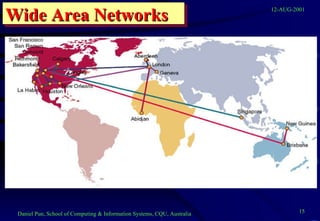
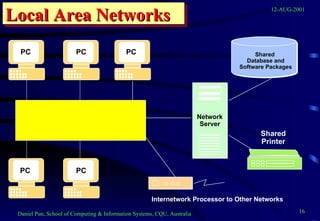
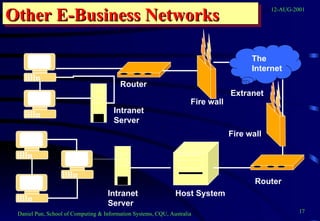
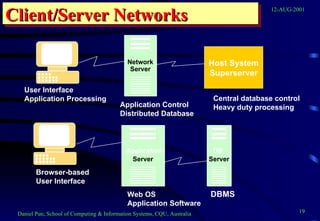
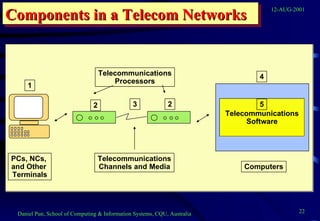
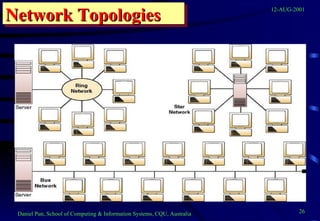
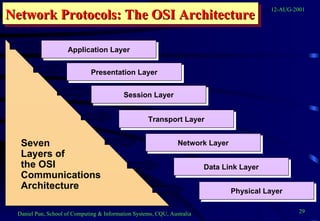
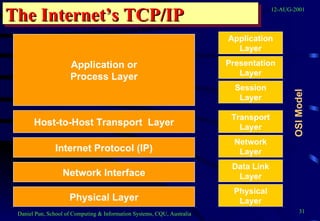
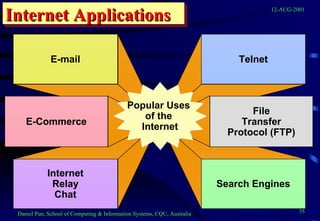
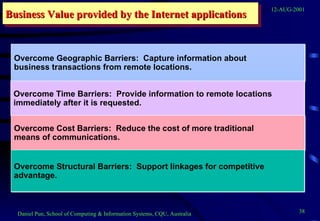
This document provides an overview of networks and telecommunications for an information systems course. It discusses the key components of telecommunications networks, including terminals, processors, channels, computers and software. It describes different network topologies like star, ring and bus configurations. The document also covers telecommunications protocols like OSI and TCP/IP, trends in telecommunications, and popular business uses of the internet like email, e-commerce and overcoming barriers.