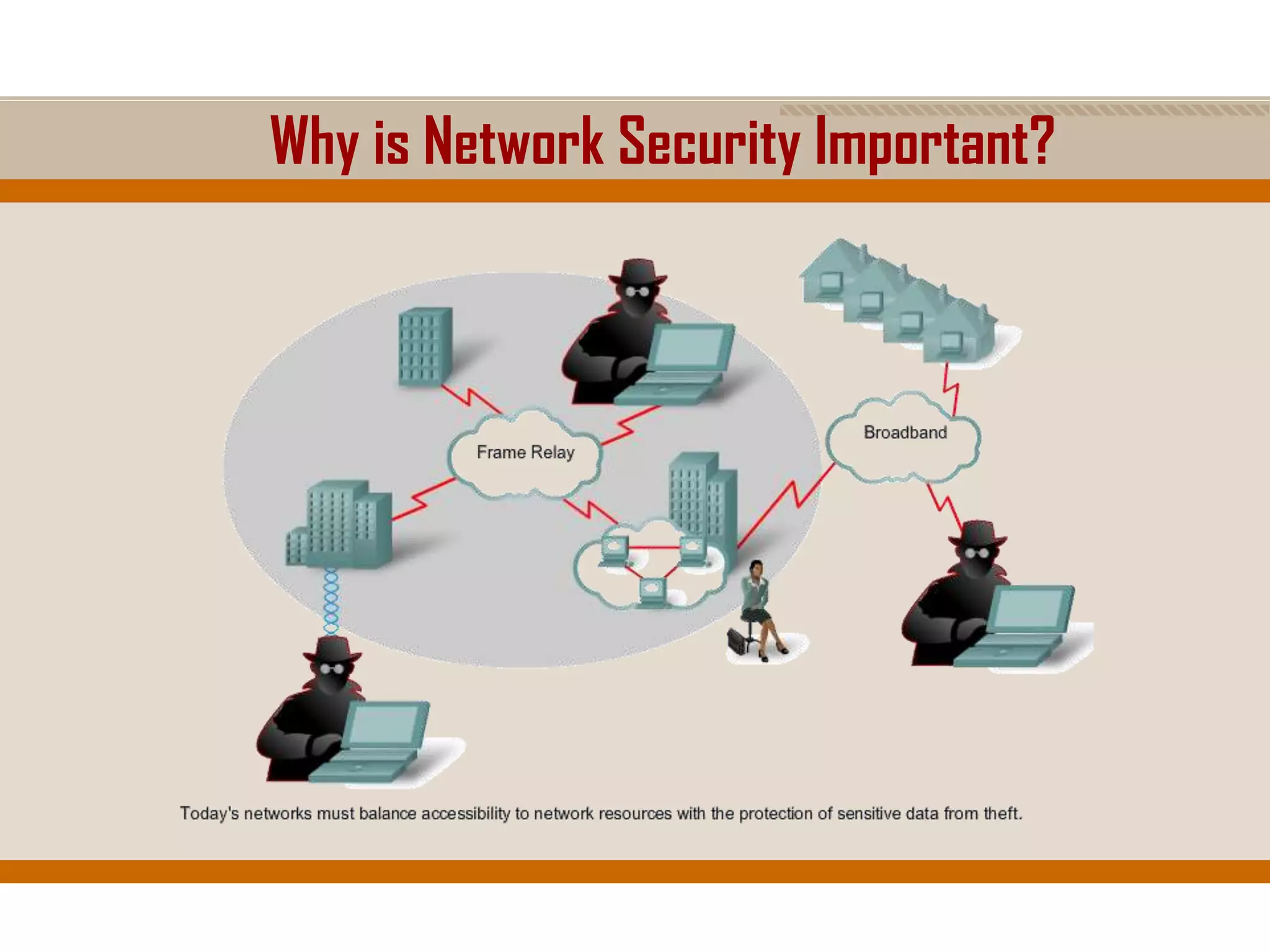
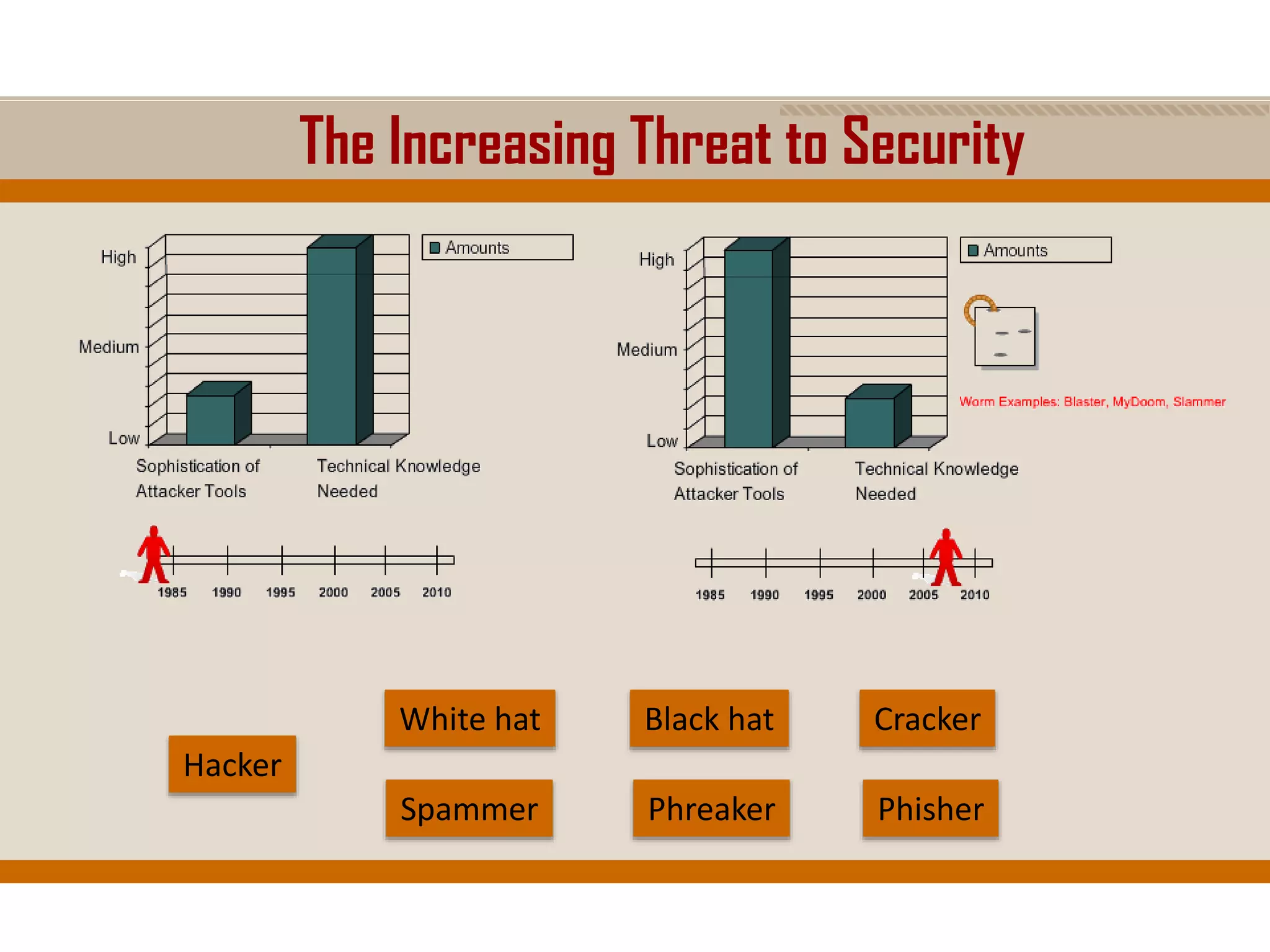
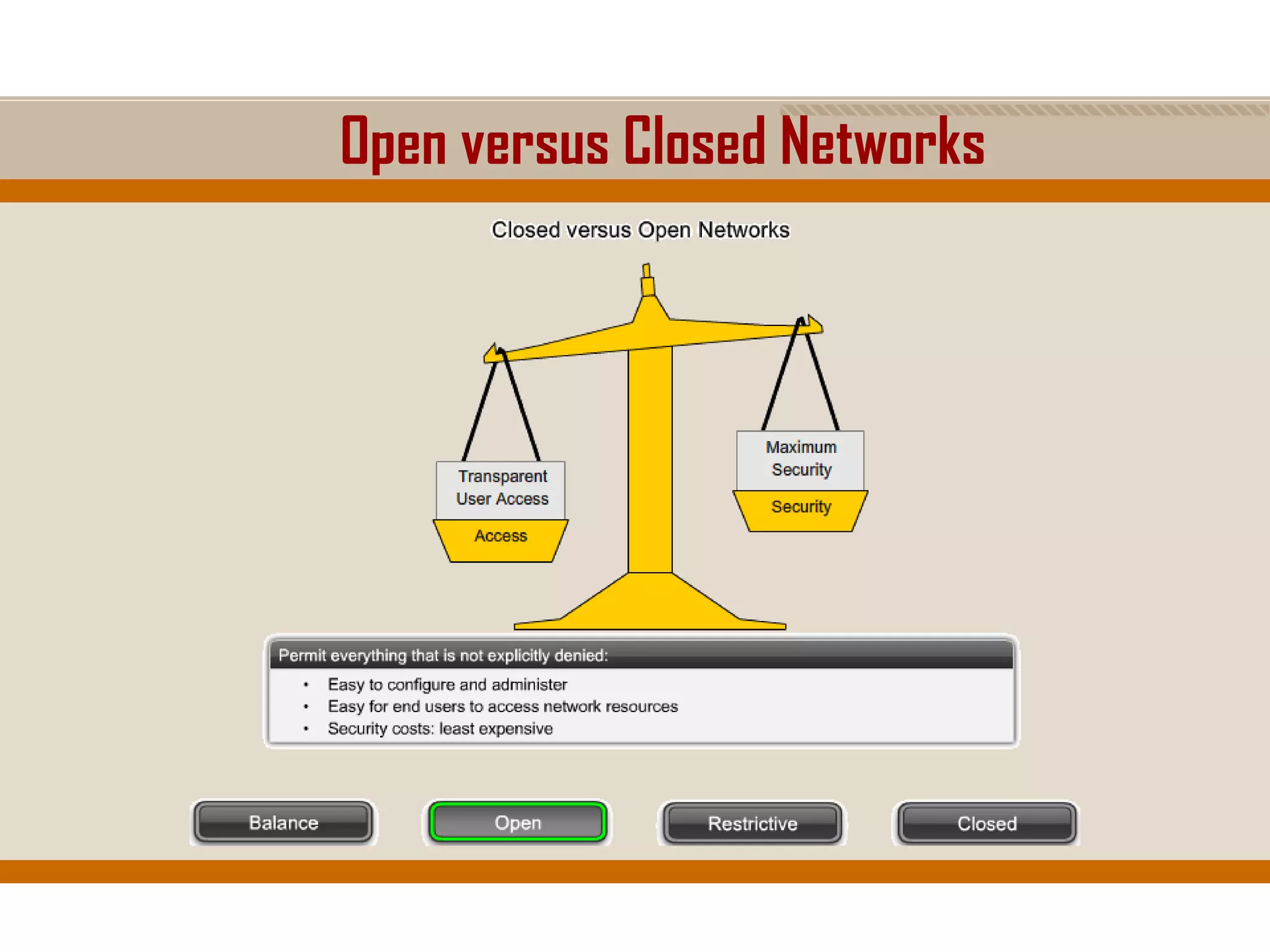
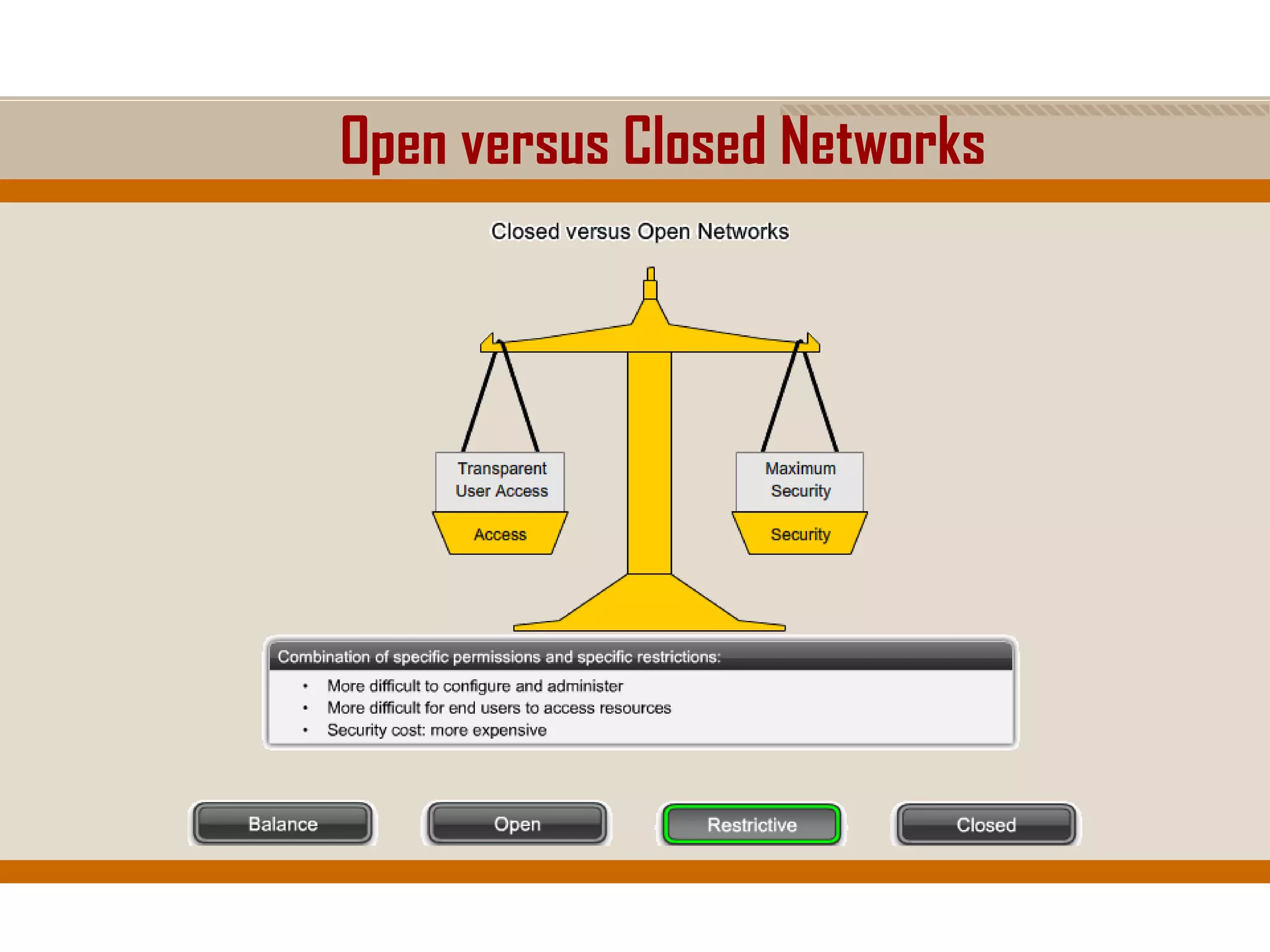
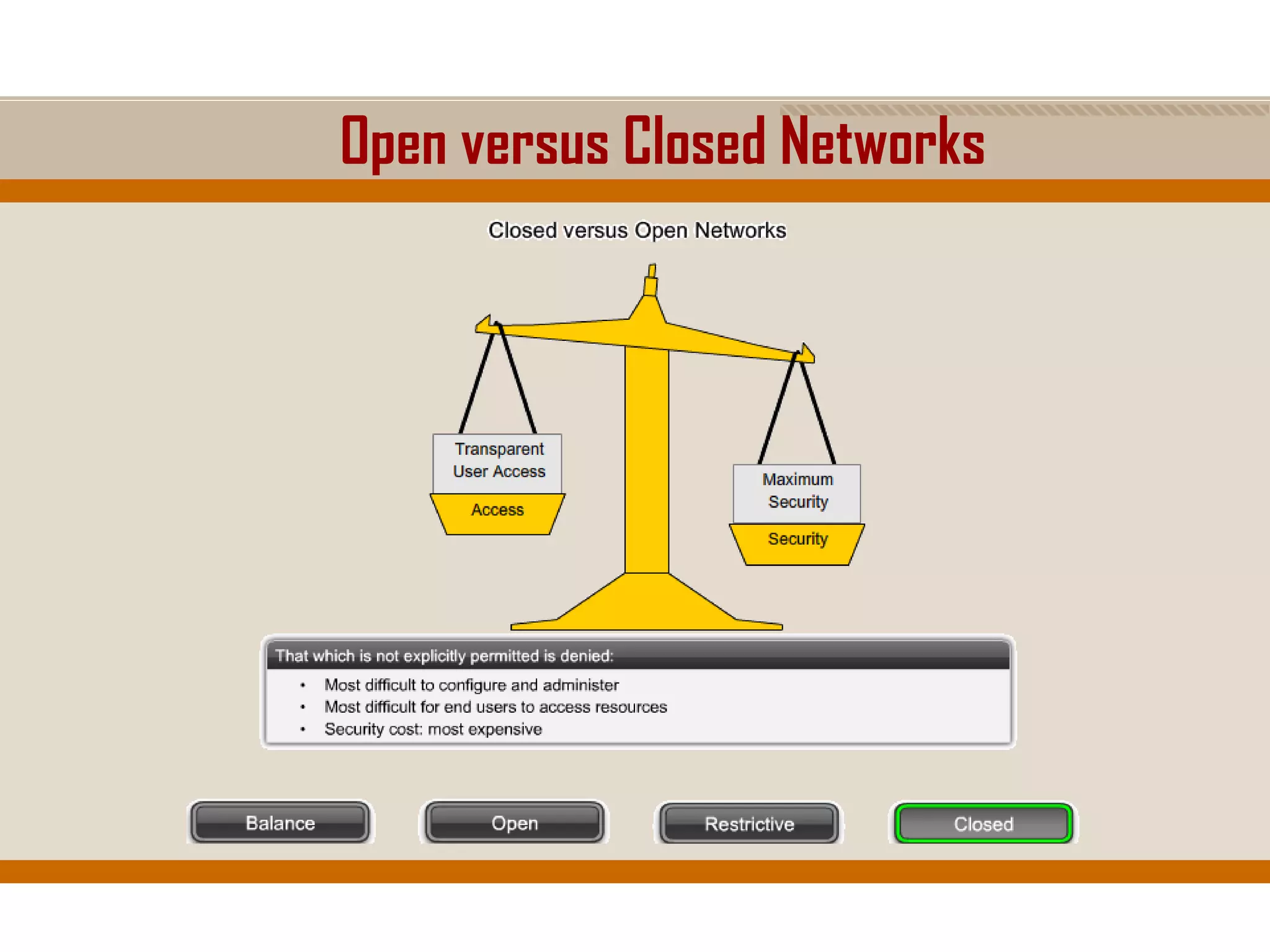
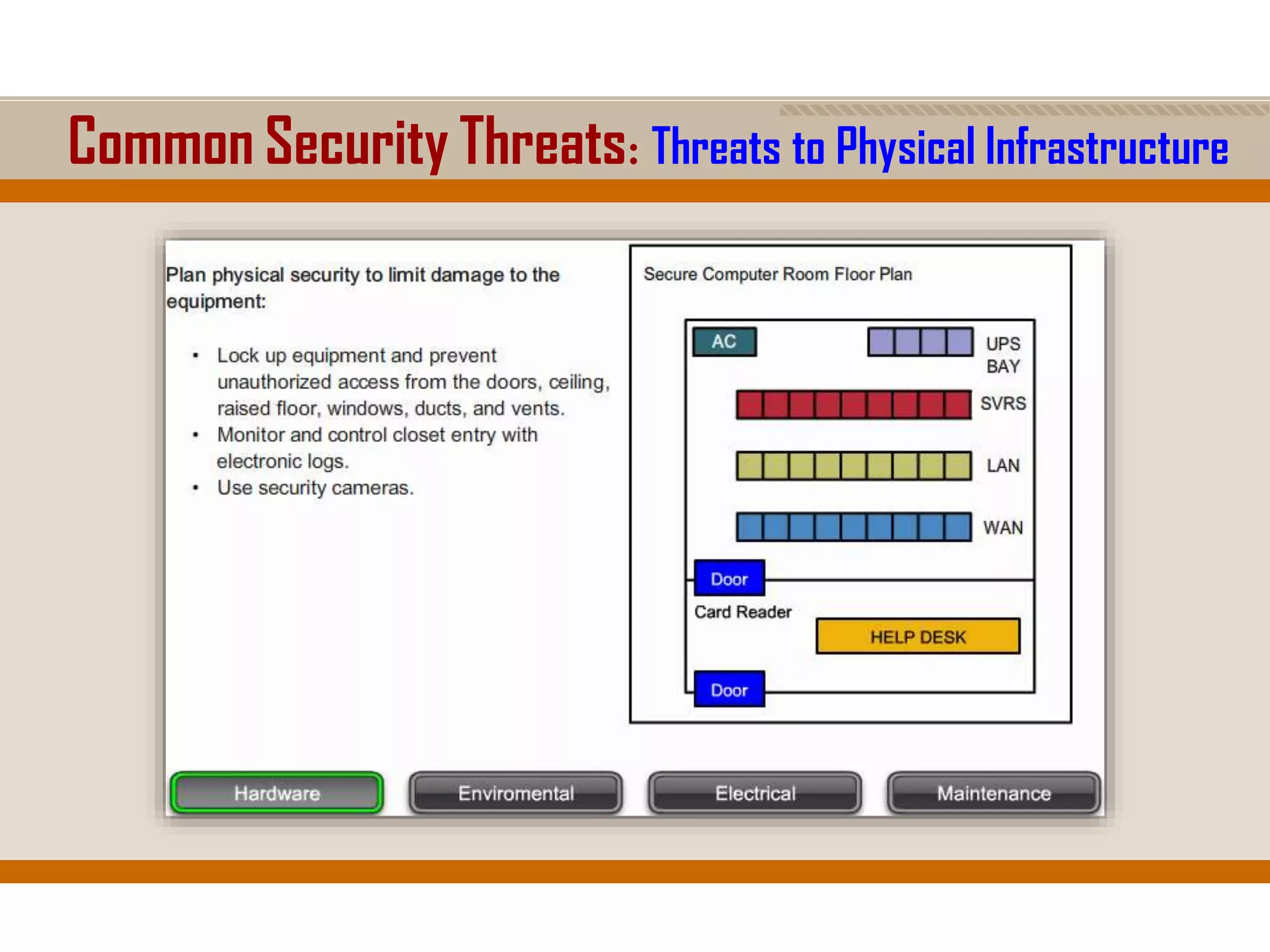
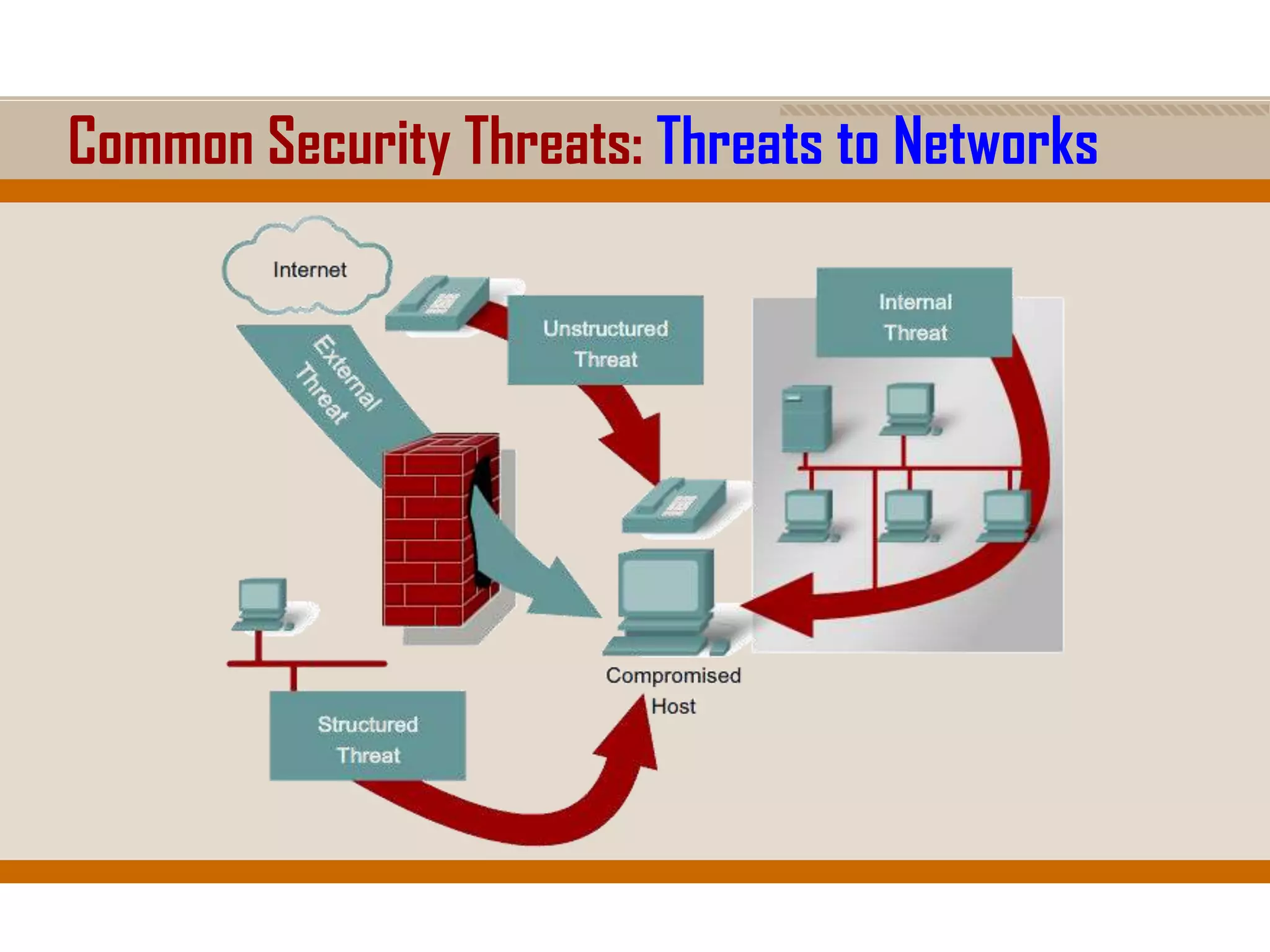
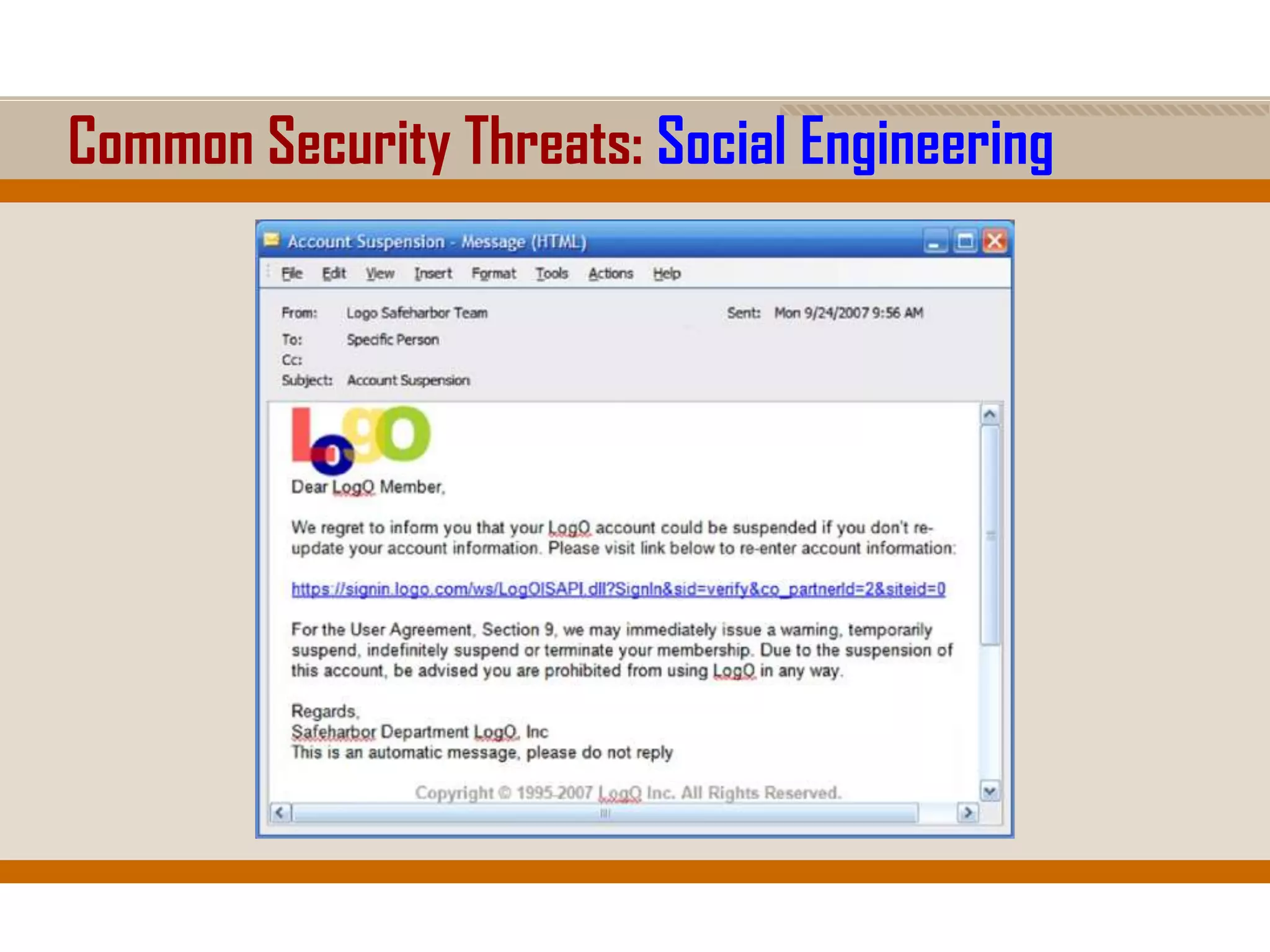
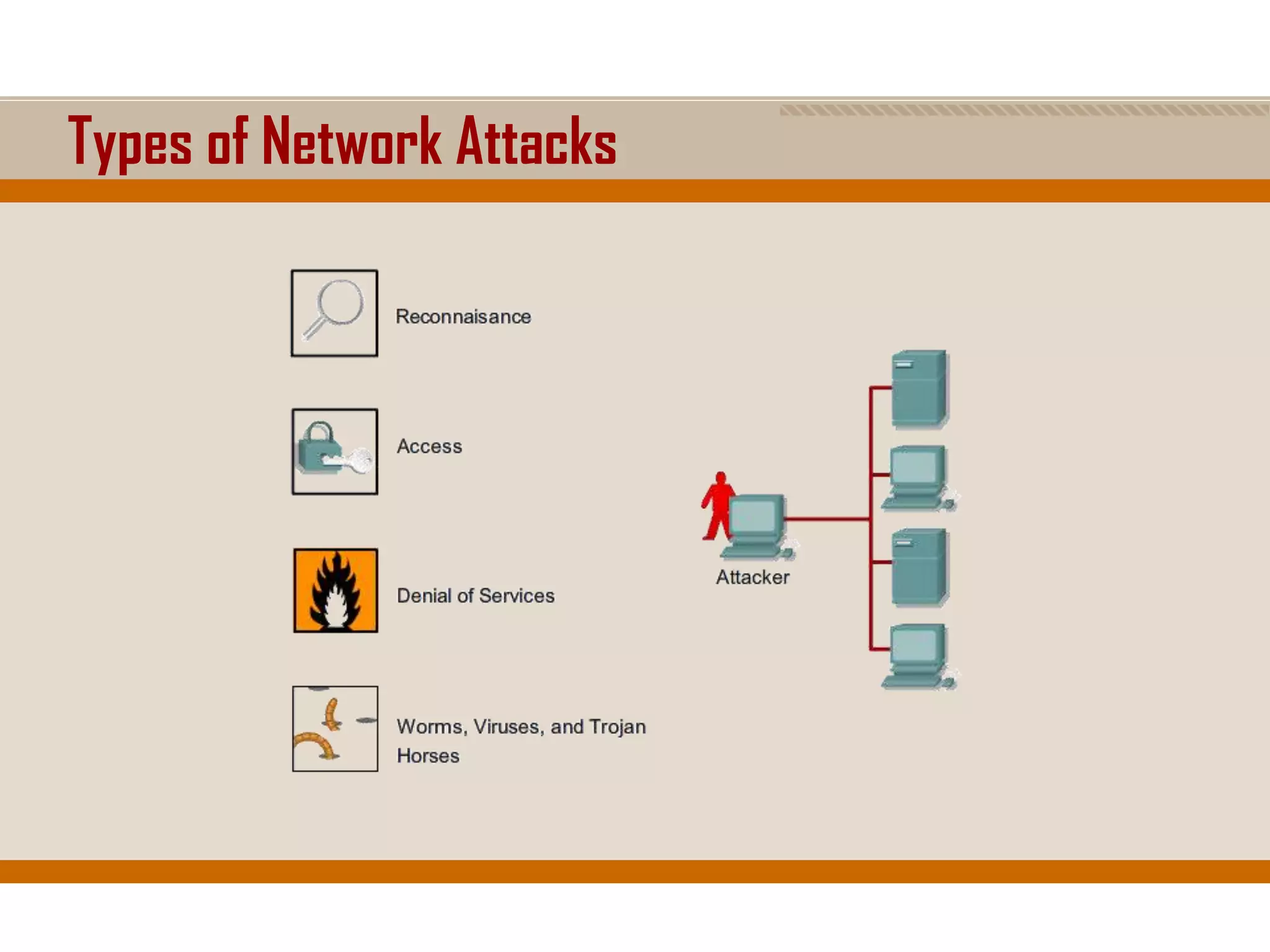
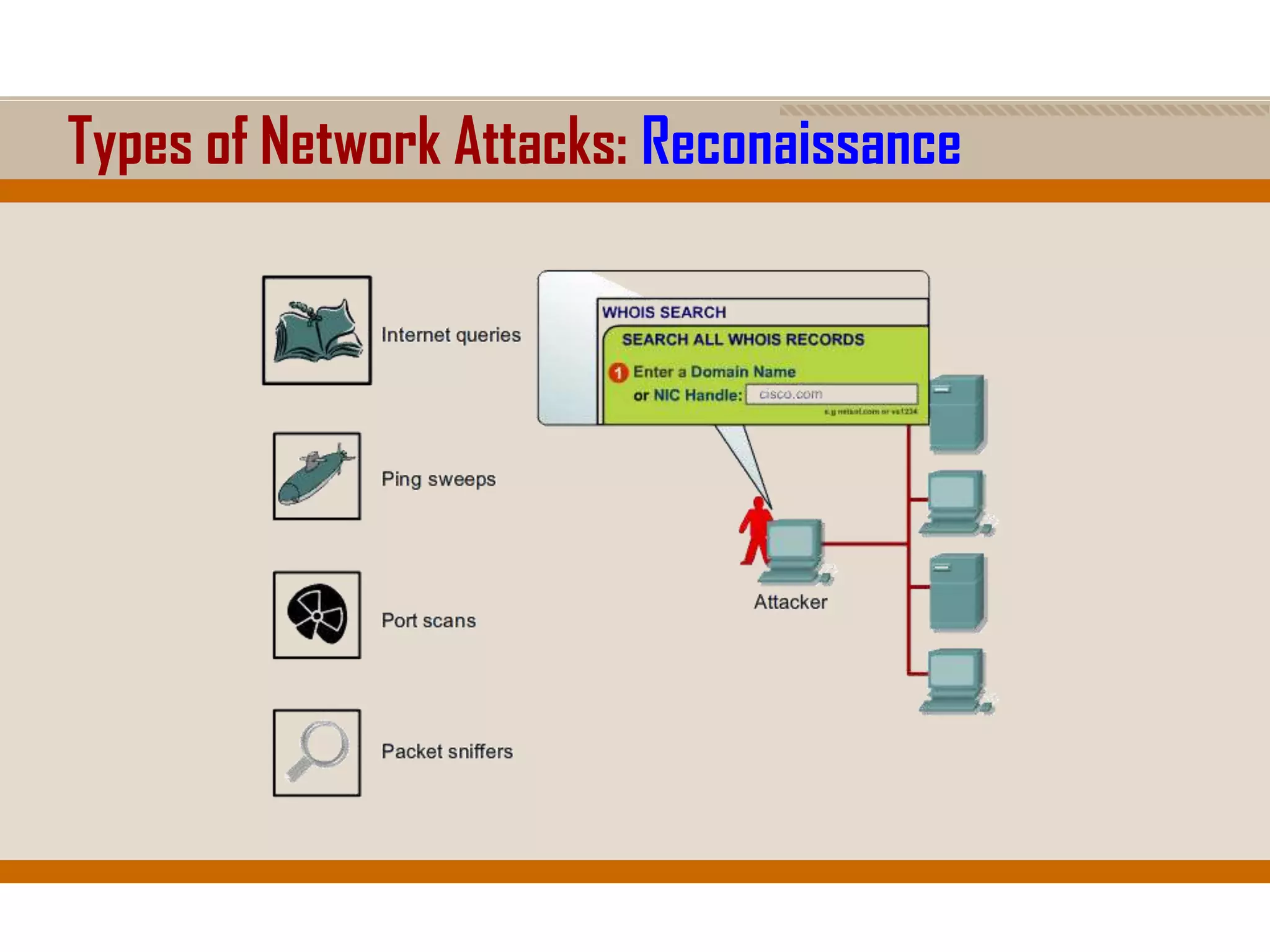
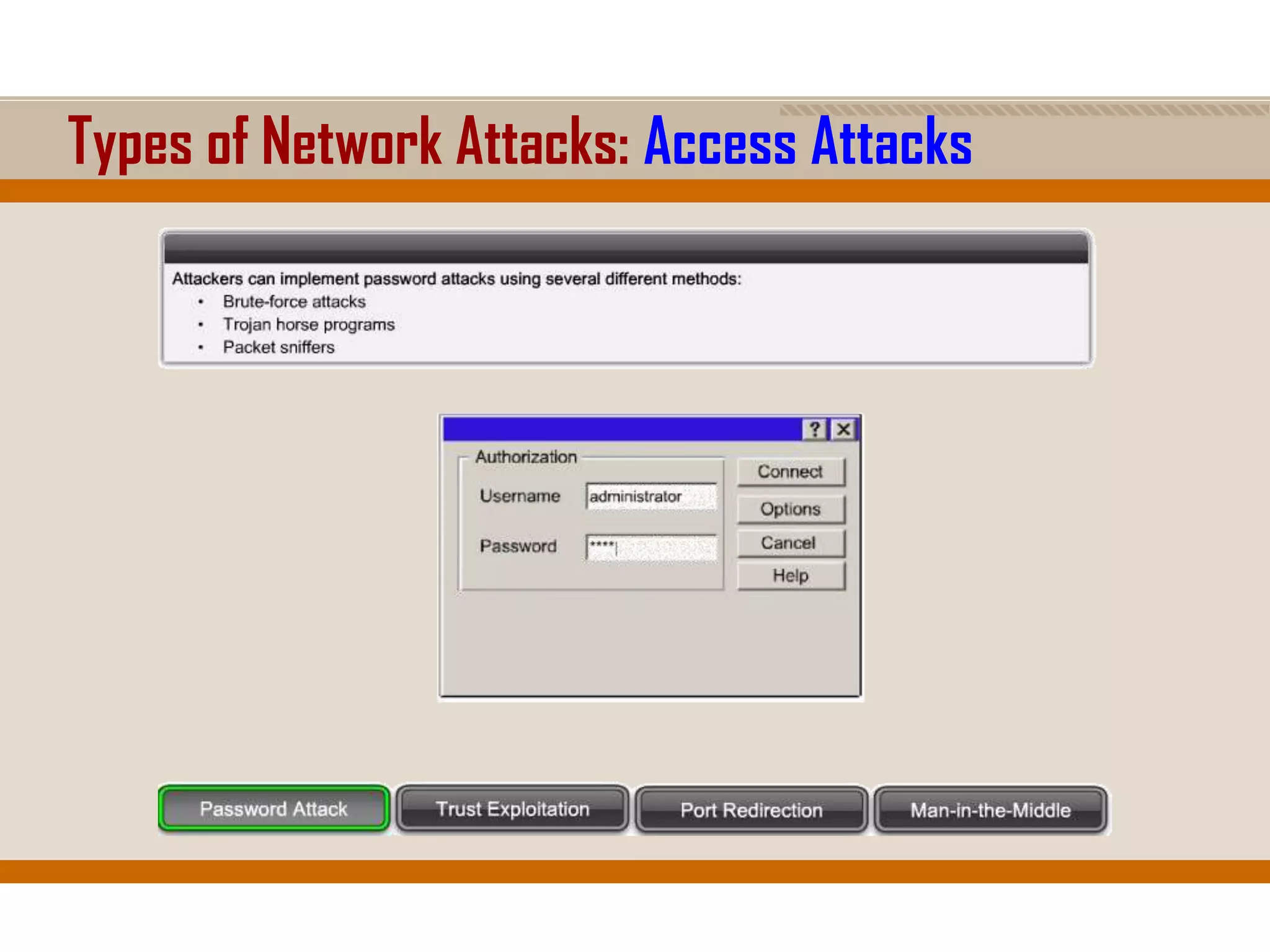
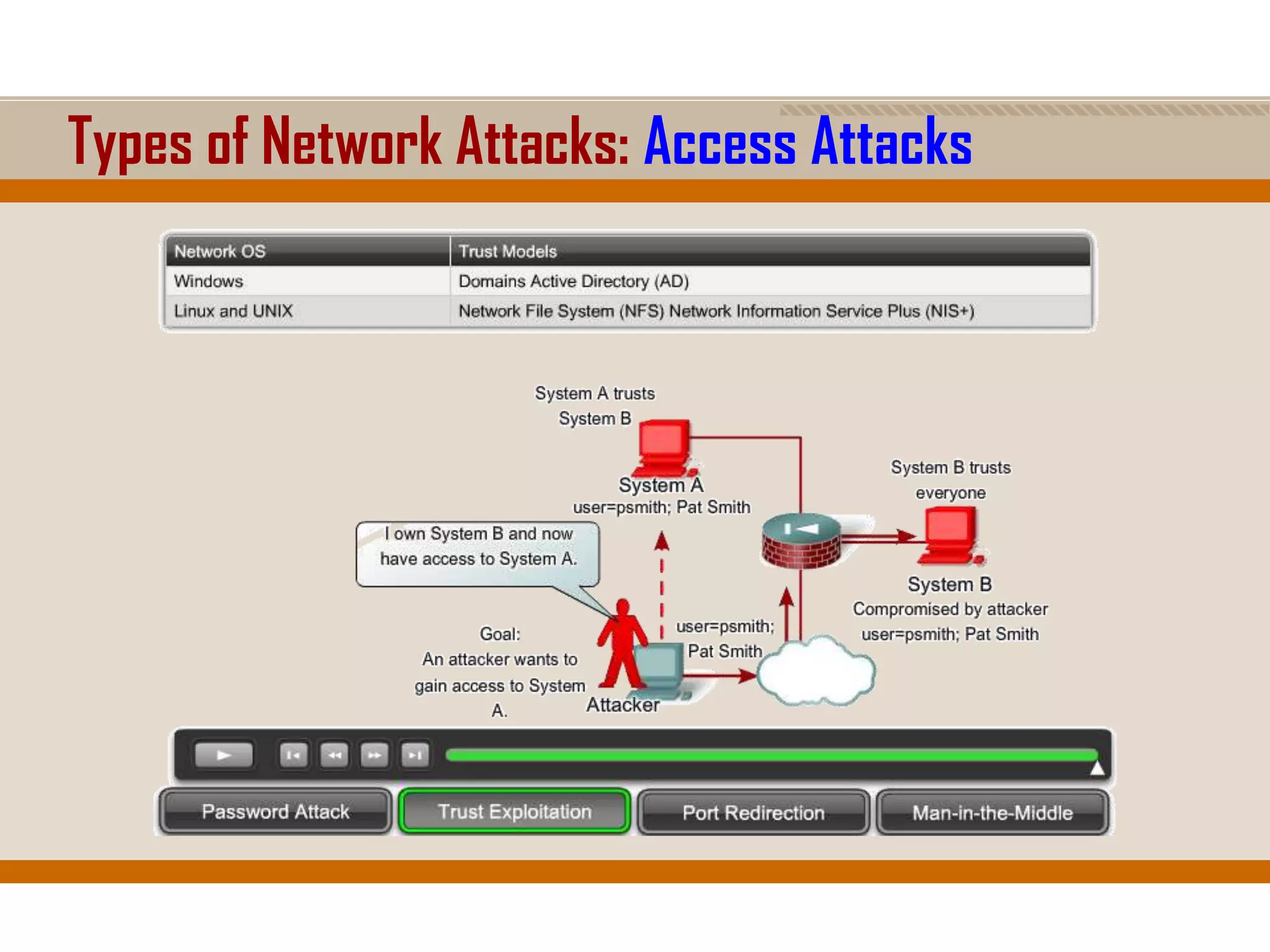
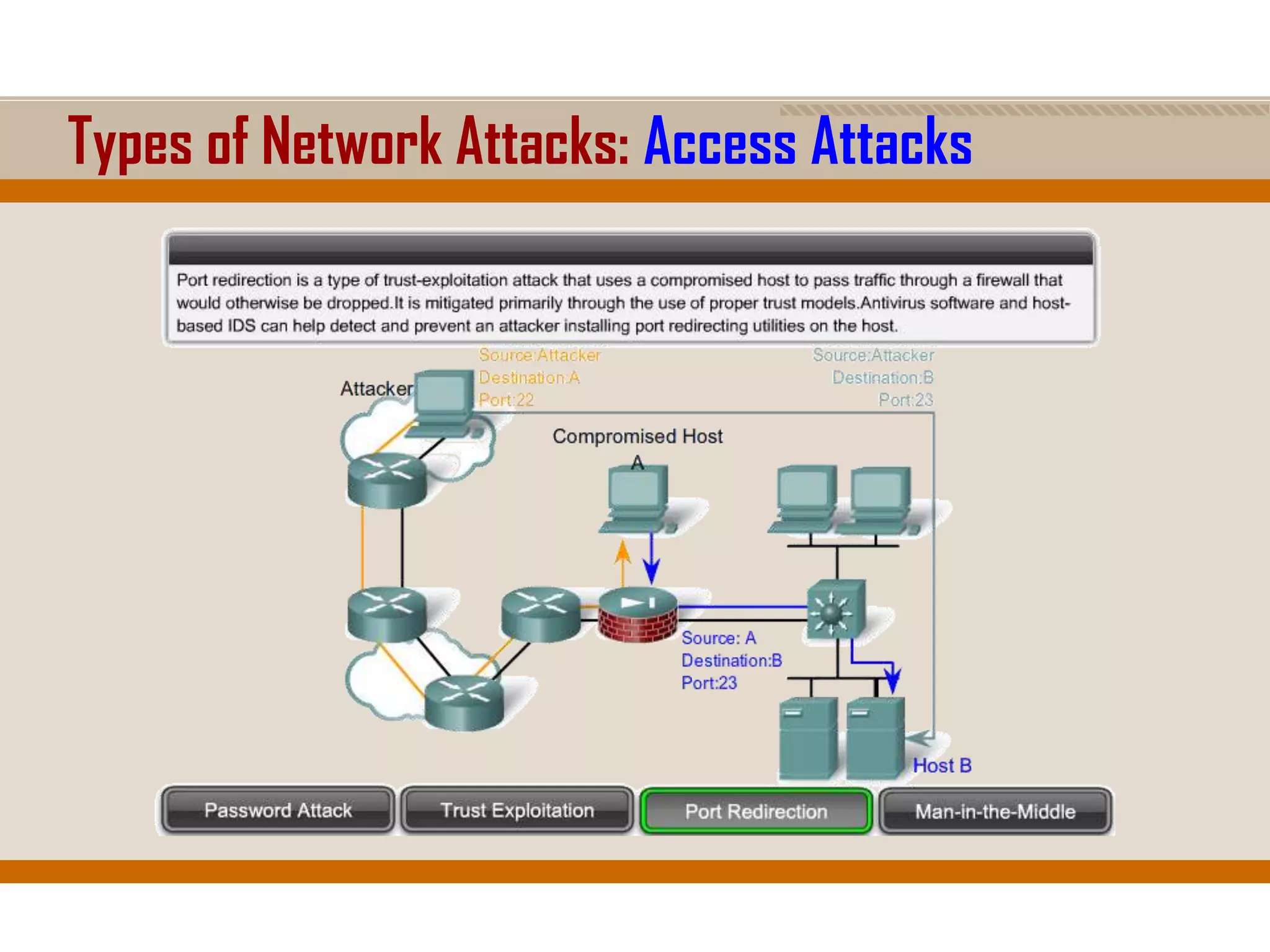
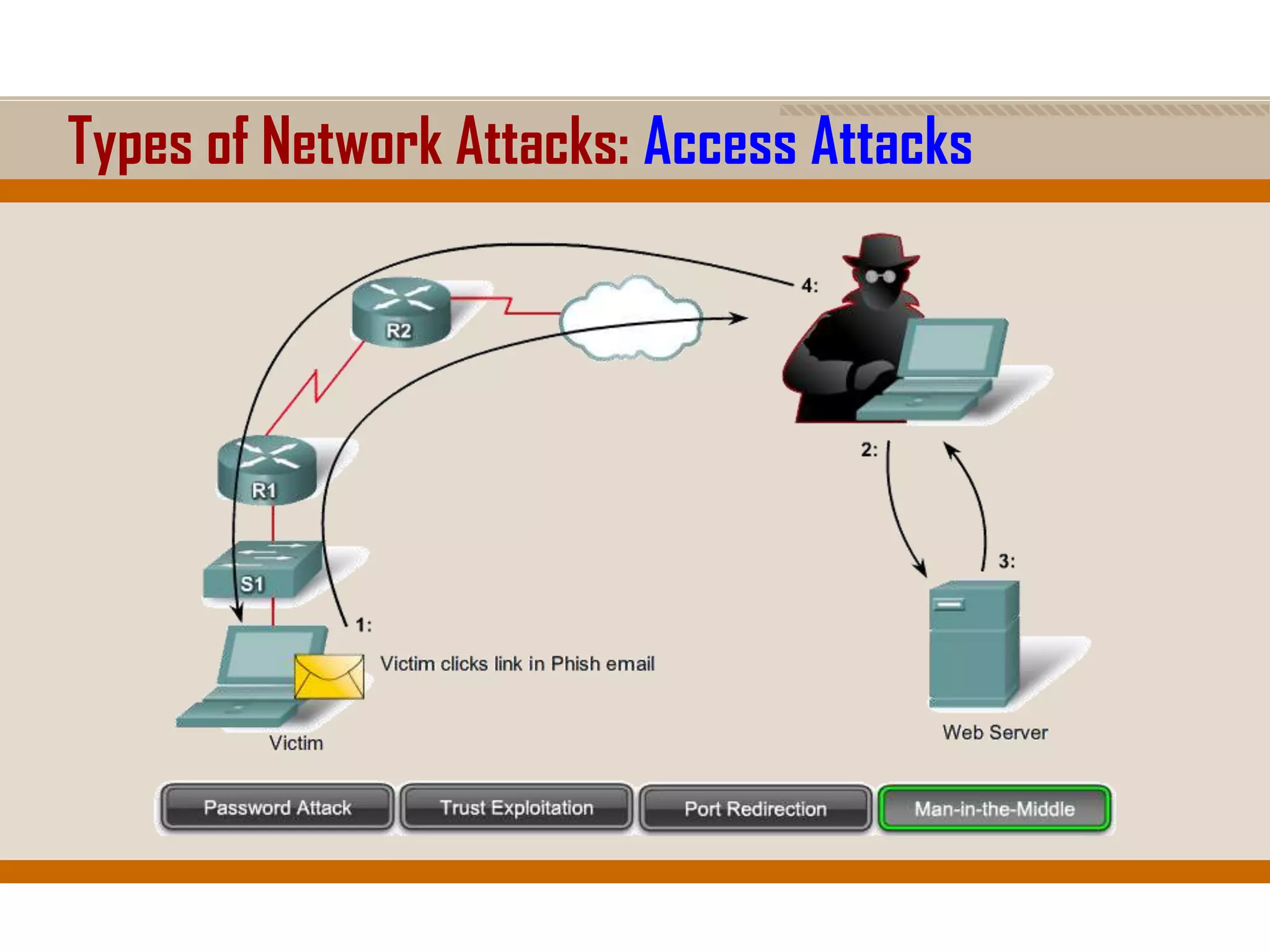
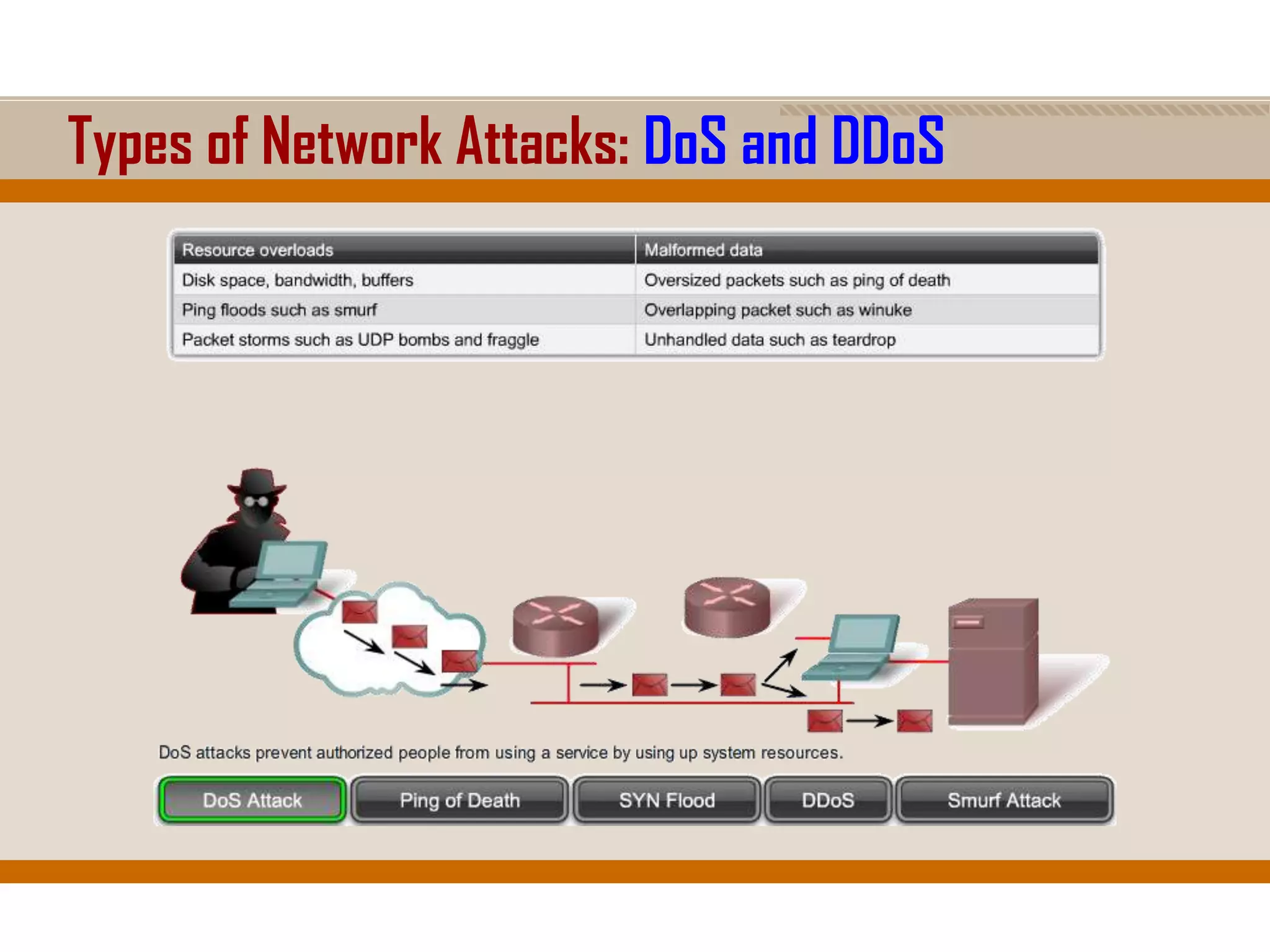
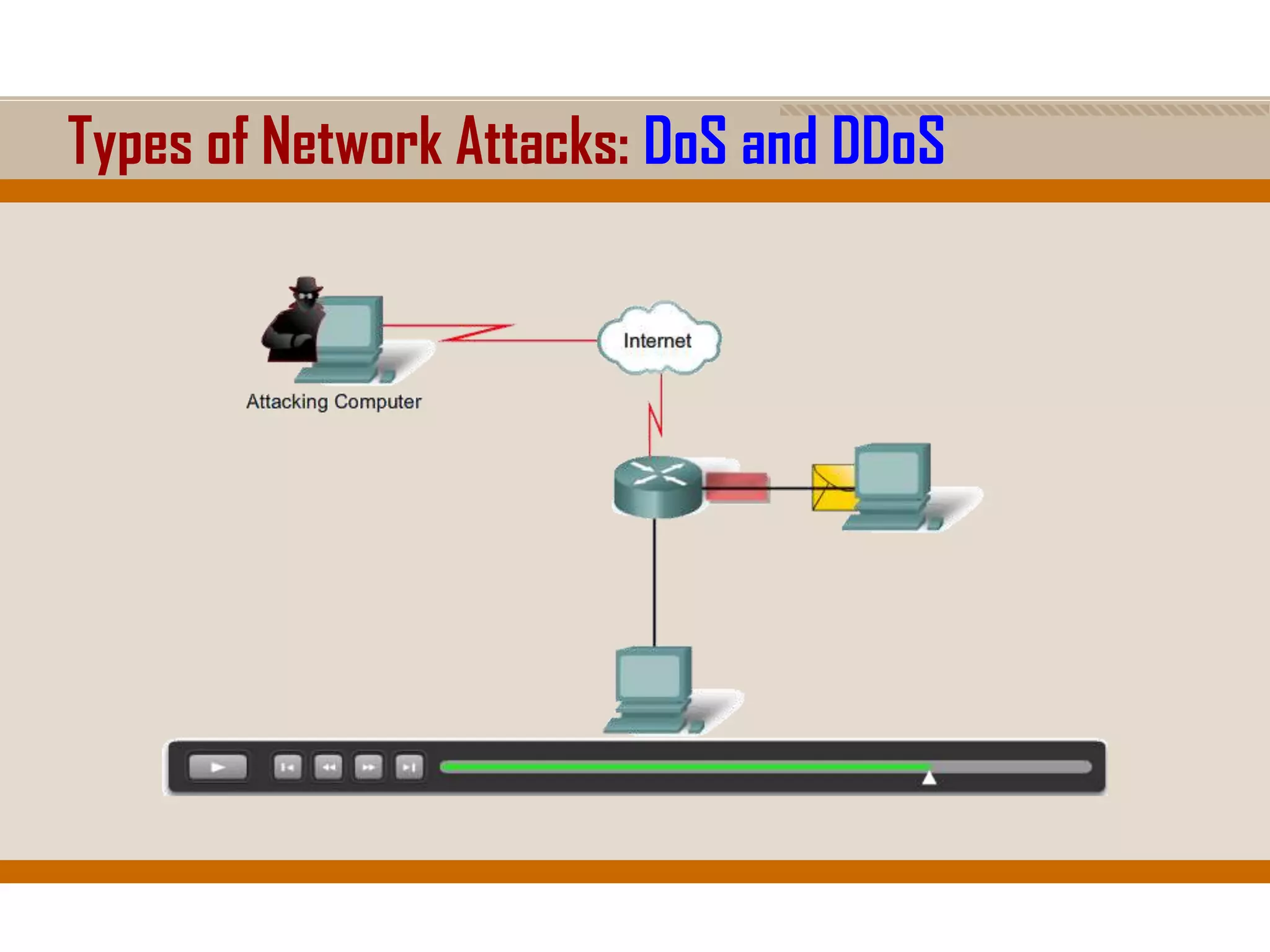
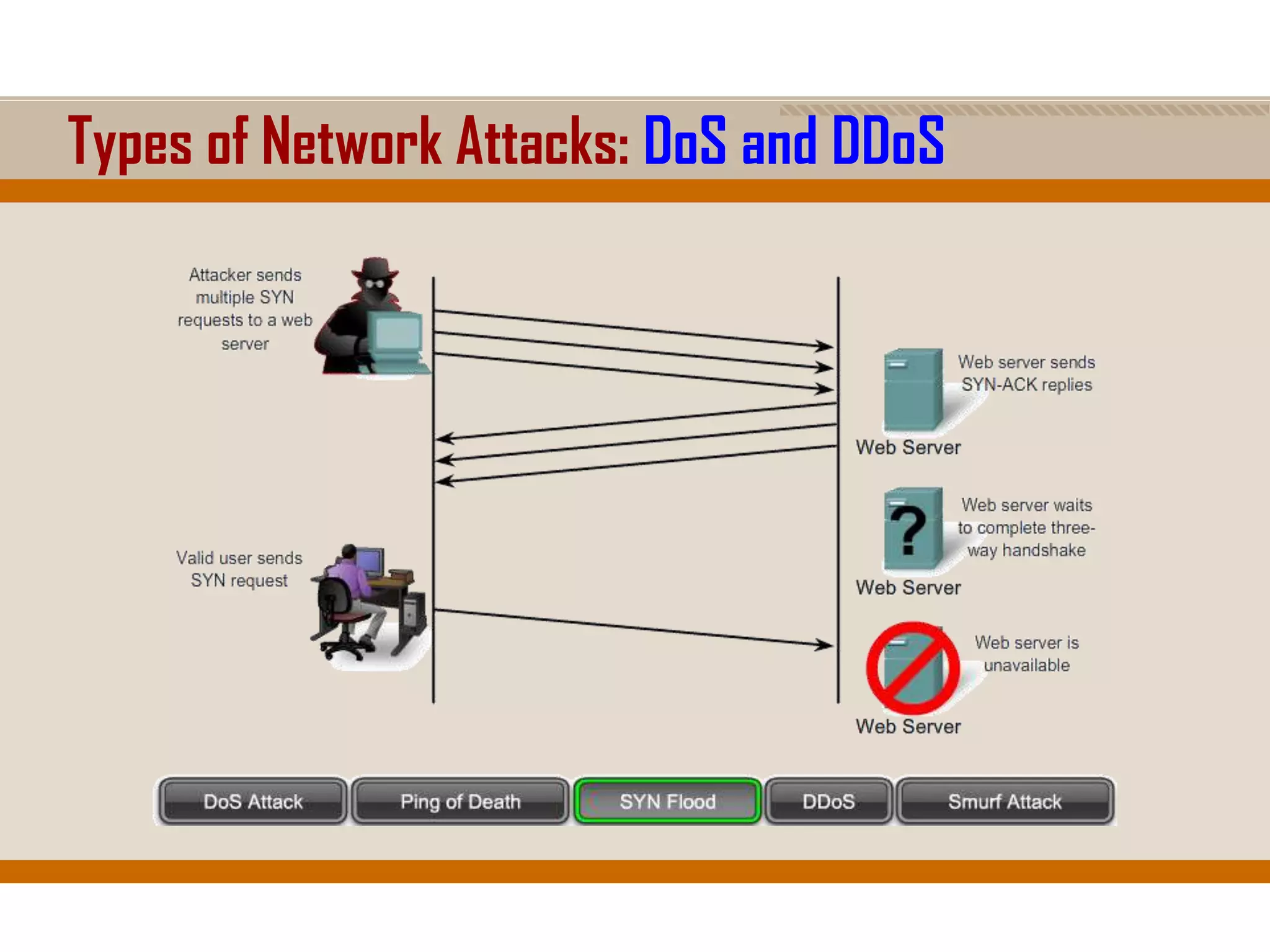
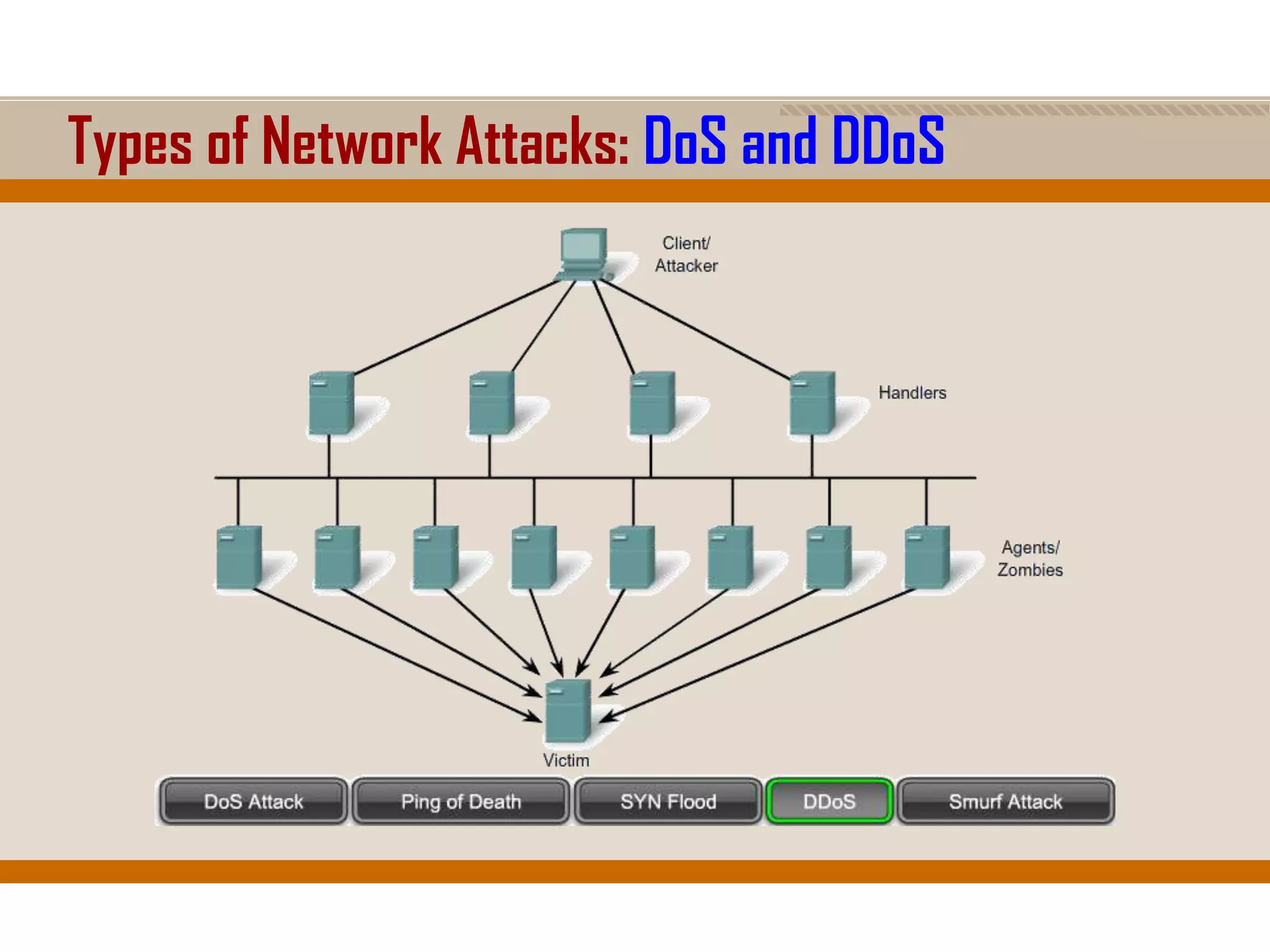
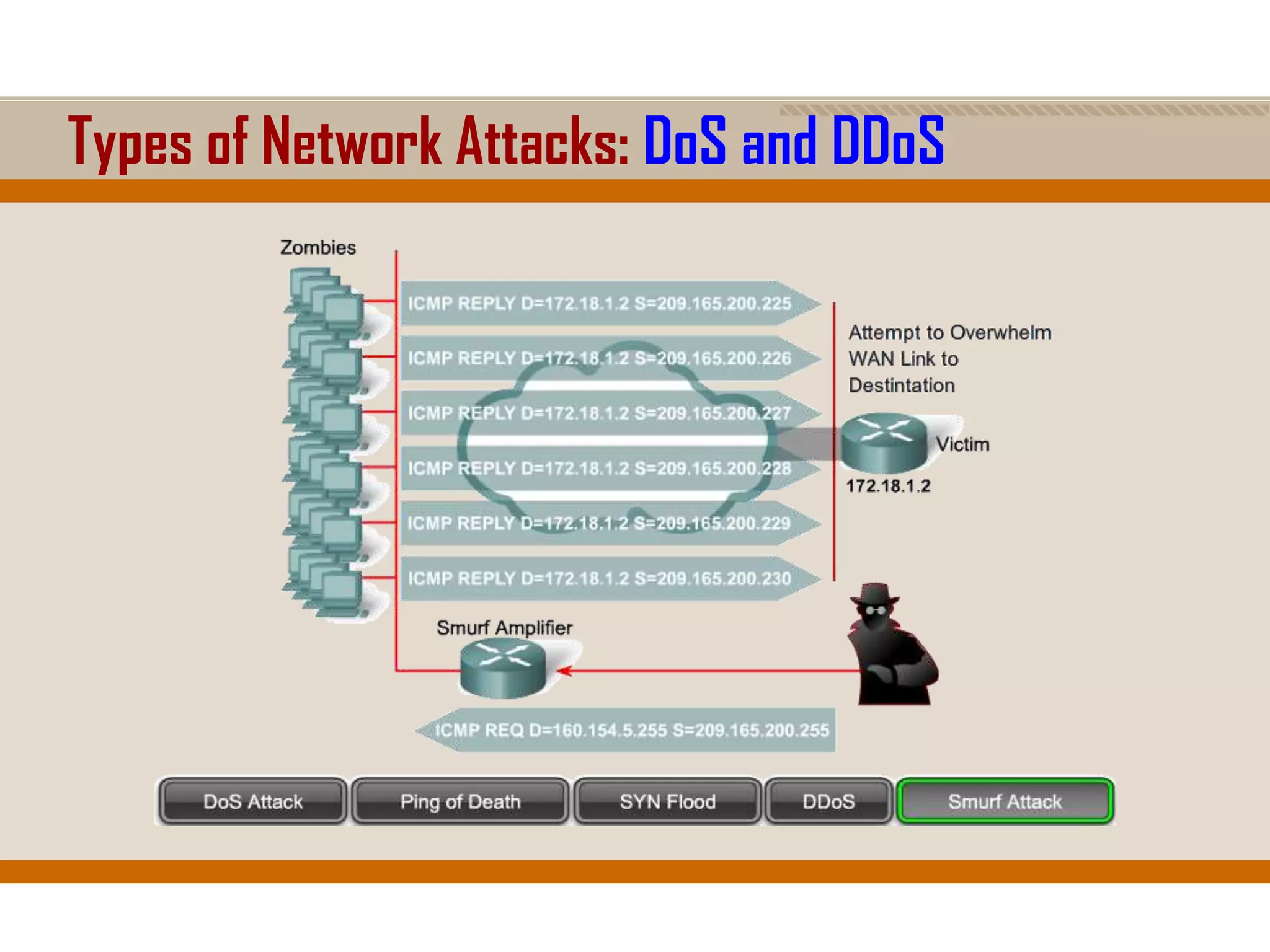
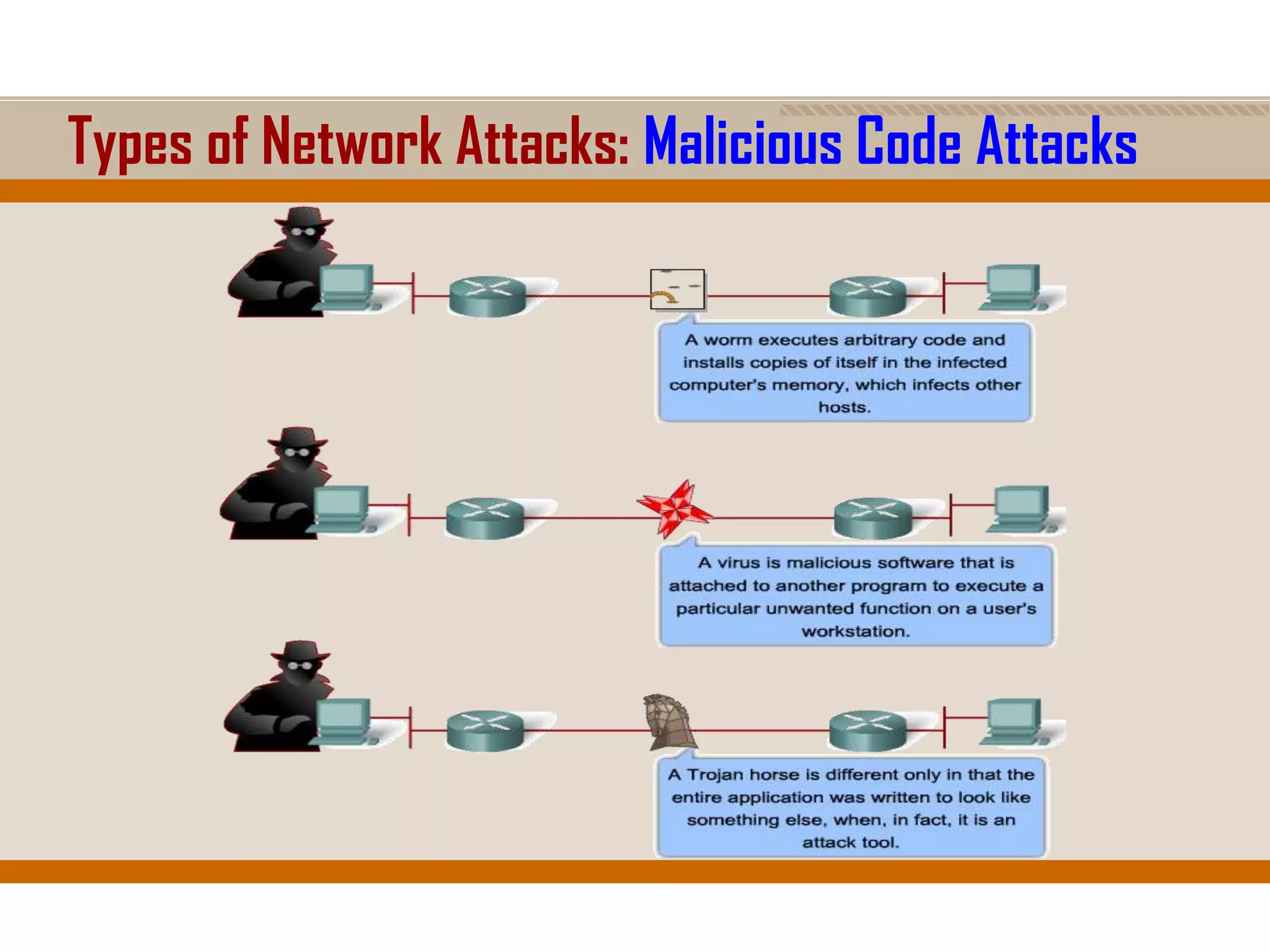
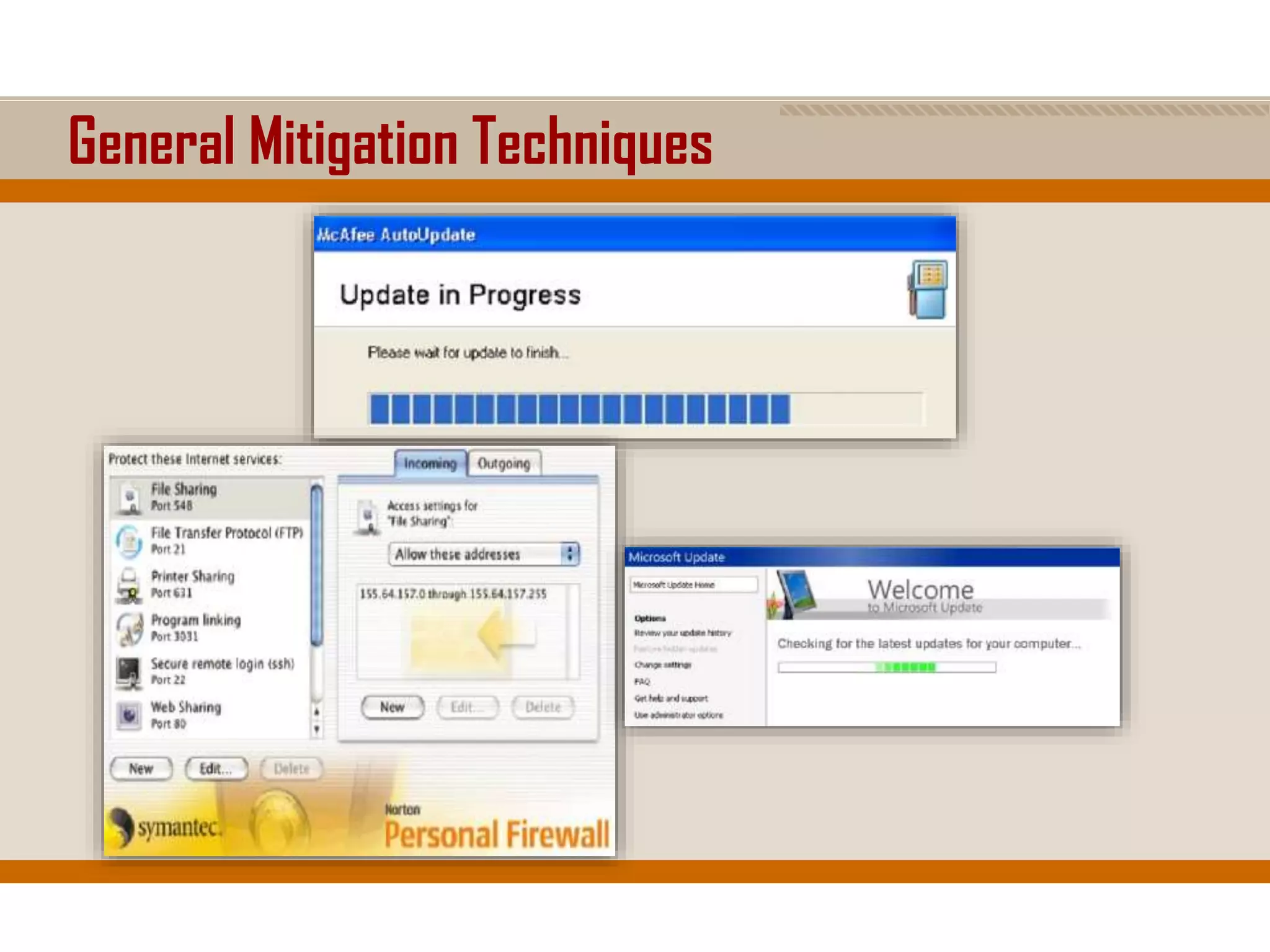
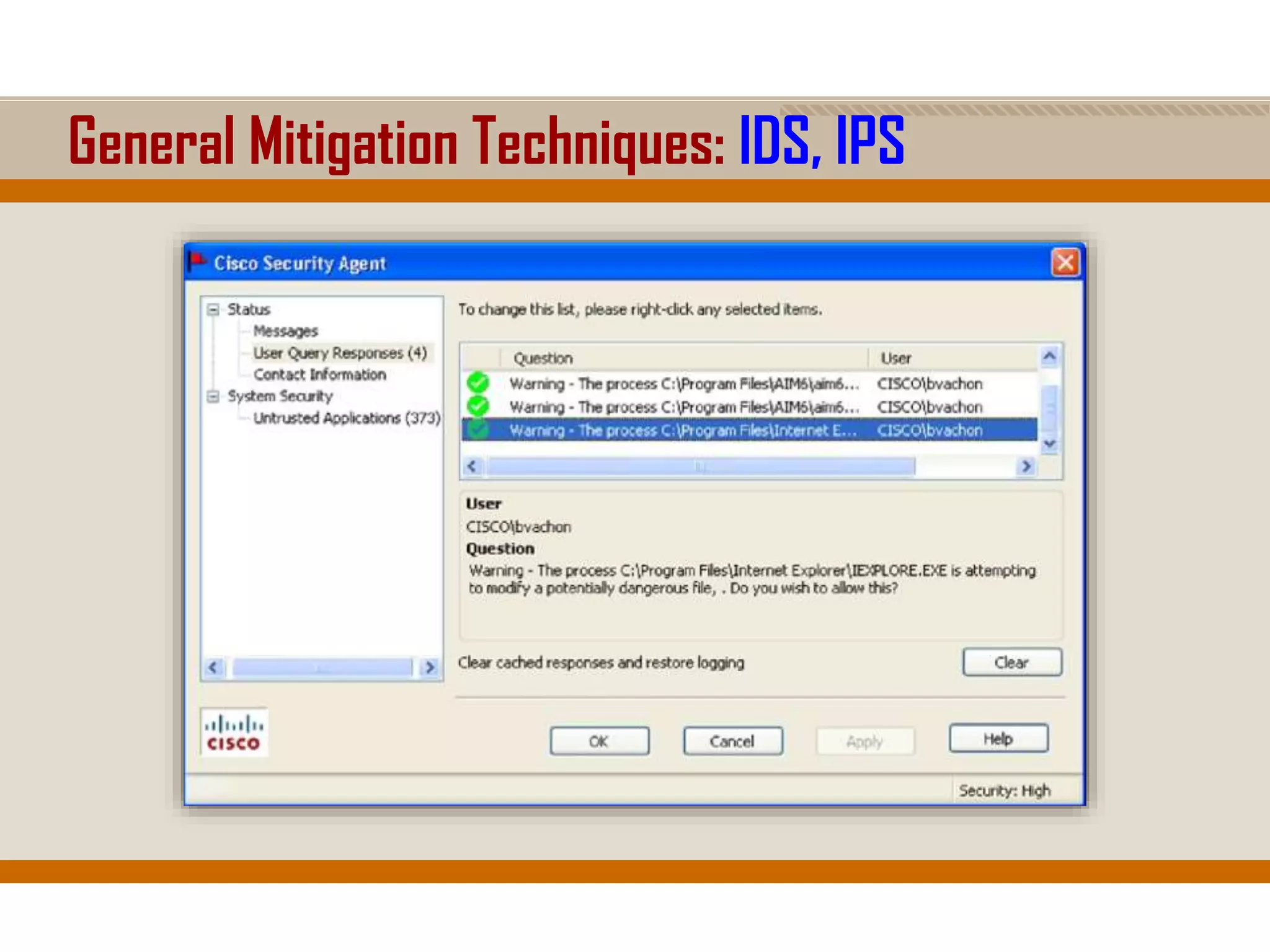
The document discusses network security, emphasizing the importance of a formal security policy that defines rules for protecting technology and information assets. It identifies common threats and vulnerabilities, including physical threats to infrastructure, social engineering, and various types of network attacks. The document also highlights general mitigation techniques, such as intrusion detection systems and network admission control.