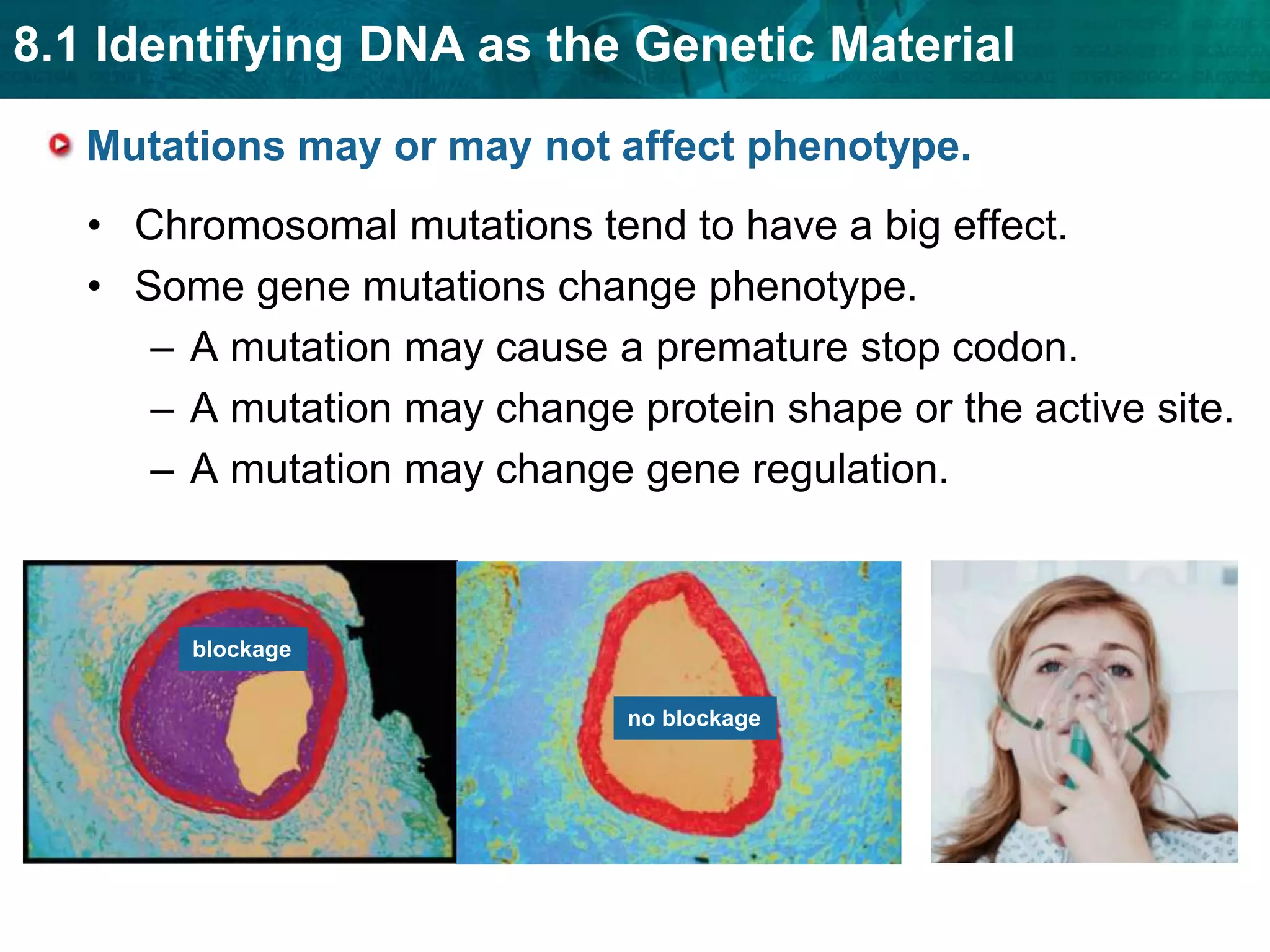
Translation converts mRNA messages into polypeptides through the use of codons, anticodons, transfer RNA (tRNA), and ribosomes. A codon is a sequence of three nucleotides that codes for a specific amino acid. The ribosome helps form a polypeptide bond between amino acids specified by mRNA codons. Gene expression is regulated at transcription and RNA processing in both prokaryotes and eukaryotes. Mutations are changes in DNA that may or may not affect phenotype and can occur through replication errors, mutagens like UV rays, or during chromosomal crossover.