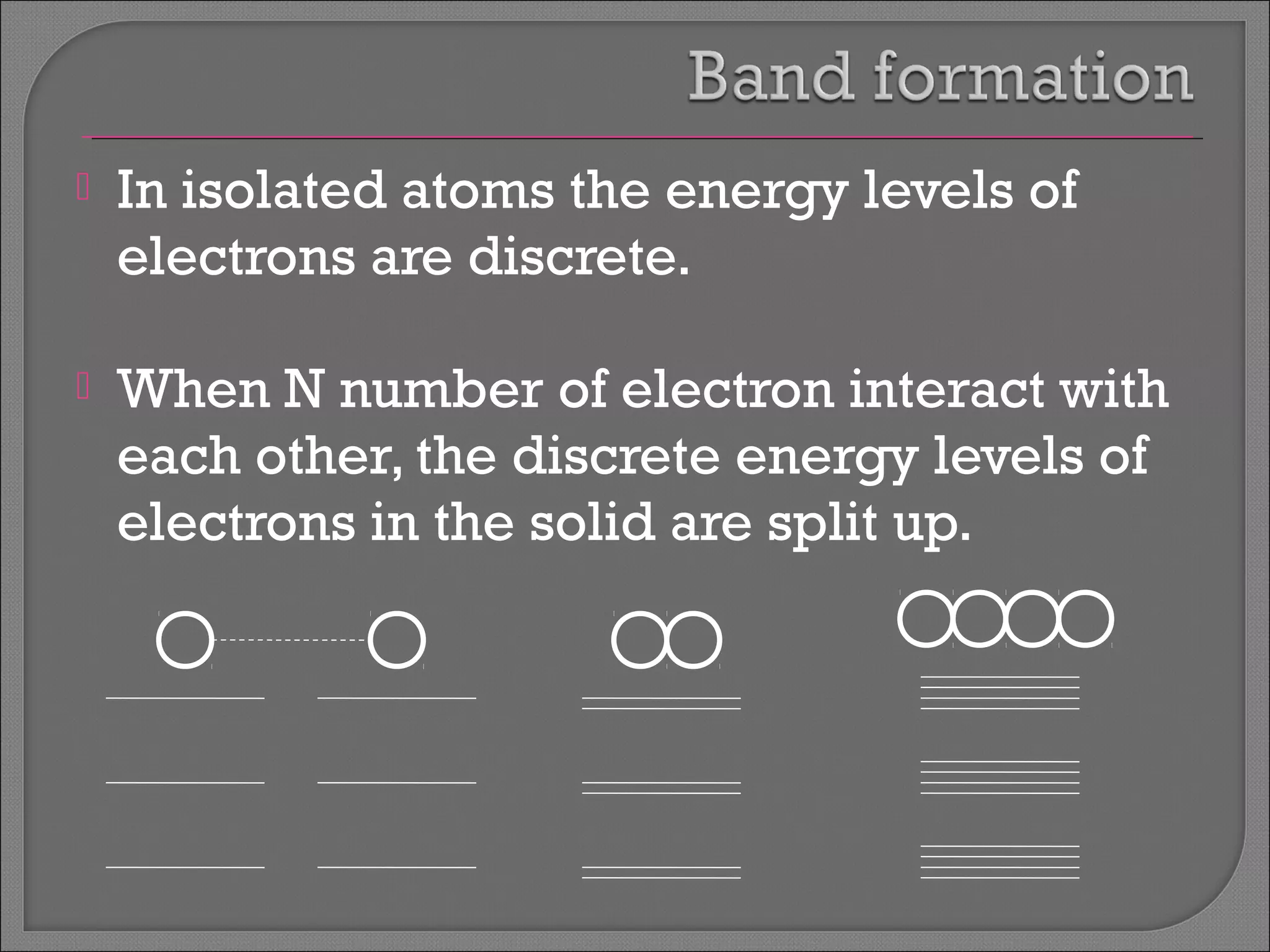
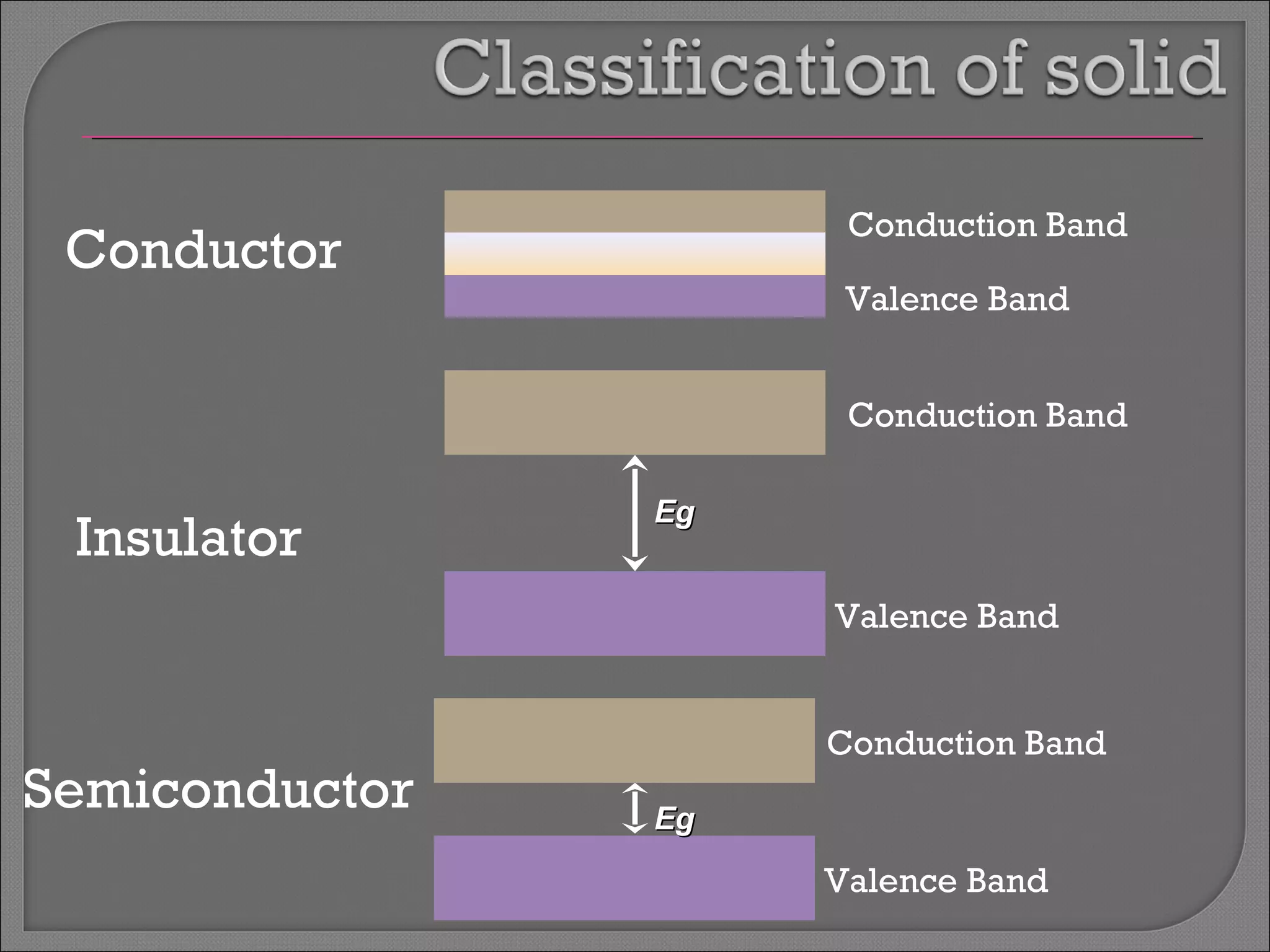
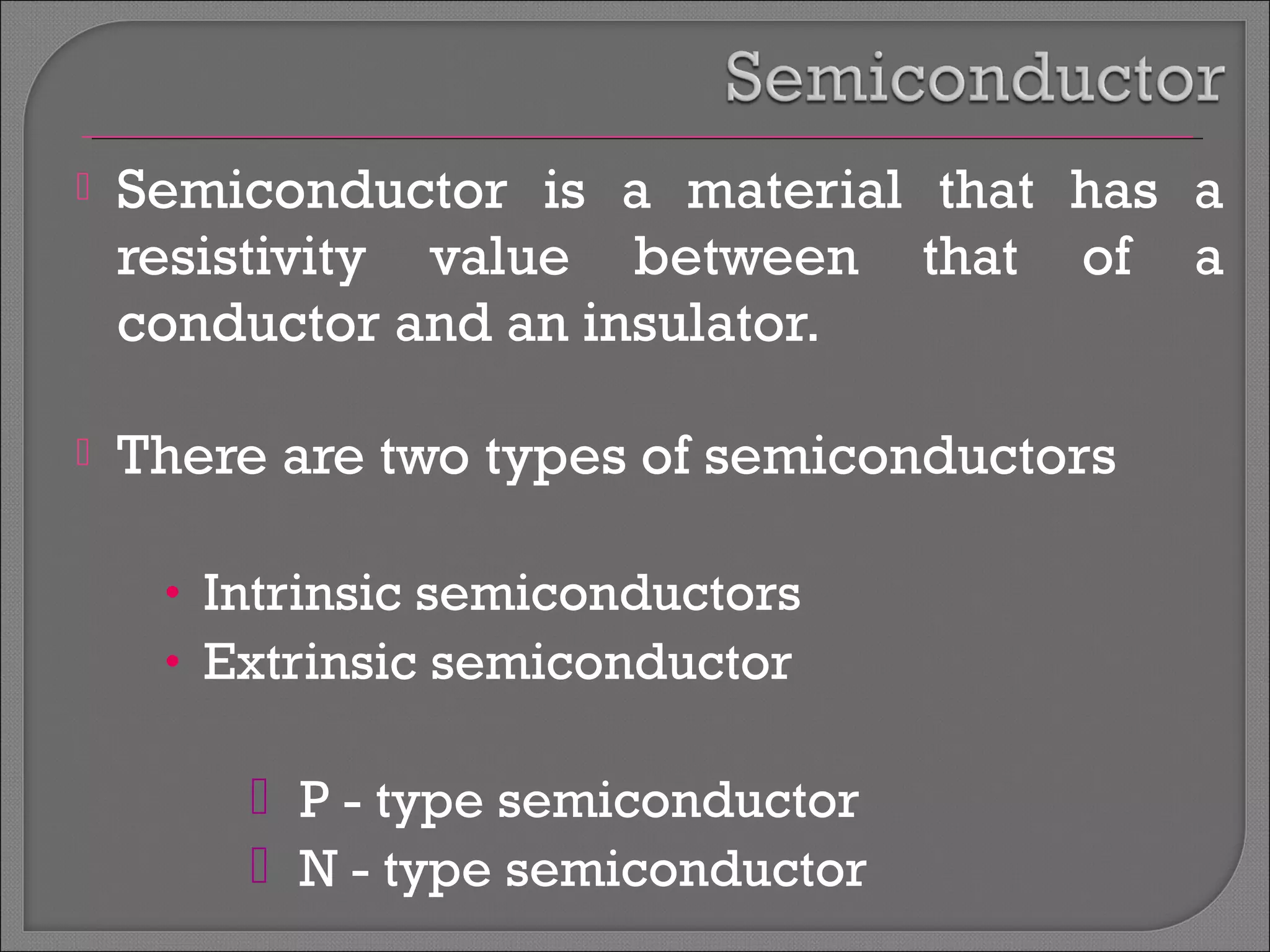
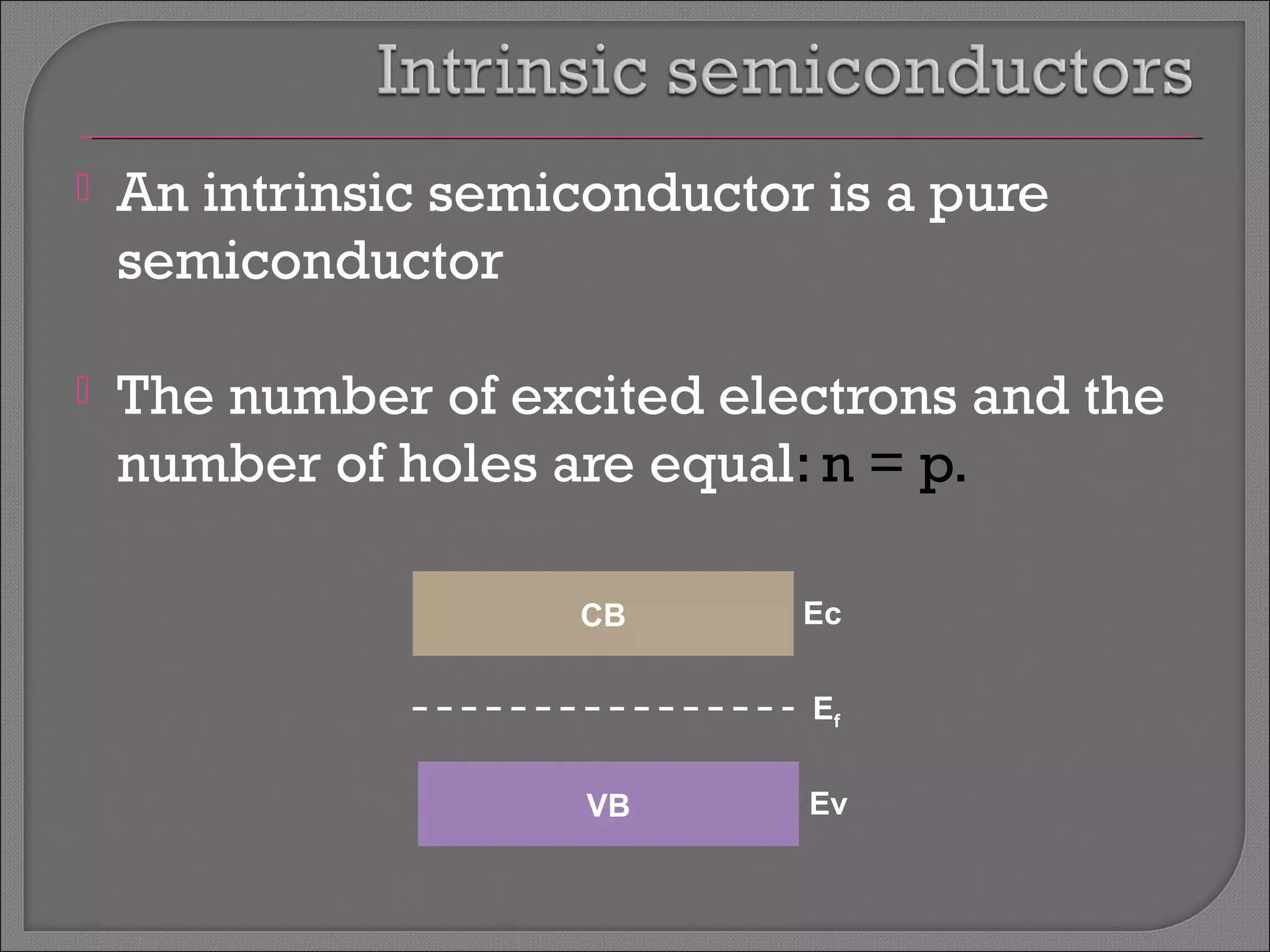
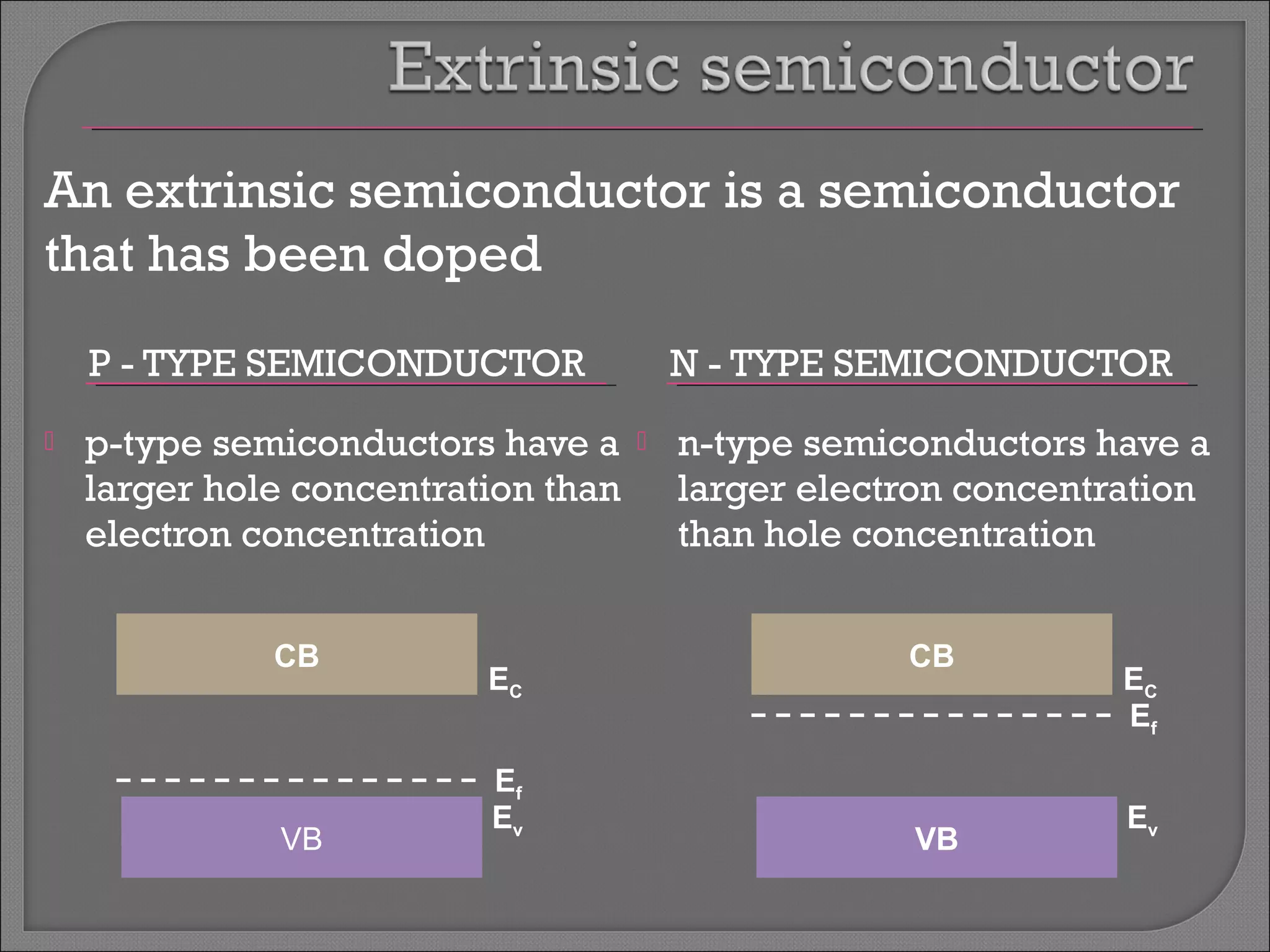
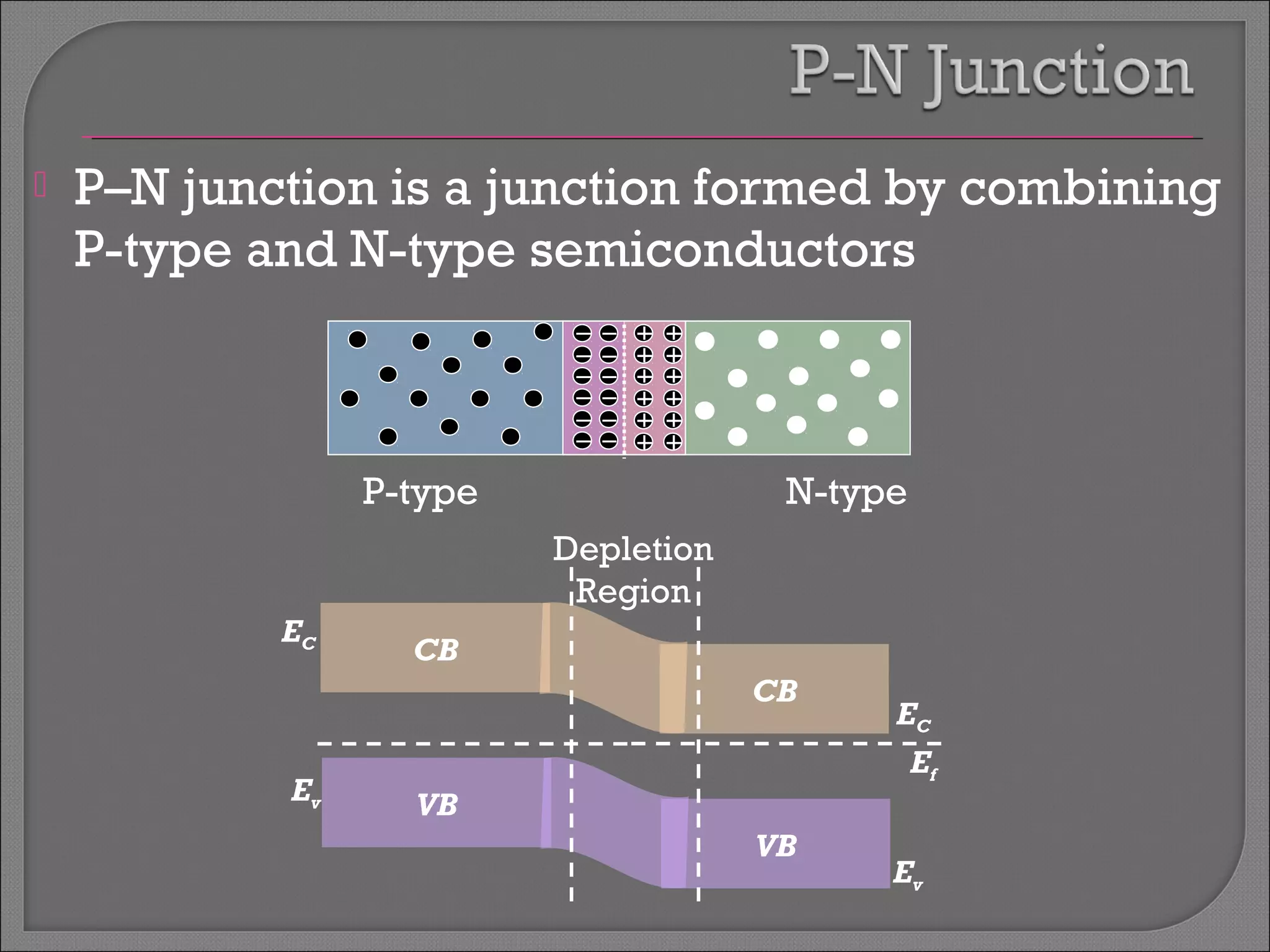
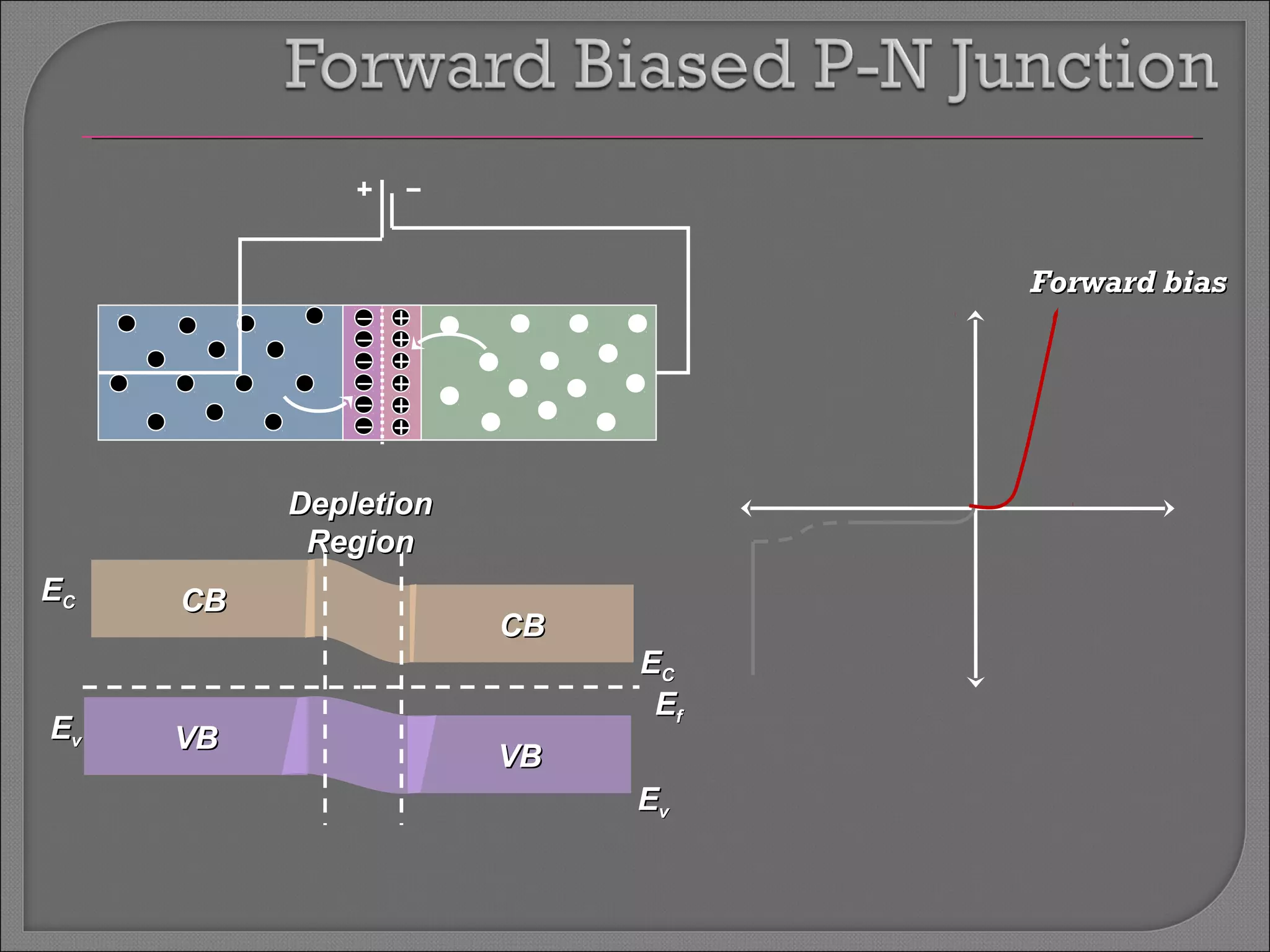
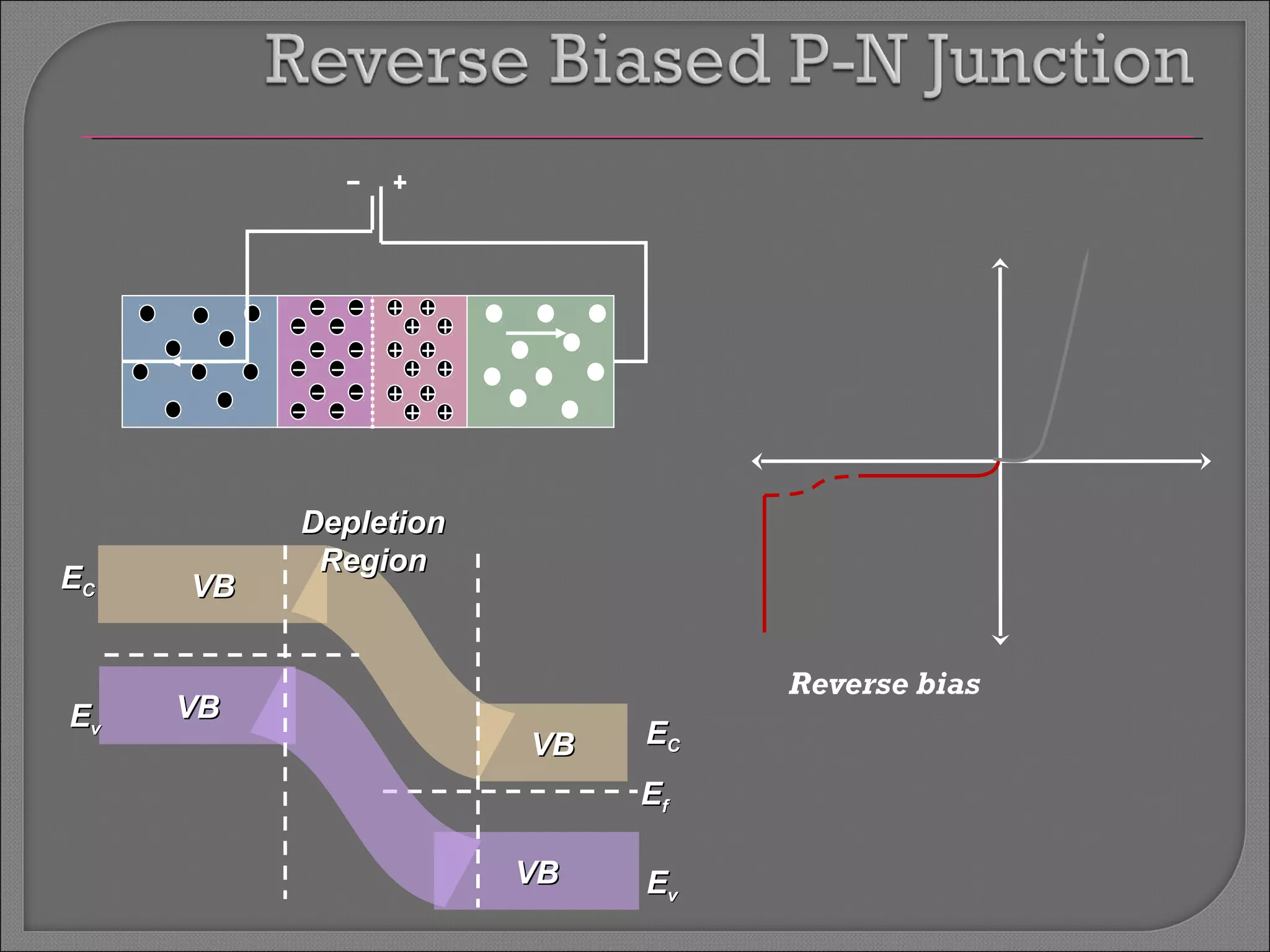
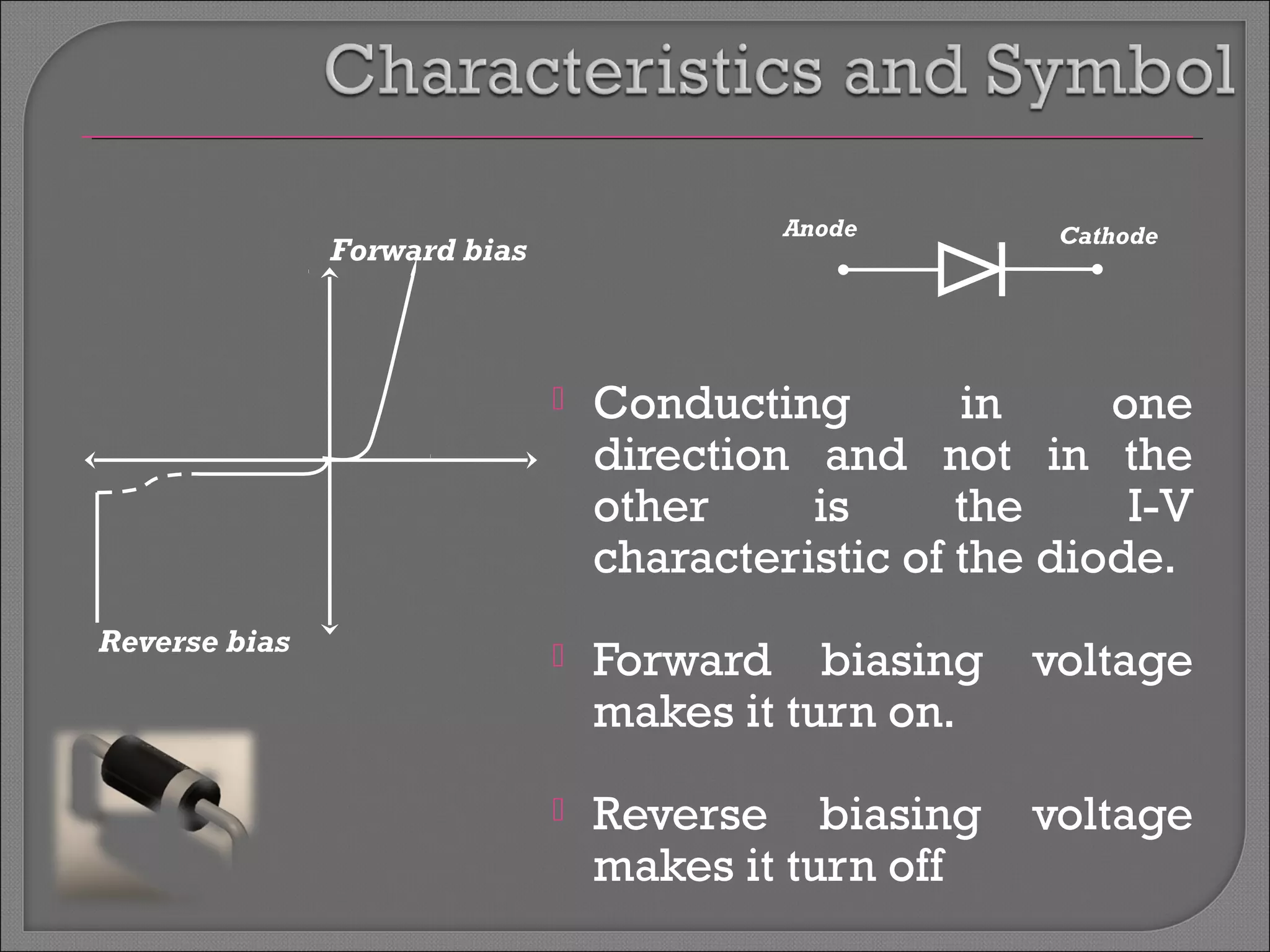
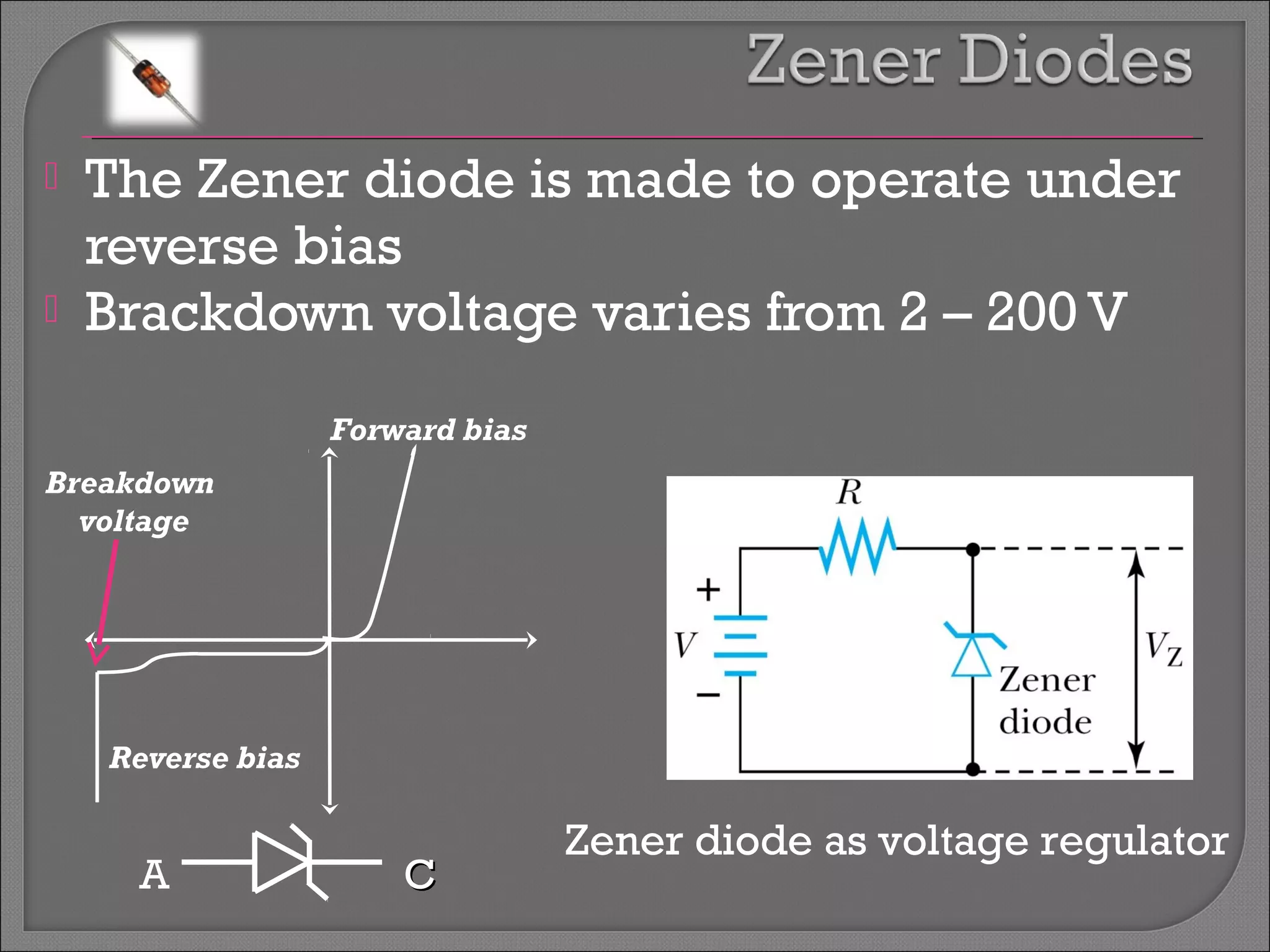
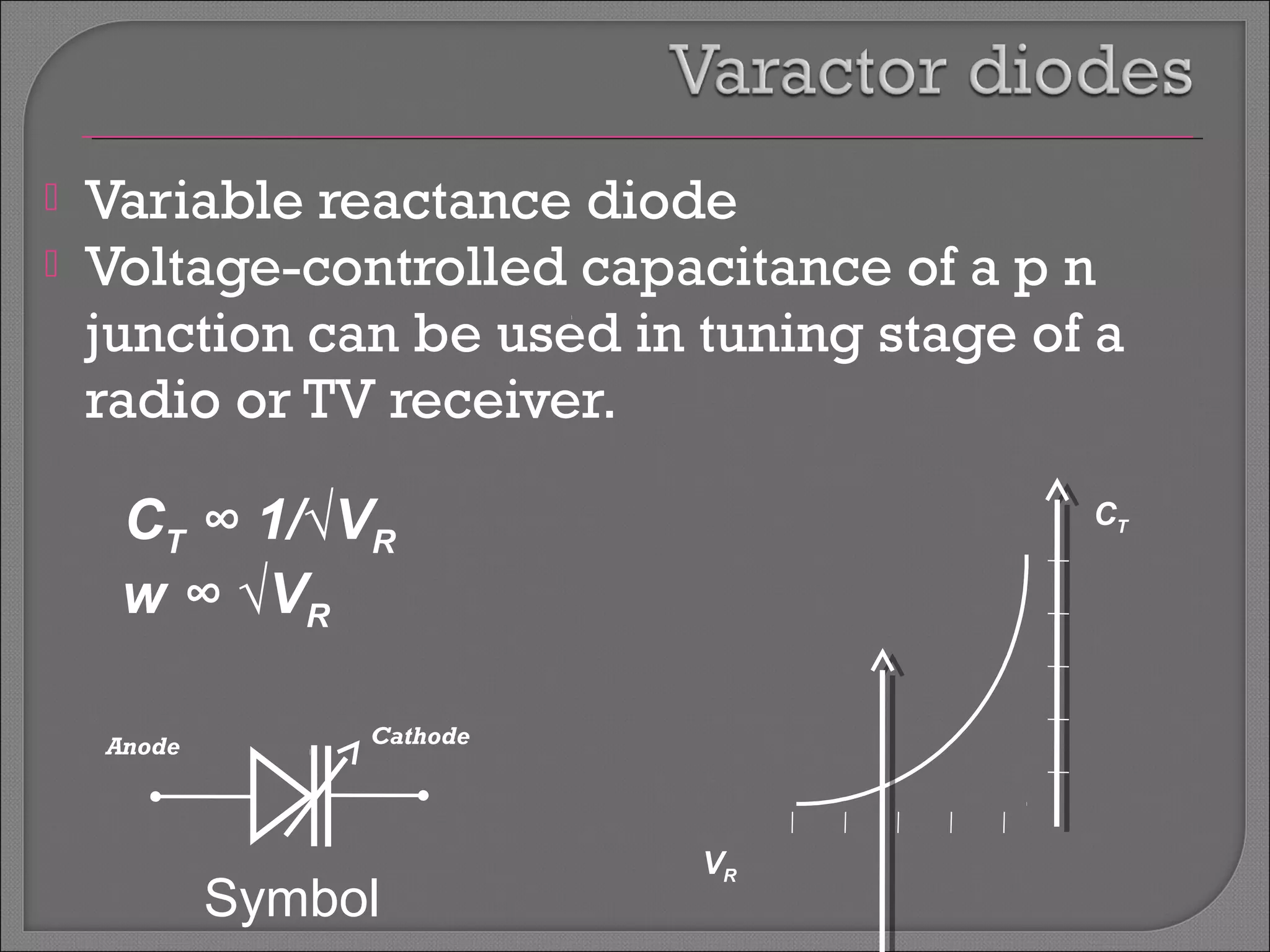
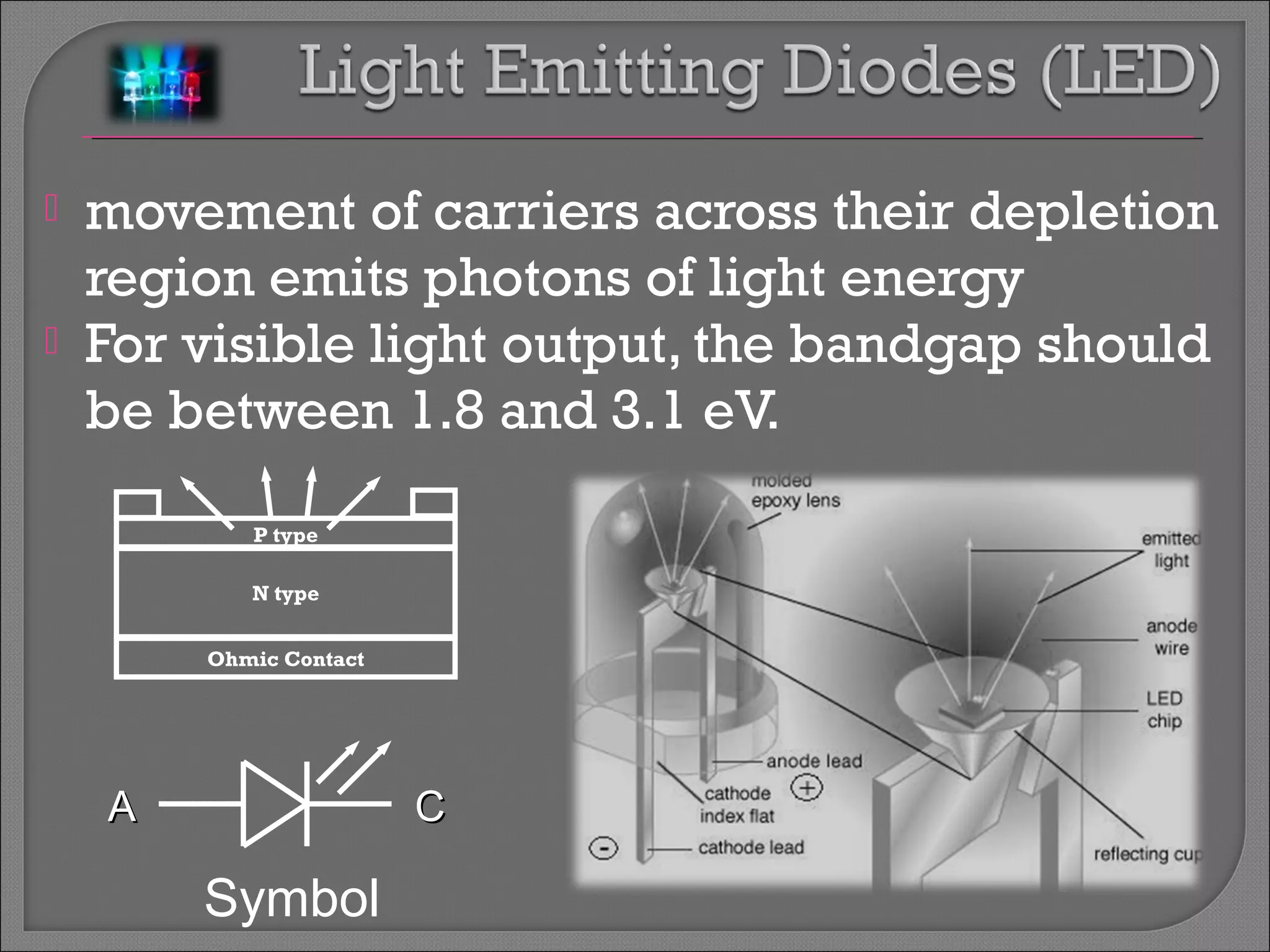
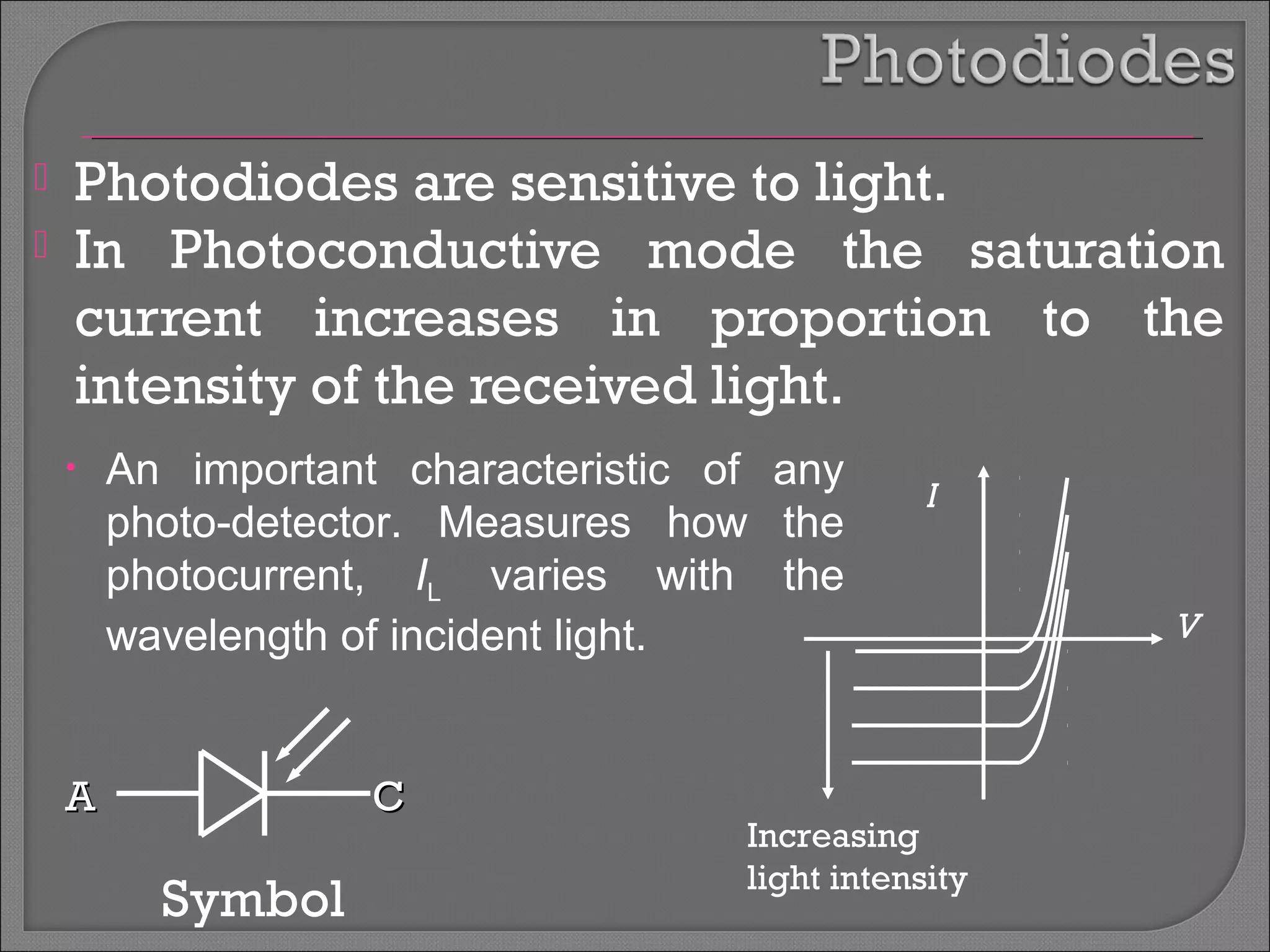
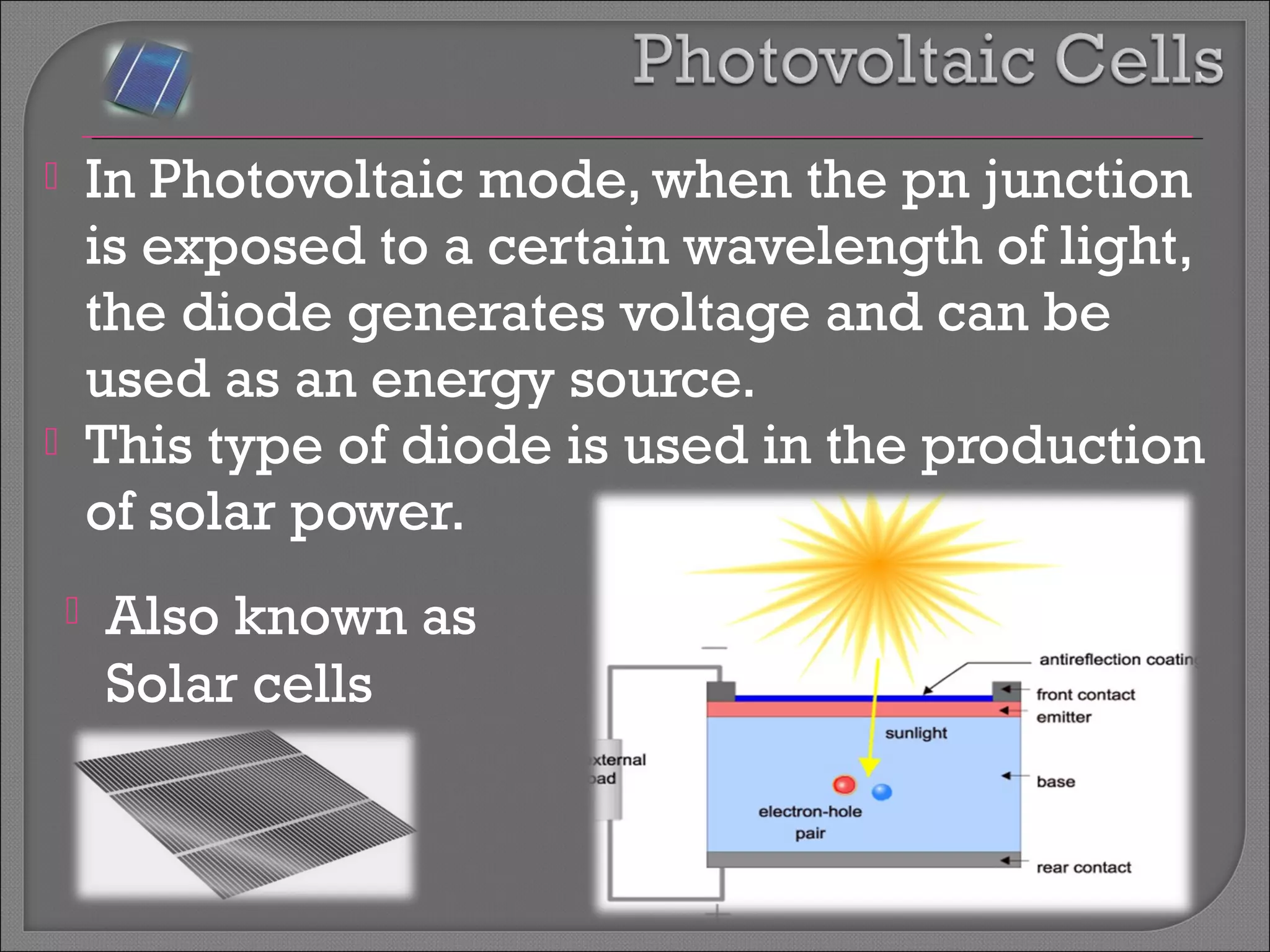
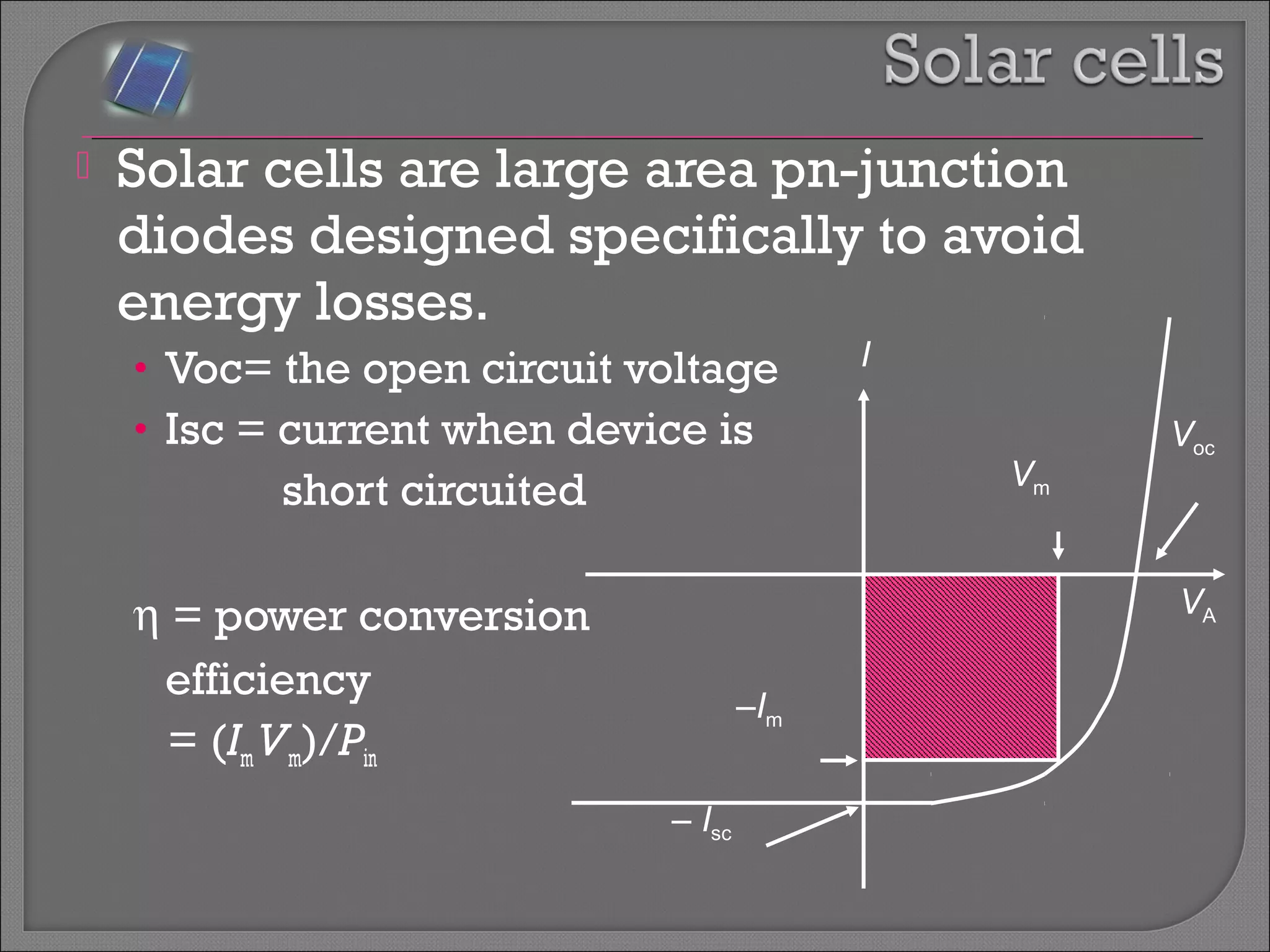
The document discusses band theory of solids and semiconductor devices. It explains that in solids, discrete electron energy levels split into bands. The valence band is fully filled while the conduction band is empty or partially filled, with a band gap separating the two. Semiconductors have a smaller band gap than insulators. Intrinsic semiconductors have equal numbers of electrons and holes, while extrinsic ones are doped with impurities. PN junctions are formed by combining P-type and N-type materials and act as diodes, allowing current in one direction. Diodes have applications as rectifiers, transistors, and other devices that convert between electrical and optical signals.