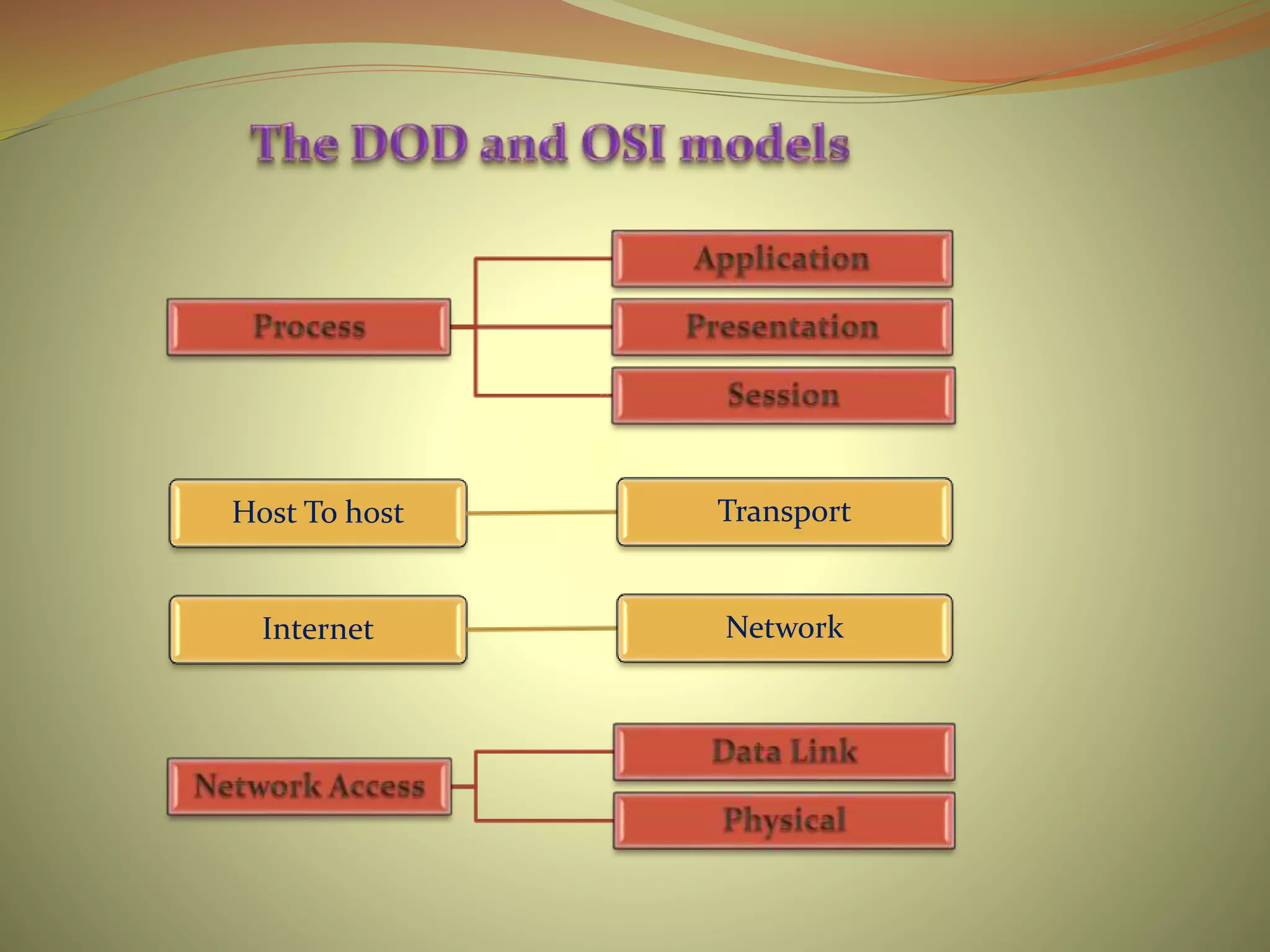
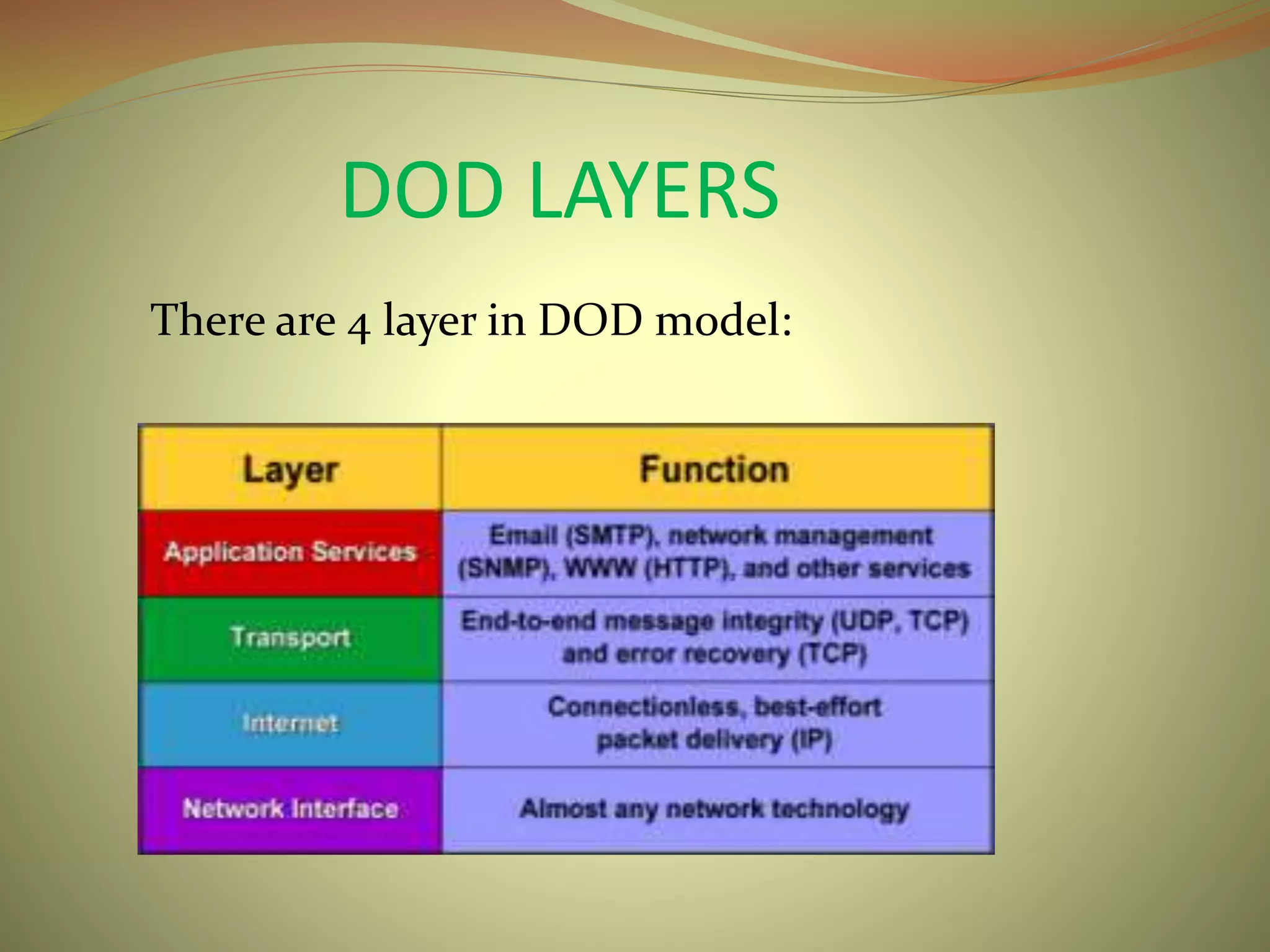
The document compares and contrasts the OSI and DOD network models. The OSI model has 7 layers and defines the process of network communication by dividing it into distinct groups of related functions. It includes the application, presentation, session, transport, network, data link, and physical layers. The DOD model is a condensed version with only 4 layers - process, host-to-host, internet, and network access layers. Both models provide conceptual frameworks for understanding how applications can communicate over a network.