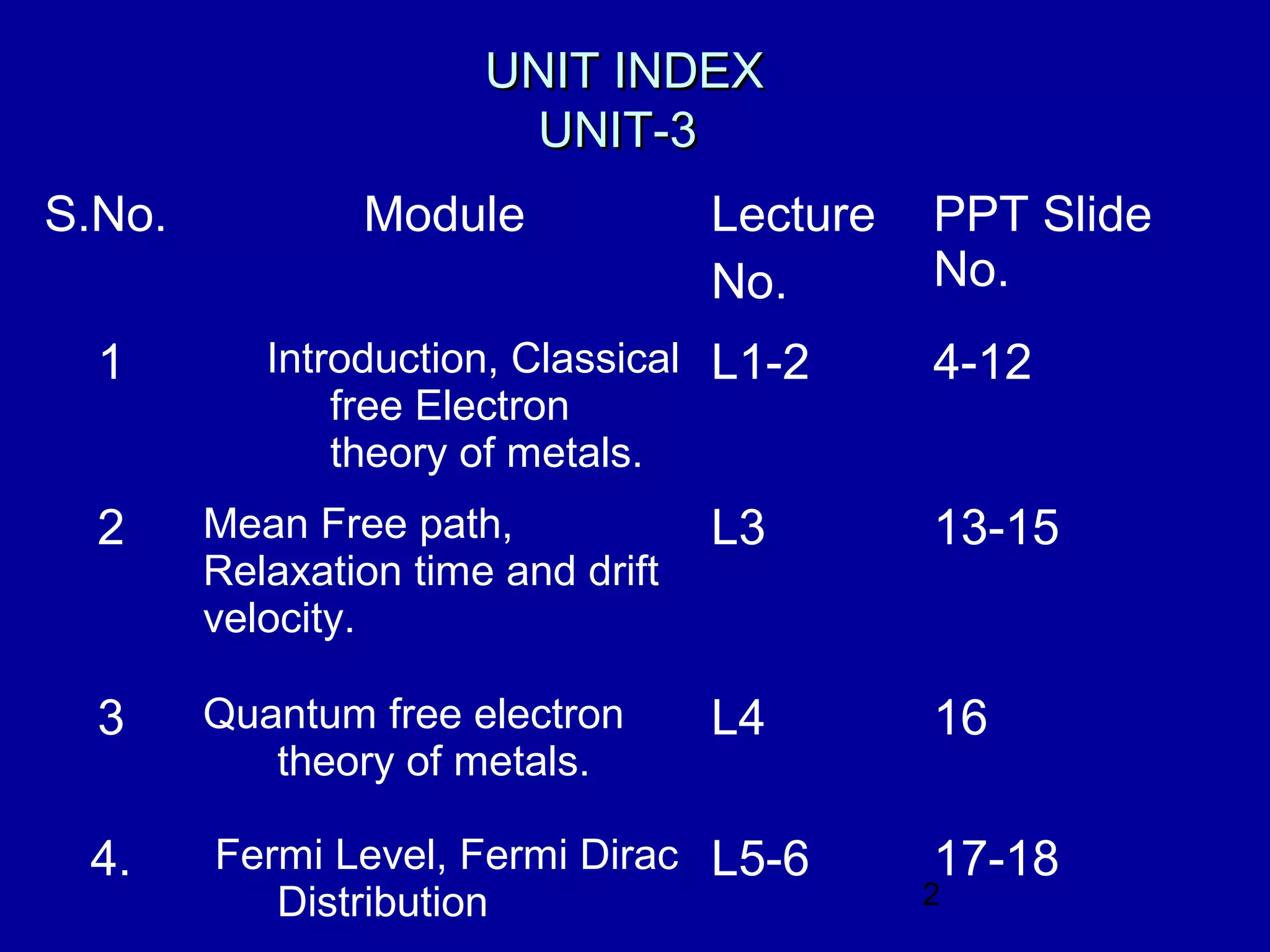
This document provides an overview of the key topics in Unit 3 of the Applied Physics course. The unit covers:
1. Classical and quantum free electron theories of metals, including the Drude-Lorentz model and Sommerfeld's quantum model.
2. Mean free path, relaxation time, and drift velocity of electrons in metals.
3. The Fermi level and Fermi-Dirac distribution of electron energies.
4. Classification of materials as insulators, semiconductors, or conductors based on their band structure and energy gaps.