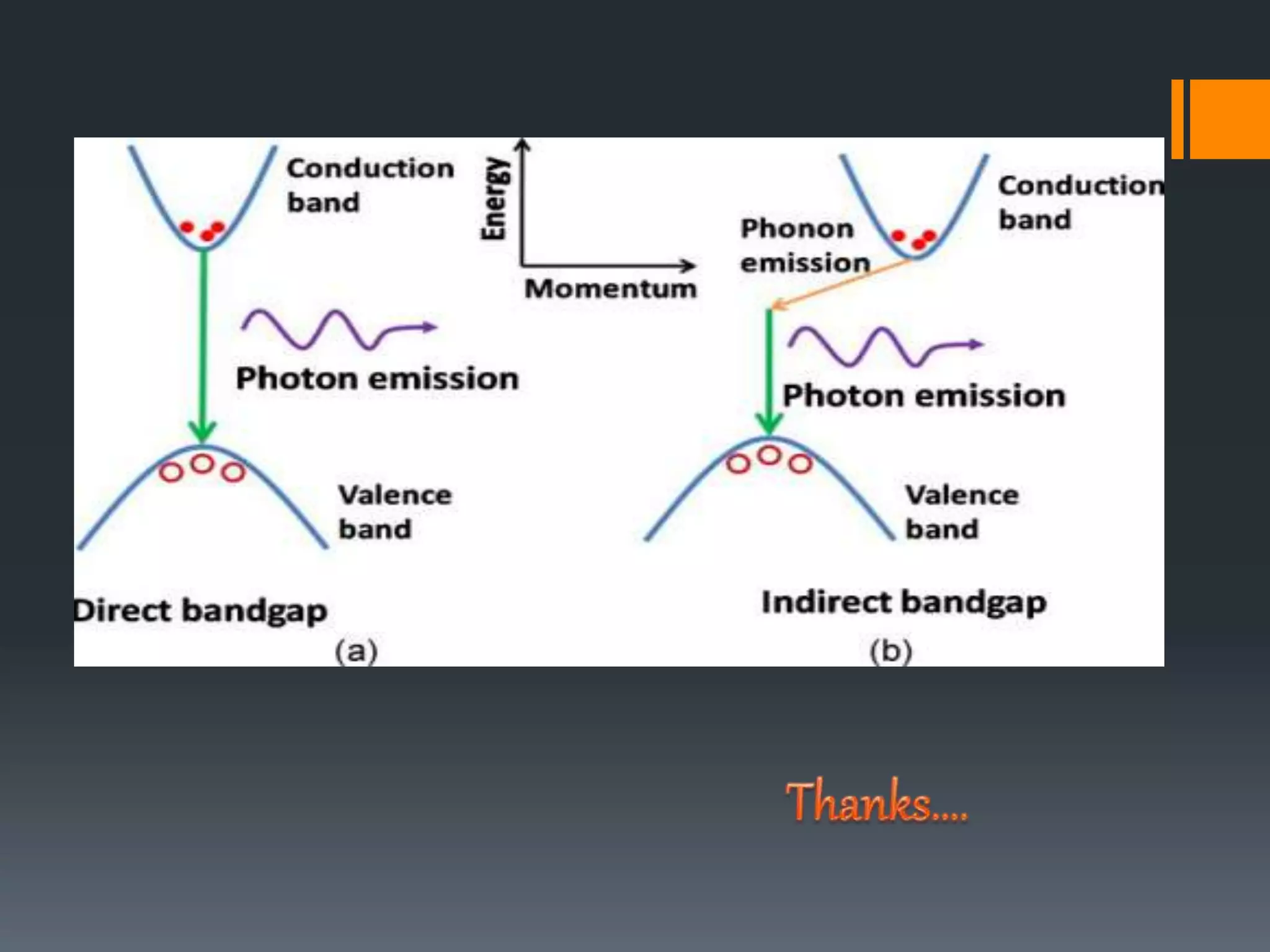
This document summarizes a presentation on energy bands and gaps. It defines energy bands as ranges of allowed electron energies in solids, and energy gaps as ranges where no electron states can exist. Specifically, it describes the valence band containing bound electrons, the conduction band containing free electrons, and the forbidden band or gap between them. It explains direct and indirect band gaps, where electrons either do or do not change momentum when transitioning between bands. The purpose is to provide information on these fundamental concepts of electronic band structure in solids.