This document provides an introduction to computer communication networks. It discusses the motivation to learn about networks, including benefits to business, science, education and industry. The topics to be covered include data communications, networks, the Internet, and protocols and standards. Specifically, it defines data communications and networks, describes the components and flow of data communications, different network types and models, and standards organizations. The Internet is introduced as a global system of interconnected networks that has revolutionized information sharing.
![Unit 0
[ Prerequisite ]
Introduction
to
Computer Communication Networks](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/unit0introduction-140901094117-phpapp02/75/Unit-0-introduction-1-2048.jpg)



![a) Effectiveness of a Data Communication System
The effectiveness of a data communication system depends on
the following four fundamental characteristics :
~ Delivery [ Destination reached should be correct ]
~ Accuracy [ The data should be 100 % same, as it was, when transmitted ]
~ Timeliness [ The delay should be insignificant ]
~ Jitter [ The speed should be uniform for all data packets ]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/unit0introduction-140901094117-phpapp02/85/Unit-0-introduction-5-320.jpg)
![b) Components of Data Communication System
The five important components of Data Communications are :
~ Message [ Message is the information to be communicated ]
~ Sender [ The sender is the device that sends the message ]
~ Receiver [ The receiver is the device that receives the message ]
~ Transmission Medium [ It is the physical path through which a message travels from sender to receiver ]
~ Protocol [ It is a set of rules that govern data communications ]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/unit0introduction-140901094117-phpapp02/85/Unit-0-introduction-6-320.jpg)
![c) Data Representation
The data can come in different forms such as :
~ Text [ e.g. a, b, c, X, Y , Z . ]
~ Numbers [ e.g. 0,1,2 , . . . . . . . 9 ]
~ Images [ e.g. *.jpeg , *.png files ]
~ Audio [ e.g. *.mp3 files ]
~ Video [ e.g. *.mp4 , *.avi files etc.]
Text
Data
Form
Numbers
Audio Images
Video](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/unit0introduction-140901094117-phpapp02/85/Unit-0-introduction-7-320.jpg)

![b) Network Criteria
~ Performance [ maximum throughput and minimum delay ]
~ Reliability [ the work should continue in spite of any catastrophe ]
~ Security [ Protecting data from manipulation or damage ]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/unit0introduction-140901094117-phpapp02/85/Unit-0-introduction-11-320.jpg)
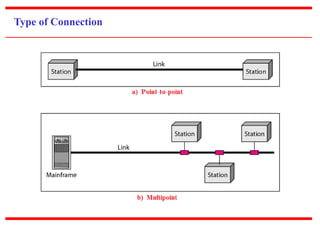
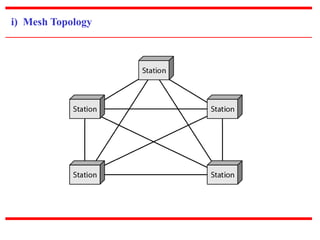
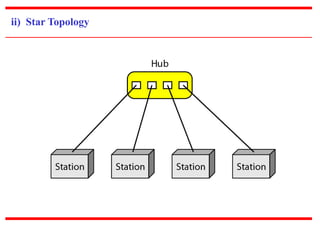
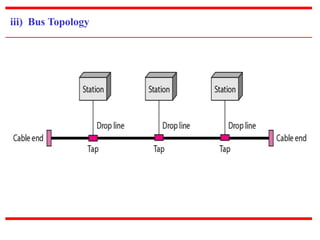
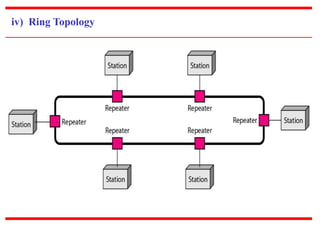
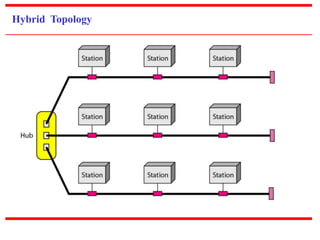
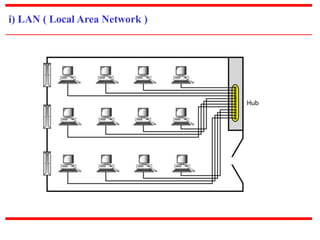
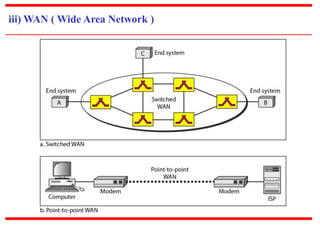
![c) Physical Structures
~ Type of Connection
[based on type of link]
~ Physical Topology
[based on network’s physical layout ]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/unit0introduction-140901094117-phpapp02/85/Unit-0-introduction-12-320.jpg)


![ii) MAN ( Metropolitan Area Network )
Typical Cable TV Network
[ An example of MAN ]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/unit0introduction-140901094117-phpapp02/85/Unit-0-introduction-23-320.jpg)
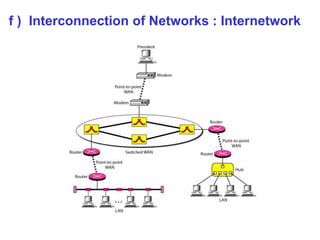

![ Brief History of Internet
~ In mid-1960s’, mainframe computers in research organization were stand-alone devices.
~ In 1967, ARPA ( Advanced Research Projects Agency ) presented the idea for ARPANET.
~ By 1969, ARPANET was a reality. [ Four Universities in USA were interconnected ]
~ In 1973, Vint Cerf and Bob Kahn present the landmark paper outlining the foundations
for TCP/IP.
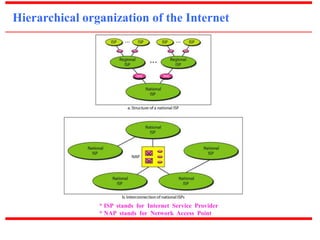
Internet Today
~ The Internet has come a long way since the 1960s’. It complexity has grown enormously.
~ It is difficult to give an accurate representation of the Internet because it is continually
changing.
~ Hierarchy in Internet Usage : IISPs’ ⇋ NISPs’ ⇋ RISPs’ ⇋ LISPs’ ⇋ Users’.
Note : ISP stands for Internet Service Provider](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/unit0introduction-140901094117-phpapp02/85/Unit-0-introduction-27-320.jpg)