Embed presentation


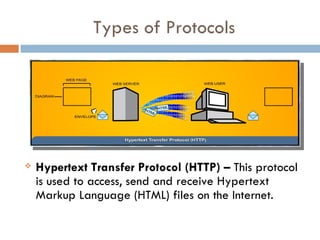




A protocol is a set of rules for exchanging data between devices and defines how messages should be formatted, transmitted and acknowledged. Some common protocols include HTTP for accessing web pages, SMTP for sending email, FTP for file transfers, TCP for reliable packet delivery across networks, and IP for logical addressing to route information between networks.






