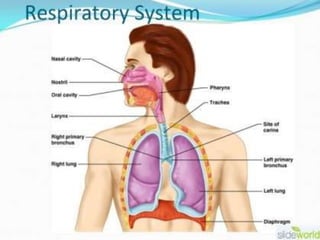
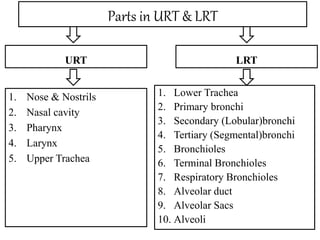
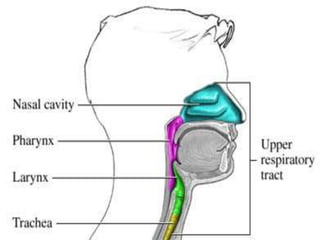
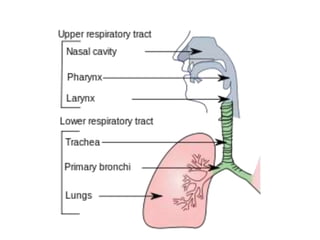
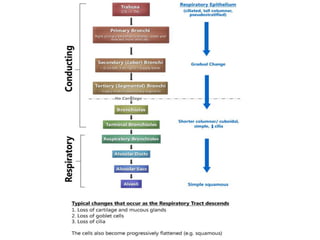
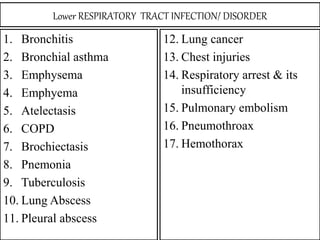
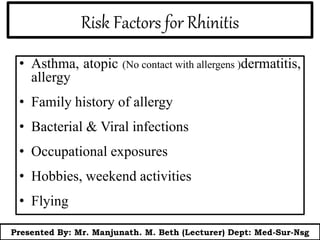
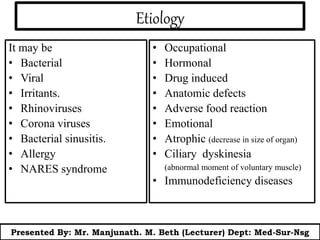
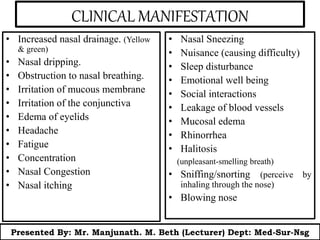
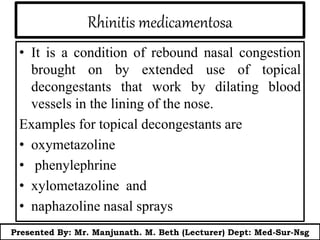
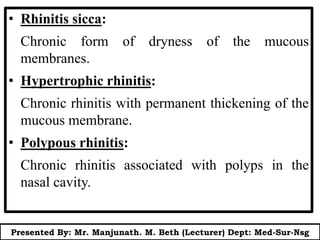
This document presents information on rhinitis from a lecture given by Mr. Manjunath Beth. It defines rhinitis as inflammation of the nasal mucosa. It describes the parts of the upper and lower respiratory tract. It then discusses different types of rhinitis such as infectious, allergic, vasomotor and rhinitis medicamentosa. The document outlines signs and symptoms, risk factors, diagnostic evaluation including physical examination and nasal smear tests. It concludes with discussing medical management of rhinitis through medications, decongestants, antihistamines and steroids.