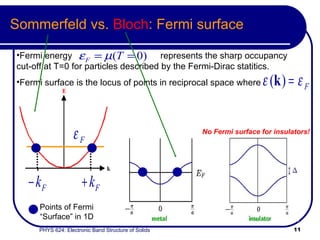
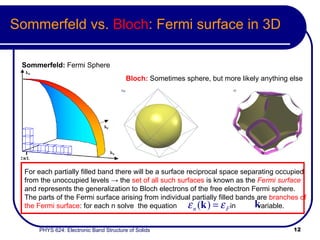
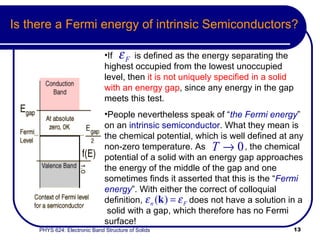
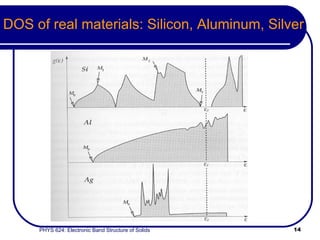
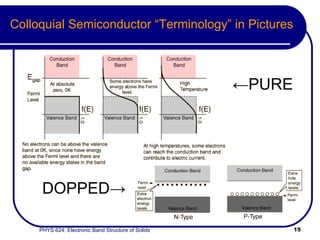
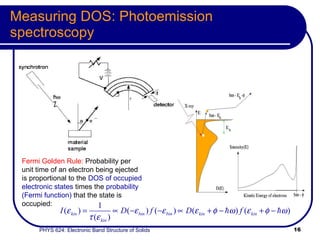
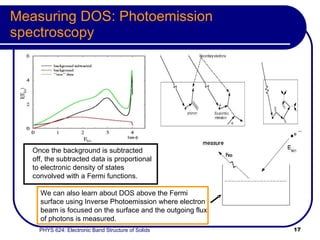
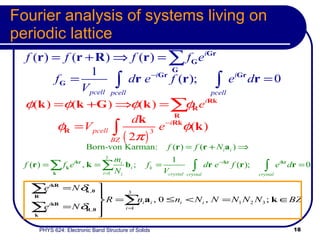
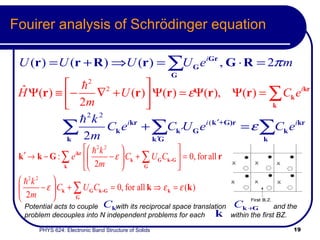
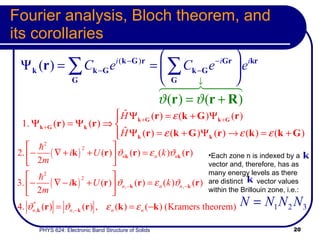
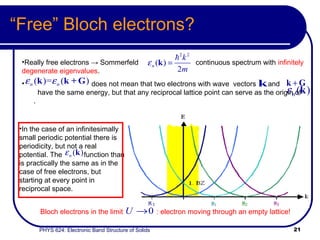
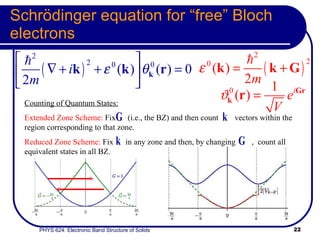
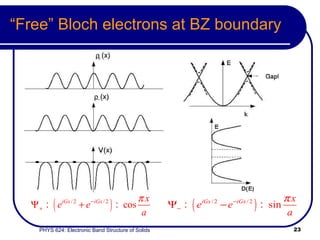
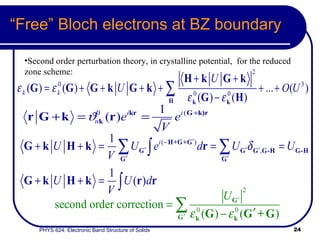
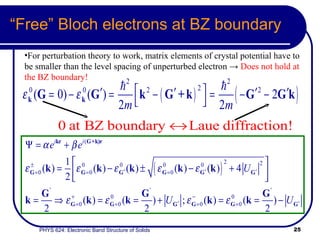
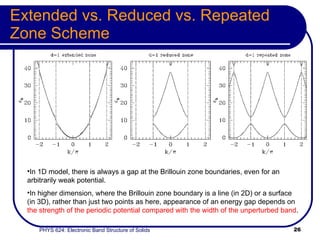
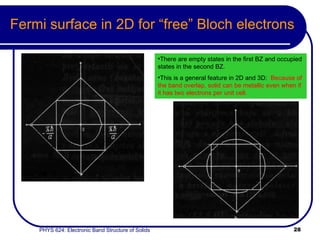
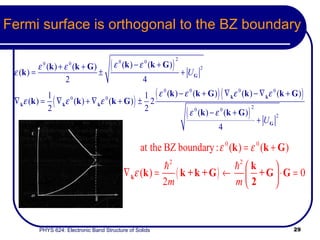
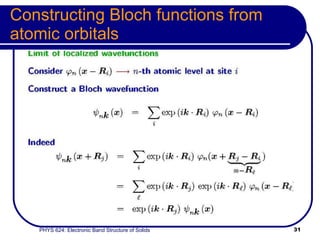
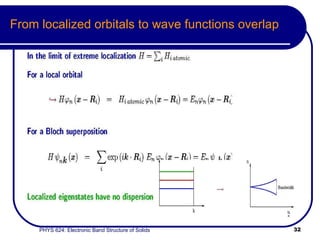
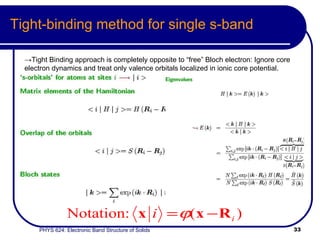
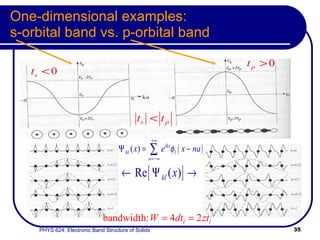
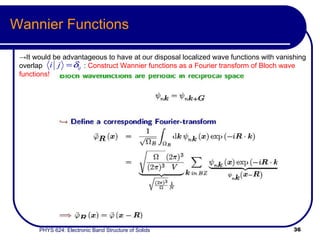
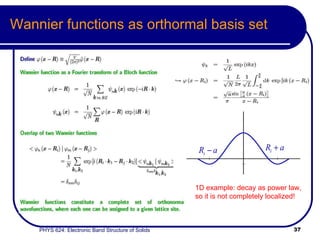
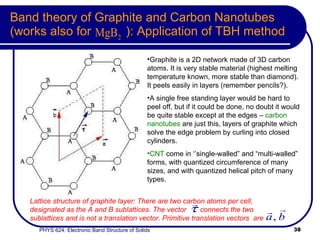
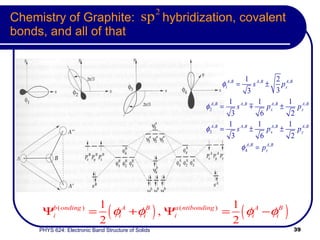
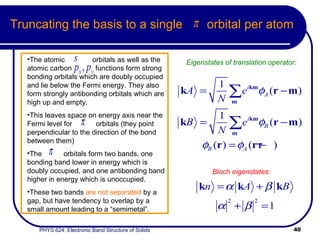
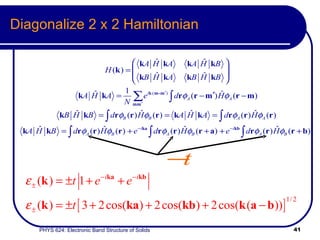
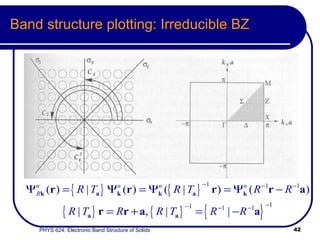
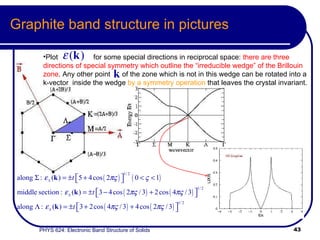
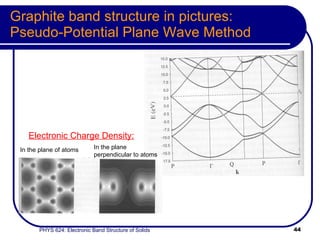
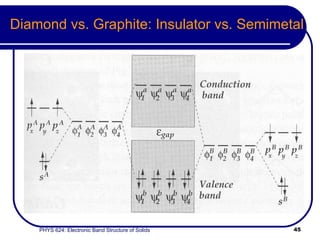
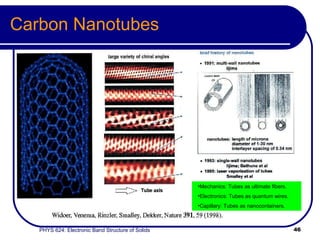
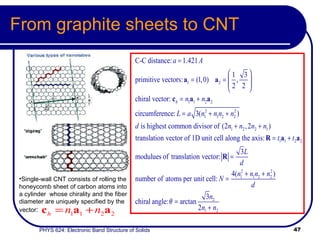
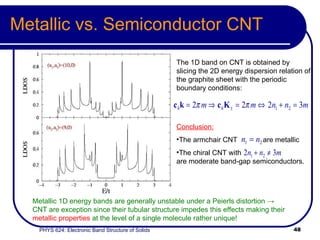
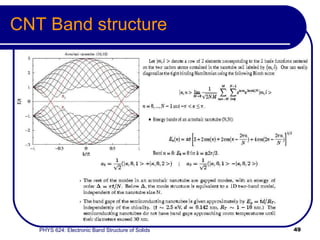
This document provides an overview of electronic band structure and Bloch theory in solid state physics. It discusses the differences between the Sommerfeld and Bloch approaches to modeling electron behavior in periodic solids. Key points include:
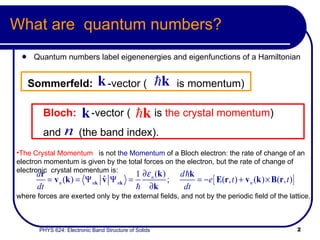
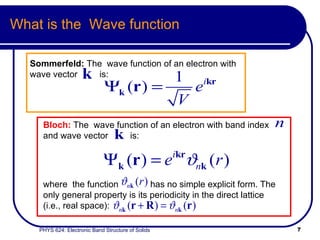
- Bloch's treatment models electrons using band indices and crystal momentum rather than just momentum.
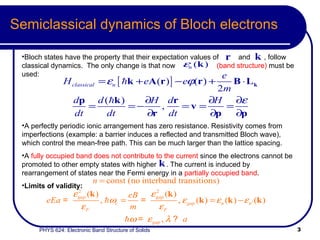
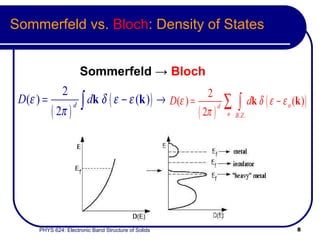
- Bloch states follow classical dynamics on average, with crystal momentum replacing ordinary momentum.
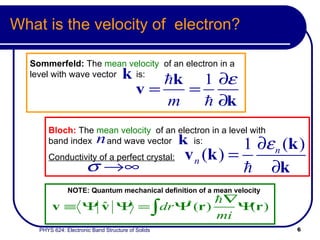
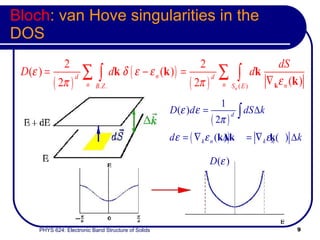
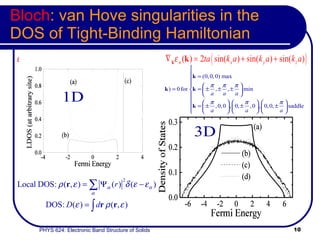
- The band structure determines allowed electron energies and velocities for a given crystal momentum.
- Bloch's theory accounts for periodic potentials within the crystal lattice, allowing for band gaps and a more accurate description of electron behavior in solids.