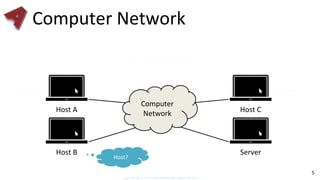
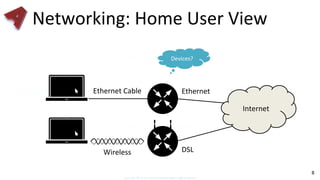
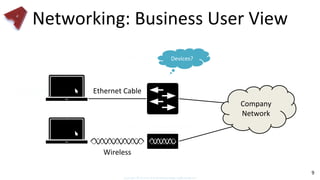
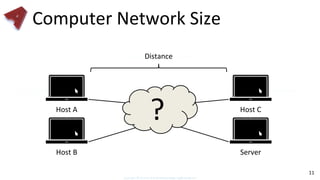
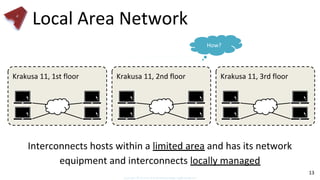
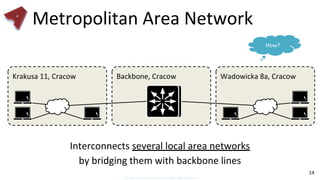
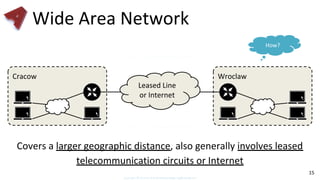
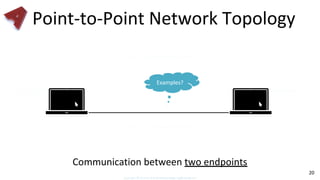
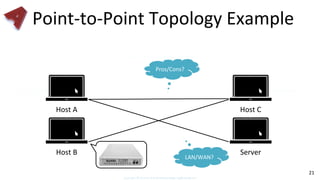
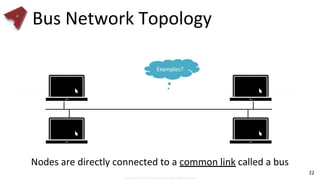
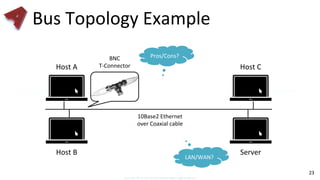
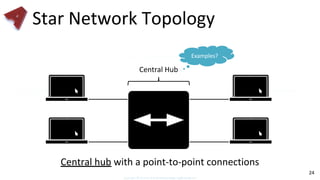
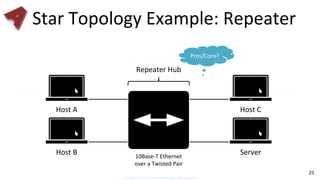
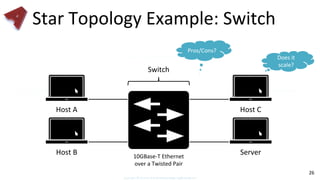
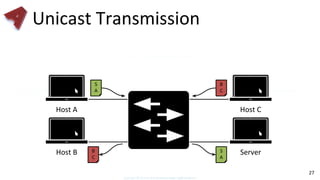
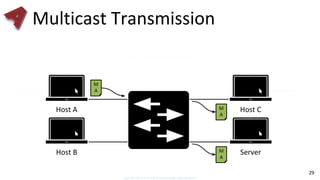
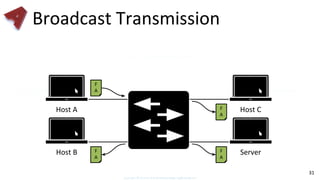
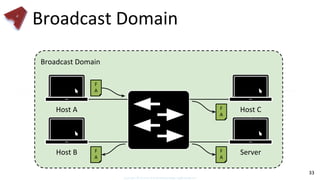
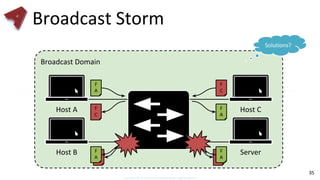
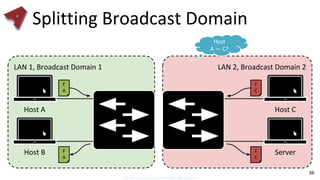
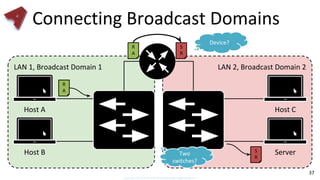
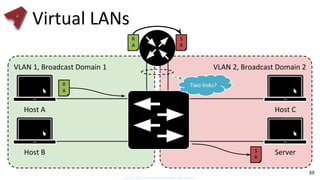
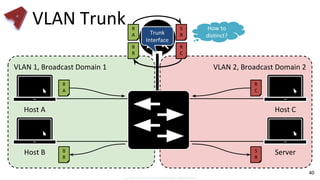
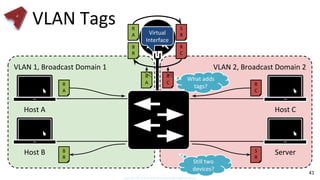
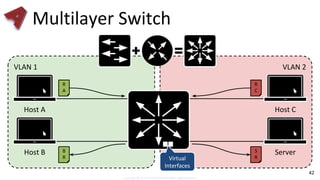
This document provides an overview of networking fundamentals including computer networks, networking models, local and wide area networks, internet protocols, routing, transport protocols, network topologies, transmission methods, broadcast domains, VLANs, switches, routers and other key networking concepts and technologies. It defines common networking terms and provides examples to illustrate networking concepts and designs at both the home/business user and infrastructure levels.