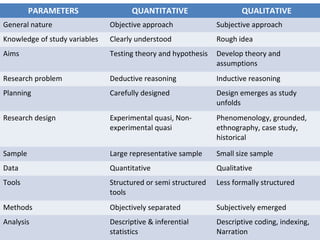
There are two main types of research: quantitative and qualitative. Quantitative research uses numerical data and statistical analysis to test hypotheses, while qualitative research uses descriptive data like words to develop theories and explore phenomena. Some key differences are that quantitative research has clearly defined variables, aims to test theories, uses large representative samples and statistical analysis, while qualitative research has a rough idea of variables, aims to develop theories, uses small samples and descriptive analysis like coding and narratives. There are also various research designs that differ based on whether they manipulate variables experimentally, use control groups, collect data prospectively or retrospectively, and in quantitative versus qualitative traditions.




























![• Primary sources ; fossils, skeleton, tools,
weapons, utensils, clothing's, buildings, pictures,
paintings.
• Oral and written testimony[ witness of the
same]- consciously used for the purpose of
transmitting information to be used in future.
• Laws, official records, letters, diaries, contracts,
wills, maps, books, research reports.
• Secondary sources; Most of history Books and
encyclopedias.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/typesofresearch-copy-180418081009/85/Types-of-research-copy-39-320.jpg)



