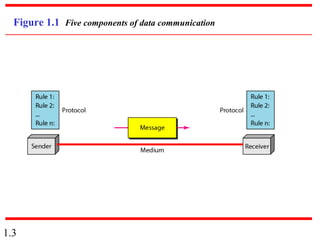
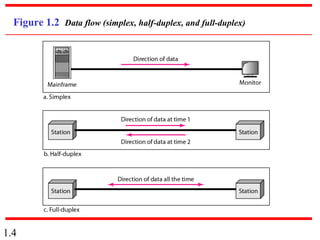
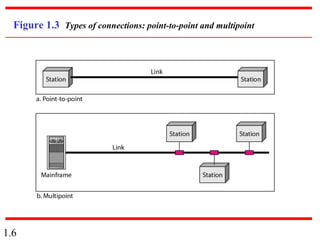
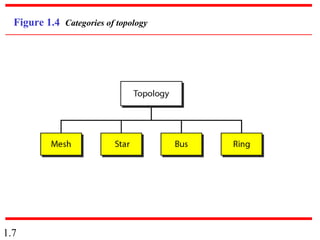
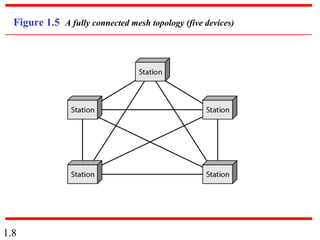
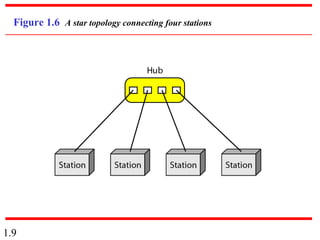
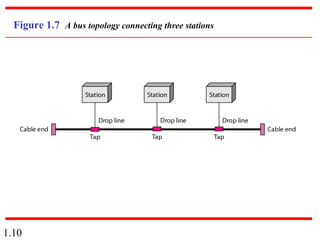
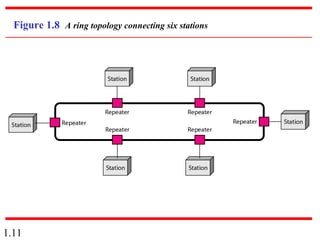
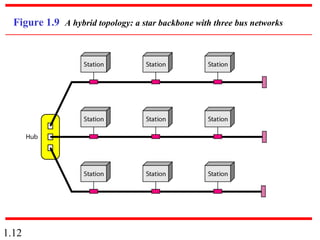
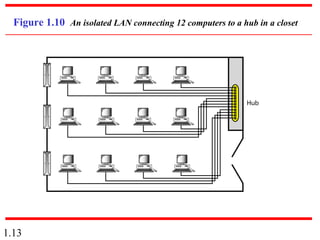
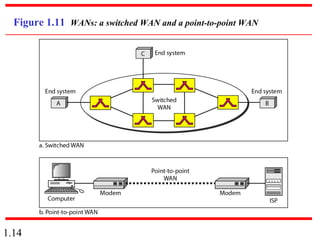
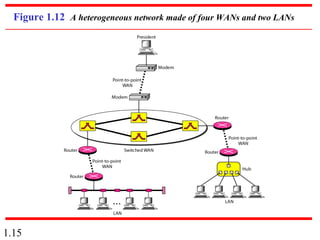
This document provides an introduction to data communications and computer networks. It discusses key topics such as data communication components like data representation and data flow. It also defines networks and describes different network topologies including point-to-point, star, bus, ring and hybrid configurations. The document then provides an overview of the Internet, including its history and role of Internet Service Providers. It concludes with definitions of protocols and standards, which are sets of agreed upon rules, and discusses standards organizations and their role in establishing Internet standards.