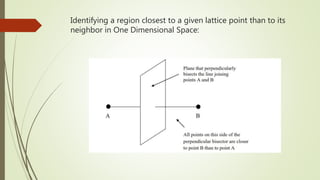
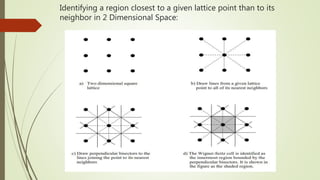
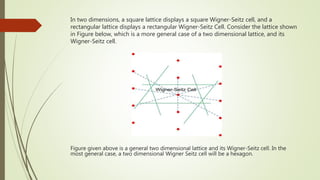
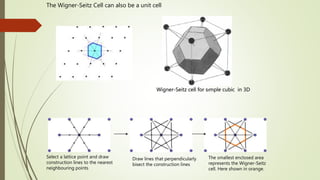
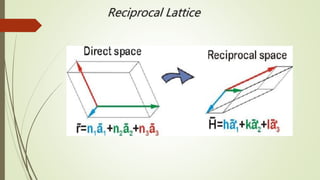
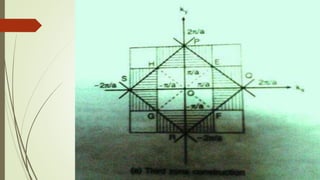
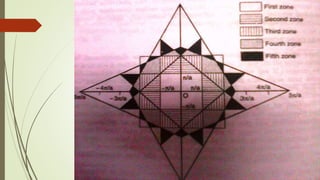
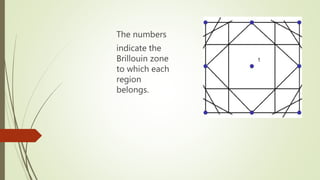
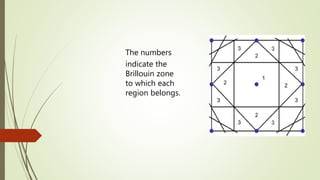
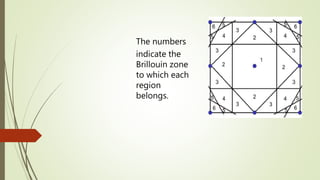
The Wigner-Seitz cell is a Voronoi cell used to study crystalline solids in physics. It is defined as the region in space closer to a given lattice point than any other. The Wigner-Seitz cell of the reciprocal lattice is called the first Brillouin zone. In one dimension the Wigner-Seitz cell is an interval, in two dimensions it is typically a hexagon, and in three dimensions it takes the shape of the smallest polyhedron enclosing the lattice point and its nearest neighbors. Higher order Brillouin zones are identified by planes perpendicular to reciprocal lattice vectors, with the first zone being the smallest such region around the origin.