This document discusses different methods for collecting primary data, including observation, interviews, questionnaires, and schedules. It provides details on each method, such as advantages and limitations. Some key points covered include:
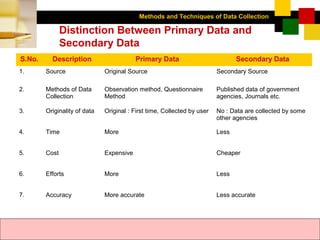
- Primary data is originally collected for the specific research purpose, while secondary data was previously collected by others.
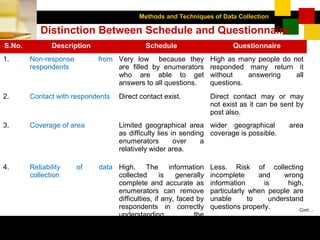
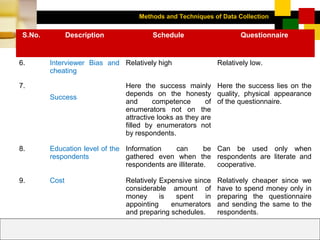
- Observation allows collecting data without respondent bias but provides limited information. Interviews can obtain more depth but are more expensive and time-consuming.
- Questionnaires standardize responses but response rates may be low. They are cheaper than interviews and can reach more geographically dispersed respondents.