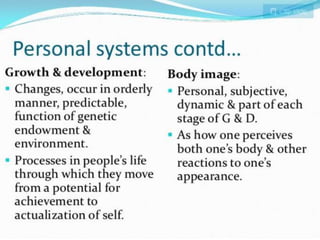
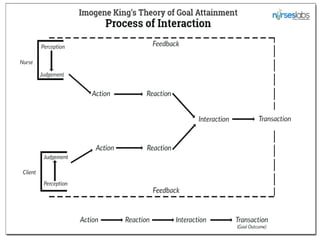
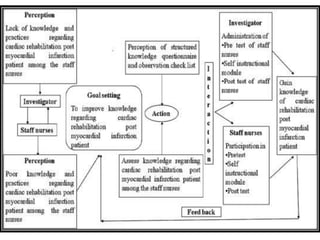
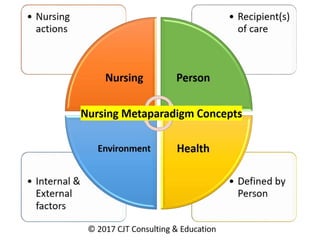
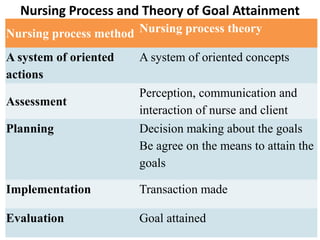
The document discusses Imogene King's Theory of Goal Attainment. The theory describes nursing as a process of human interaction between nurses and clients to set and achieve goals. It explains that accurate perception, communication, and role expectations facilitate goal attainment, while role conflict can cause stress. The theory views people as open systems interacting with their environment. It proposes that if nurses and clients make transactions through the nursing process, goals will be achieved, leading to satisfaction. The theory's concepts can be applied to each step of the nursing process.