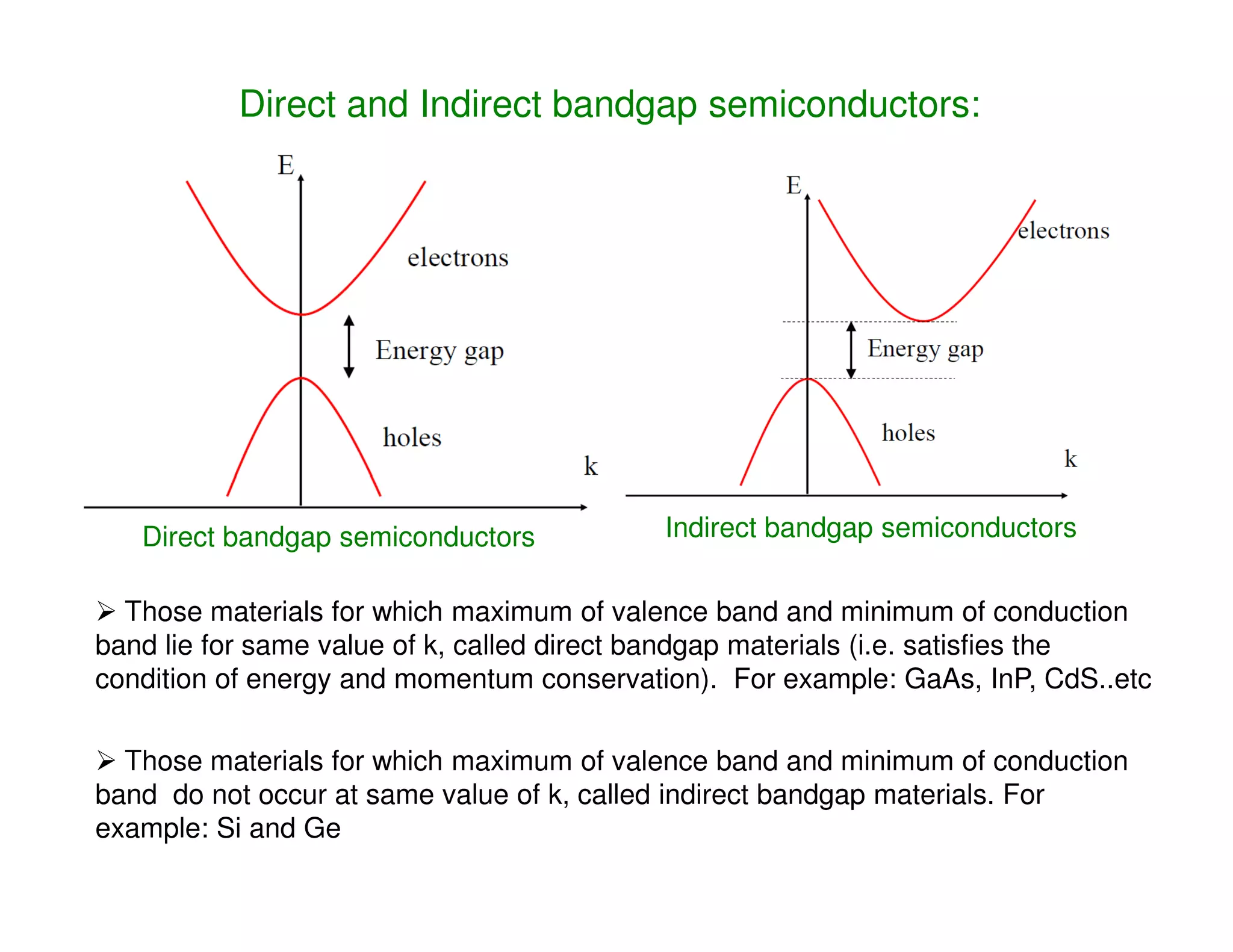
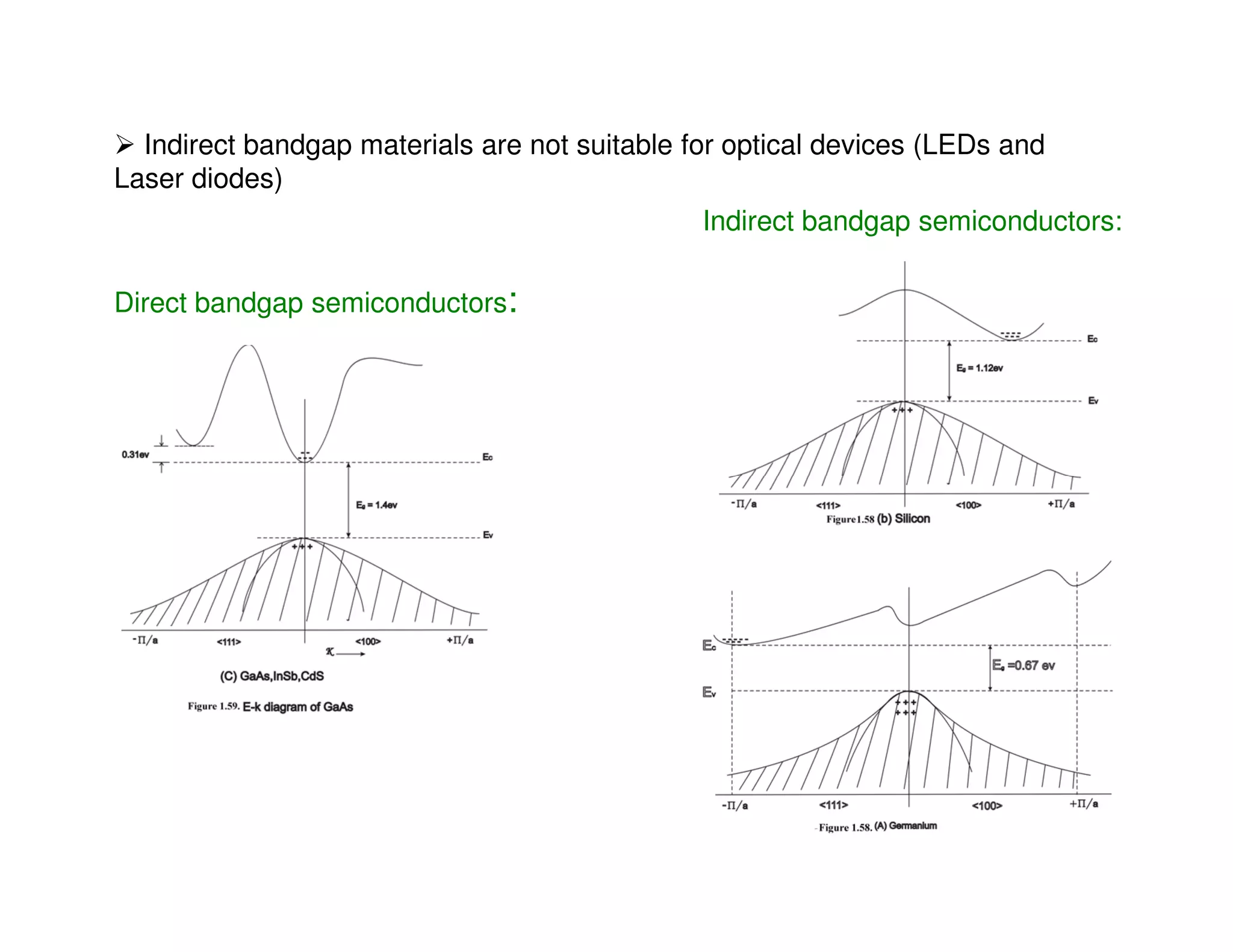
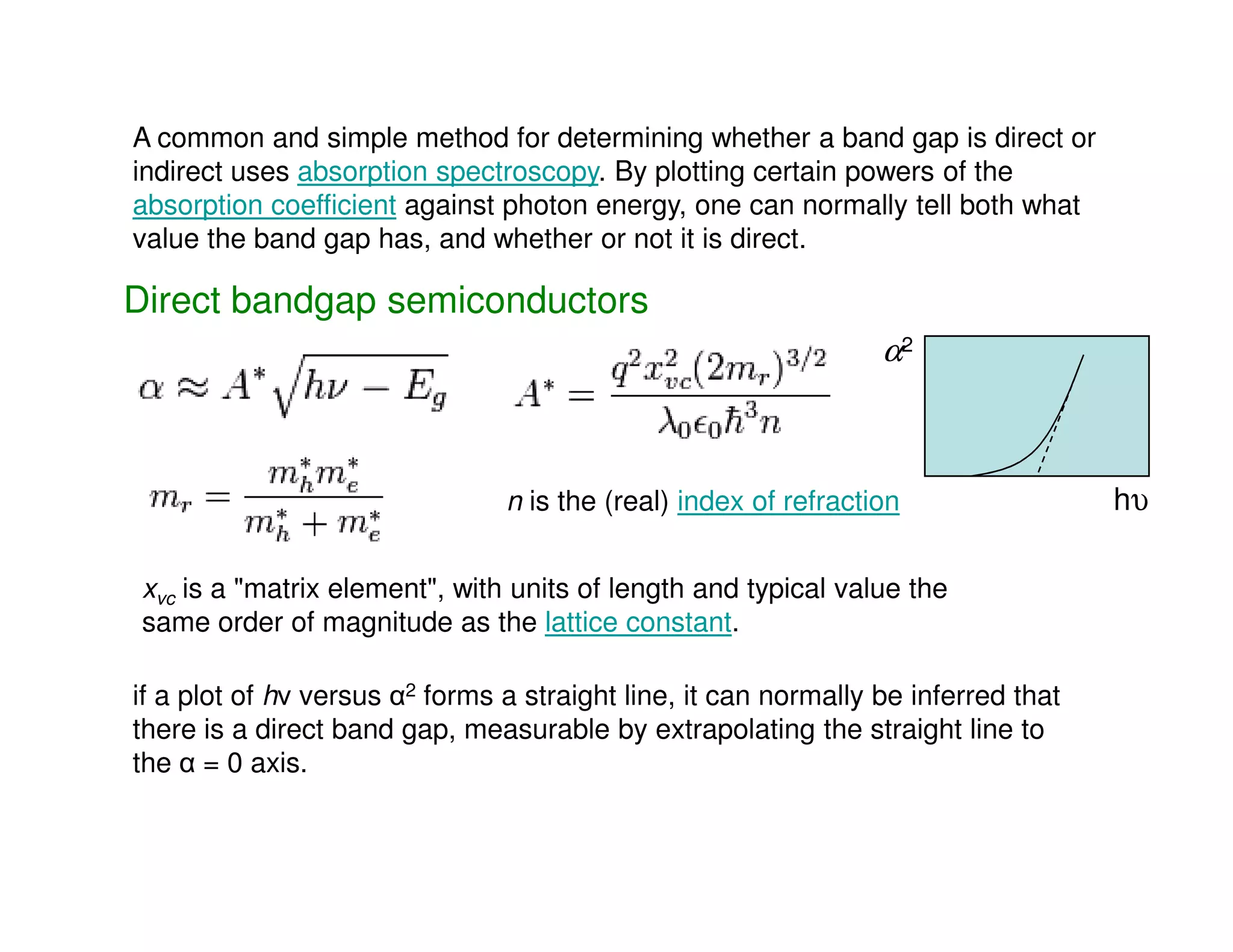
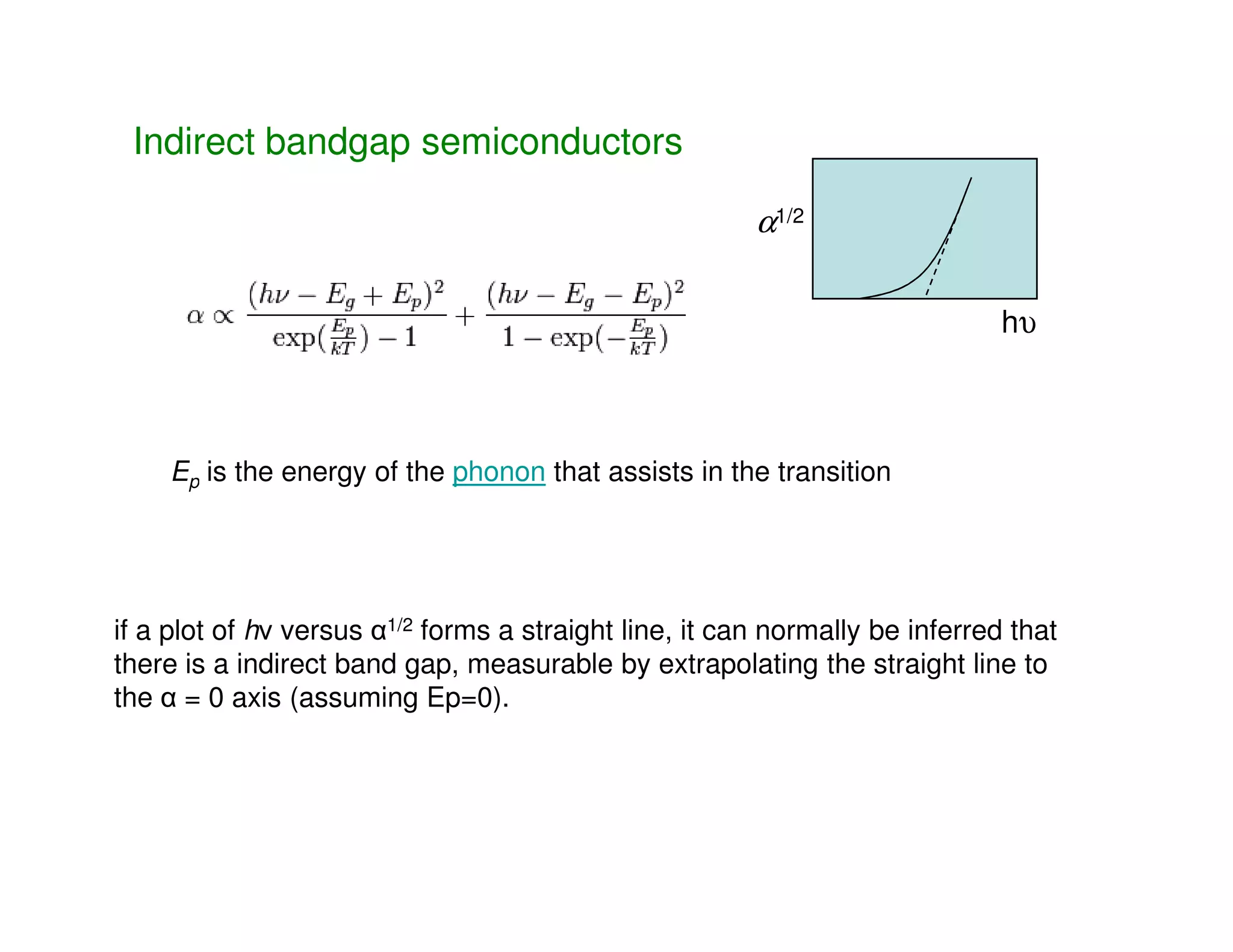
This document discusses direct and indirect bandgap semiconductors. Direct bandgap semiconductors have their valence band maximum and conduction band minimum occur at the same value of k, allowing for energy and momentum conservation. Examples include GaAs, InP, CdS. Indirect bandgap semiconductors have their bands offset in k, making them unsuitable for optical devices. The document also describes methods to determine if a bandgap is direct or indirect using absorption spectroscopy plots of the absorption coefficient. Finally, it introduces 1D, 2D and 3D quantum confinement structures and how quantum confinement can modify electron-hole pair energies and radiation wavelengths.