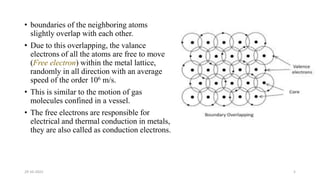
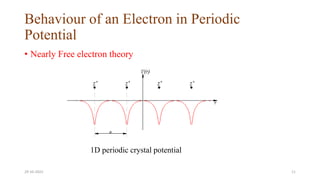
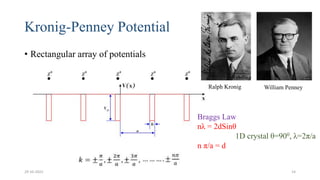
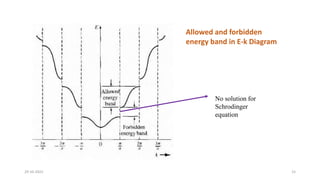
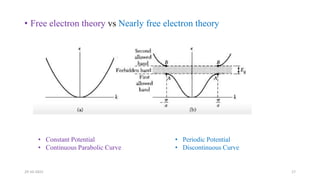
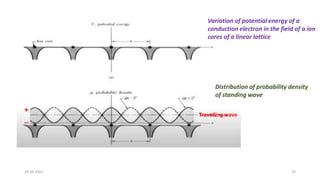
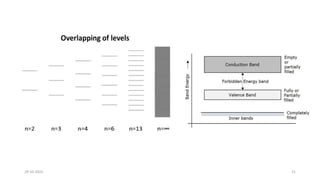
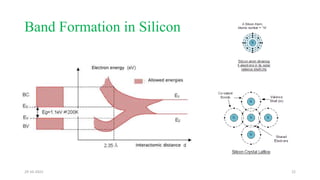
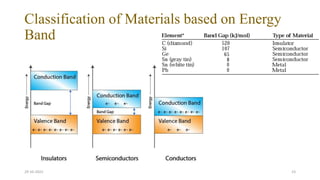
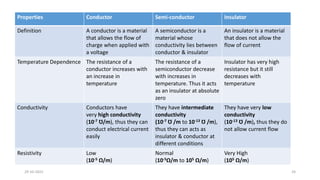
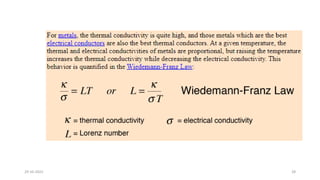
This document discusses band theory and its application to understanding the properties of materials. It begins by introducing classical and quantum free electron theories, which treat electrons in solids as free particles. The behavior of electrons in periodic potentials is then described, leading to the development of band theory. Band theory explains that the discrete energy levels of isolated atoms merge into continuous energy bands as atoms form solids. This allows classification of materials as conductors, semiconductors, or insulators based on whether their energy bands are fully filled, partially filled, or fully empty. Band formation in silicon is provided as an example. The document concludes that band theory determines a material's ability to conduct electricity based on its energy band structure.