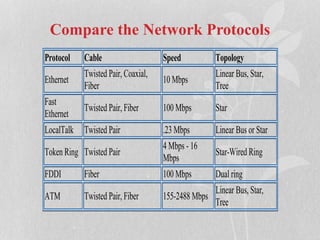
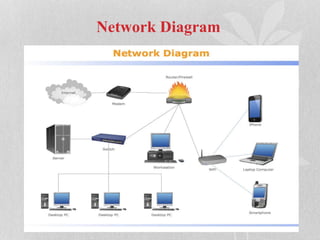
This document discusses network protocols. It defines a network as a group of connected devices that can exchange data, with each device having a unique address. Network protocols establish rules for network access methods, topologies, cabling, and data transfer speeds. The most common protocols described are Ethernet, LocalTalk, Token Ring, FDDI, and ATM, which use different access methods, cable types, speeds, and topologies to transmit data. Ethernet is the most widely used using CSMA/CD to transmit data at speeds up to 1000 Mbps over various cable types.