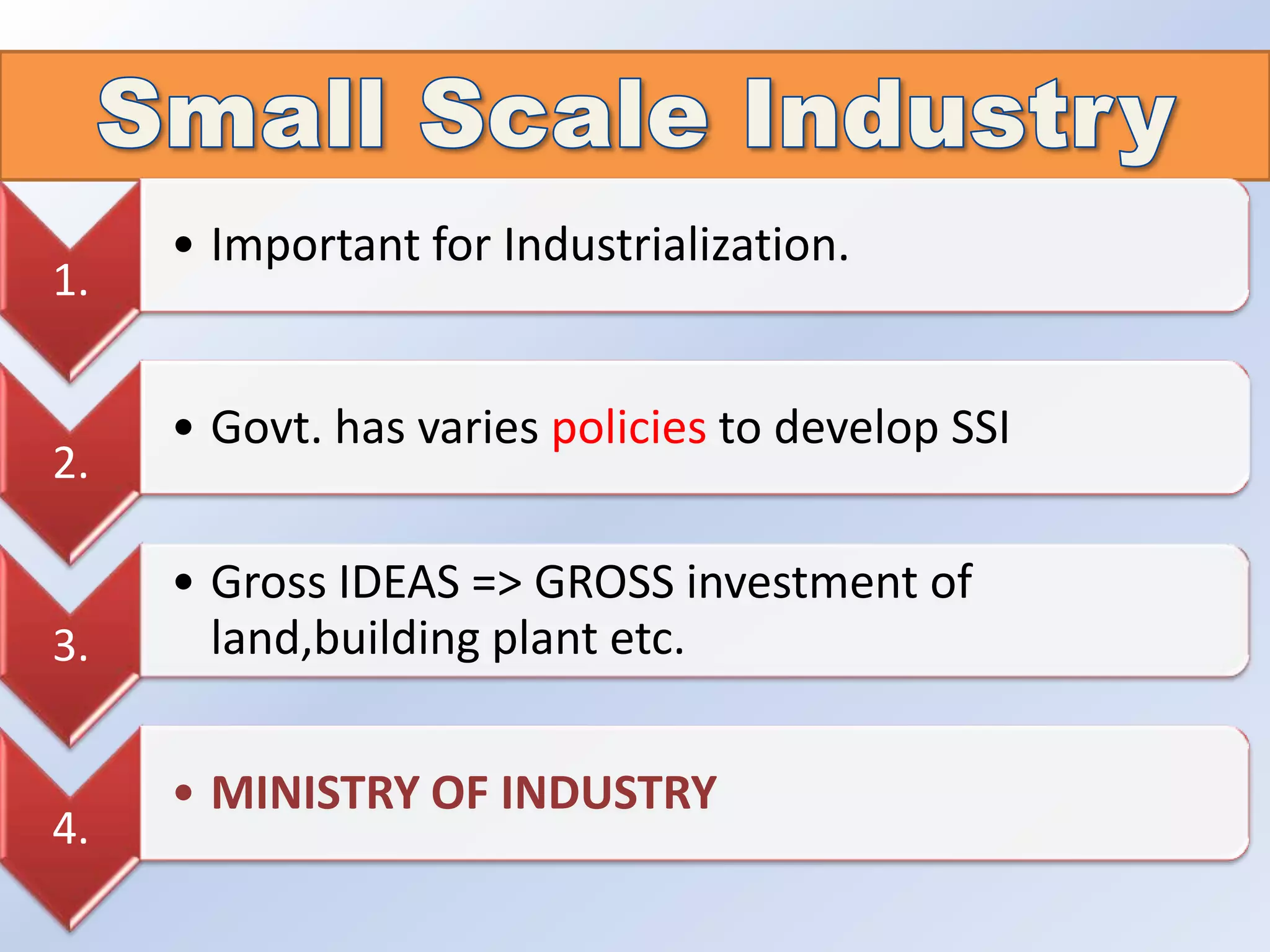
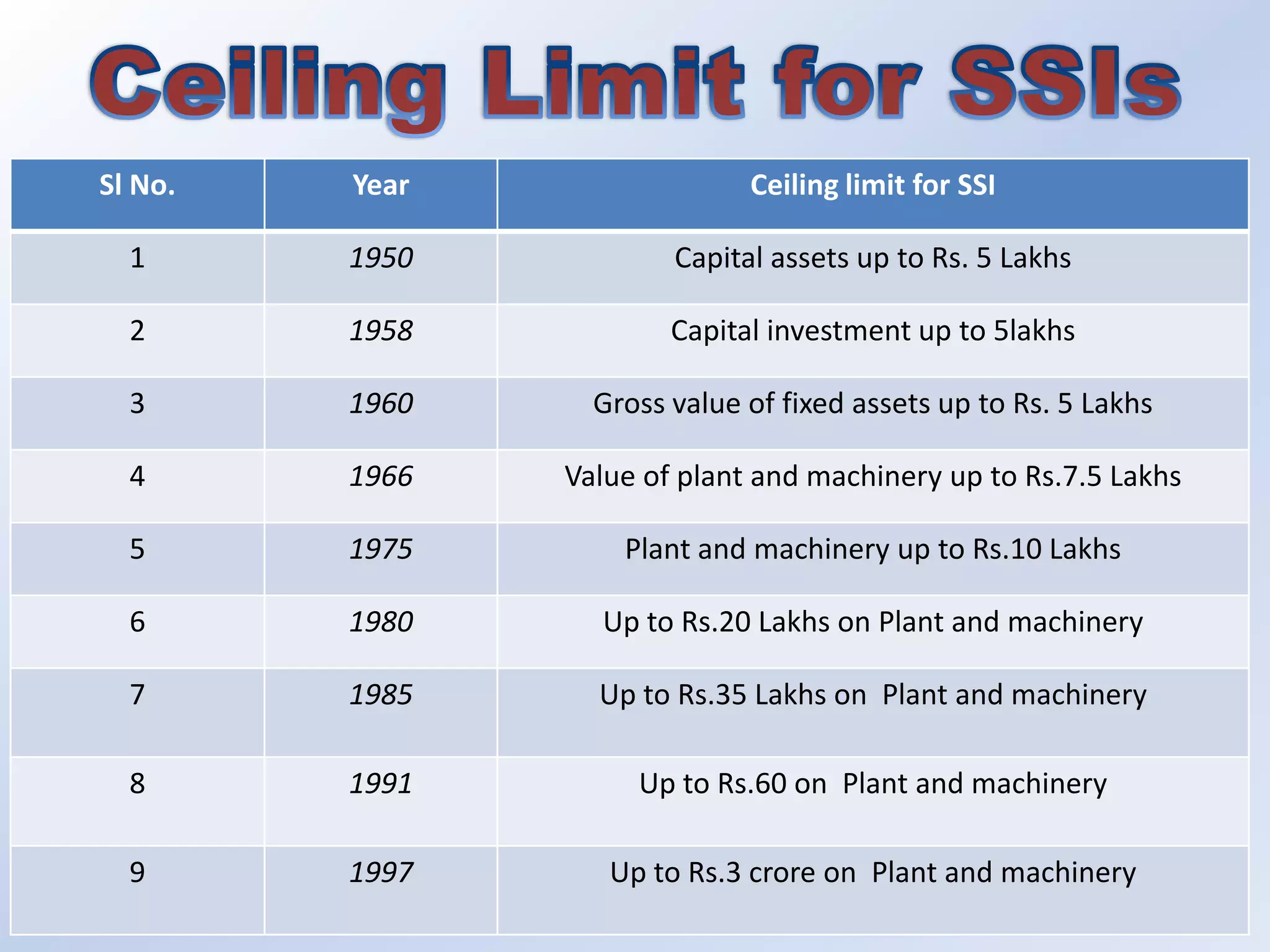
This document discusses small-scale industries (SSI) in India. It outlines how the ceiling limit for what constitutes an SSI has increased over time. SSIs are important for industrialization and the government has various policies to support their development. Key benefits of SSIs include utilizing available labor and requiring relatively low capital investment. While some SSIs may grow larger, others are at risk of becoming obsolete. The document also outlines the scope and common areas that SSIs cover in India, as well as their growth and impact on employment and exports. Steps for starting an SSI are provided.