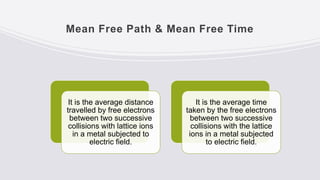
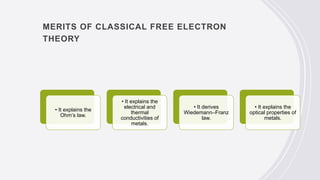
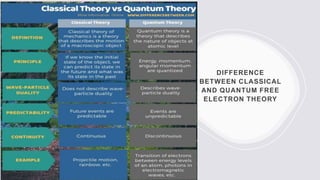
This document provides an overview of classical and quantum free electron theories of metals. The classical theory postulates that valence electrons in metals are free and move randomly, colliding with ions. When an electric field is applied, free electrons drift in the opposite direction. The quantum theory assumes electrons have wave-like properties and their energy levels are quantized. The classical theory can explain electrical and thermal conductivity but fails to explain various quantum effects. The quantum theory resolves issues like temperature-independent paramagnetism.