Unit4 (2)
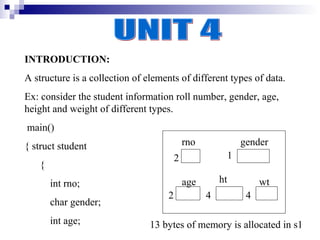
- 1. INTRODUCTION: A structure is a collection of elements of different types of data. Ex: consider the student information roll number, gender, age, height and weight of different types. main() { struct student rno gender 2 1 { int rno; age ht wt 2 4 4 char gender; int age; 13 bytes of memory is allocated in s1
- 2. 13 bytes of memory is allocated to s2 float ht; age gender float wt; 2 1 }; age ht wt 2 4 4 struct student s1,s2; } When all these data items are grouped under on single variable name, we can get some meaningful information. struct is a keyword used to create a new user defined data type. In some other high level programming languages the structures are named as records
- 3. DEFINING A STRUCTURE: syntax: Example: struct user defined datatype struct student { { int rno; datatype member1; int age; char gender; datatype member2; float ht; ……………. float wt; }; ………… datatype membern: };
- 4. In the given syntax struct is keyword used to create new user defined data type. An user defined data type name may be any valid ‘c’ identifier ( user defined name). The data type may be a valid simple data type or compound data type. The member names may be any valid ‘C’ identifiers .in the given example student is a new user defined data type name. The variable rno, age, gender, ht, wt, are the structure members. All these structure members must be enclosed within a pair of curly braces. The structure definition should be terminated with semicolon.
- 5. DECLARING STRUCTURE VARIABLE: Once a new user defined datatype is created by using the keyboard struct then we can create any no. of structure variables of that type. syntax: struct user defined_data type name structure var1, structure var2,……….. Struct varn; Above statement is called declarative statement of structure variables and it allocates memory space to these variables. We can also declare structure variables immediately after structure definition.
- 6. ACCESSING STRUCTURE MEMBERS: . Structure member accessing operator S1.gender=‘m’; s1.age=25; Structure S1.rno=100 S1.ht=5.5; s1.wt=60.2; variable Structure member •Two operators are used to access member of structure. The structure member operator(.) also called dot operator and the structure pointer operator () also called the arrow operator. •The structure member operator accesses a structure member via structure variable name.
- 7. syntax: Ex: s1.rno, s1.age, s1.gender, s1.ht, s1.wt S1.rno=100; s1.gender=M; s1.age=25; s1.ht=5.5; s1.wt=60.2 s1 s2 rno gender rno gender 100 M age ht wt age ht wt 25 5.5 60.2 ASSIGNING VALUES TO STRUCTURE MEMBERS: By using the assignment operator(=) we can assign values to all structure members of a structure variable. Syntax: structure variable.member = value; Ex: s1.rno= 100; s1.age=25
- 8. INITIALIZING A STRUCTURE VARIABLE: Structures can be initialized using initialize lists as with arrays. To initialize a structure follow the variable name in the structure declaration with an equal sign and brace enclosed comma separated list of initializes. Ex: struct student s1={100, 25,’M’, 5.5,65.2}; int x = 10; int a[10]={ 10,20,30}; READING AND DISPLAYING THE STRUCTURE VARIABLES: The ‘C’ will not read or write an entire structure as a single command. It will read or write the members of a structure as follows: ex: scanf(“ %d, %d, %c, %f” ,&s1.rno,&s1.age,&s1.gender,&s1.ht); printf(“ %d %d %c %f”, s1.rno, s1.age, s1.gender, s1.ht);
- 9. PROGRAM USING STRUCTURES: Reads the details of 2 students and calculate total and average marks of 2 students. #include<stdio.h> #include<conio.h> void main() { /* defining a structure */ struct student { int rno; char name[30]; float m1,m2,m3; float tot, avg; };
- 10. /* 2. declaration of structure var*/ struct student s1,s2; (1st executed) /* 3.reading 1st student details*/ printf(“ enter rno,name,m1,m2,m3 of first student n”); scanf(“ %d %s %f %f %f ”, &s1.rno,&s1.name,&s1.m1,&s1.m2,&s1.m3); /* 4. reading 2nd student details*/ printf(“ enter rno, name, m1, m2, m3,of second student n); scanf(“ %d %s%f %f %f”, &s2.rno, &s2.name,&s2.m1,&s2.m2,&s2.m3); /* calculate total and avg of first student marks*/ s1.tot= s1.m1+s1.m2+s1.m3; s1.avg = s1.tot/3;
- 11. /* 6.calculate total and avg of first student marks*/ s2.tot= s2.m1+s2.m2+s2.m3; s2.avg = s2.tot/3; /* displaying first student details*/ printf(“ first student details are n”); printf( “roll no:%dn, name:%s n, m1: %f n. m2:%f, m3:%f n”, s1.rno, s1.name, s1.m1, s1.m2, s1.m3); printf(“ total :%f n , average: %f n”, s1.tot, s1.avg); /* 8. displaying second student details*/ printf(“ second student details are:n); printf( “roll no:%dn, name:%s n, m1: %f n. m2:%f, m3:%f n”, s2.rno, s2.name, s2.m1, s2.m2, s2.m3); printf(“ total :%f n , average: %f n”, s2.tot, s2.avg); }
- 12. Array of Structures: Perhaps the most common usage of structures is an array of structures. ->To declare an array of structures you must first define a structure and then declare an array variable of that type. For example to declare a 100 element array of structures of type “student” write struct student { int rno; int m1,m2,m3; int tot,avg; } struct student s[100];-Structure Variable Declaration
- 13. DEMONSTRATING ARRAY OF STRUCTURES: #include<stdio.h> #include <conio.h> void main() { /*1.Defining an array of structures*/ struct student { int rno; int m1,m2,m3; int tot,avg; };
- 14. /*2.Creating an array of Structures*/ struct student s[100]; int i,n; clrscr(); printf(“Enter n valuen”); /*3.Read total no.of students to n*/ scanf(“%d”,&n); /*4.Reading student details*/ for(i=0;i<n;i++) { printf(“Enter details of %d studentn”,i+1); scanf(“%d”,&s[i].rno);
- 15. scanf(“%d%d%d”,&s[i].m1,&s[i].m1,&s[i].m2,&s[i].m3); /*5.Calculate tot,avg marks */ for(i=0;i<n;i++) { s[i].tot=s[i].m1+s[i].m2+s[i].m3; s[i].avg=s[i].tot/3; } /*6.Display the student details*/ for(i=0;i<n;i++) { printf(“The following are the %d student detailsn”,i+1); printf(“Rollno:%dn”,s[i].rno);
- 17. Arrays with in Structures: A member of a structure may be either a simple or compound type. simple member is one that is of any of the built-in datatypes such as integer or character. ->The compound datatypes include one dimensional and multidimensional arrays of other datatypes and structures. For example consider this Structure: struct x { int rno; int m[3];/* An Array is described as a structure member*/ int tot,avg; }
- 18. Nested Structures: when a structure variable is a member of another structure, it is called a Nested structure. ->In the below example structure variable ‘z’ is declared as structure Member to another structure. EX:struct Test { int a; int b; }; Struct Exam { int x; int y; struct Test z; };
- 19. Structures and Function: A Structure can be passed to a function as a one variable or as an individual member. The scope of a structure declaration should be external storage class whenever a function in the main(). Program Using a Structure datatype: #include<stdio.h> /*Defining a Structure*/ struct Test { int a; int b; }; /*Prototype*/
- 20. struct Test Modify(struct Test s2); void main() { struct Test T1={10,20}; T1=Modify(T1); printf(“After calling modifyn”); printf(“T1.a=%dn”,T1.a); printf(“T1.b=%dn”,T1.b); } Stuct Test Modify(struct Test s2) { s2.a=s2.a+10;
- 21. S2.b=s2.b+10; return s2; } a b a b 10 20 10 20 1 10+10 20+10 200 30 =20 =30
- 22. Union: Union is another datatype with two or more members,similar to structure.But in this case all the members share a common memory location.The members of a union can be refered by using dot operator as in the case of structure. The size of union can contain only one type of member at any one time. The size of union corresponds to the length of the longest member. Syntax: Union Userdefined_datatype { datatype member 1; datatype member n;};
- 23. Union Test { char a; int b; float c; }; We may have structures with unions and unions with in structures. Unions may also be intialized like structures.However,Since only one member can be active at a time,Usually the assigned value will go to the 1st member of union.