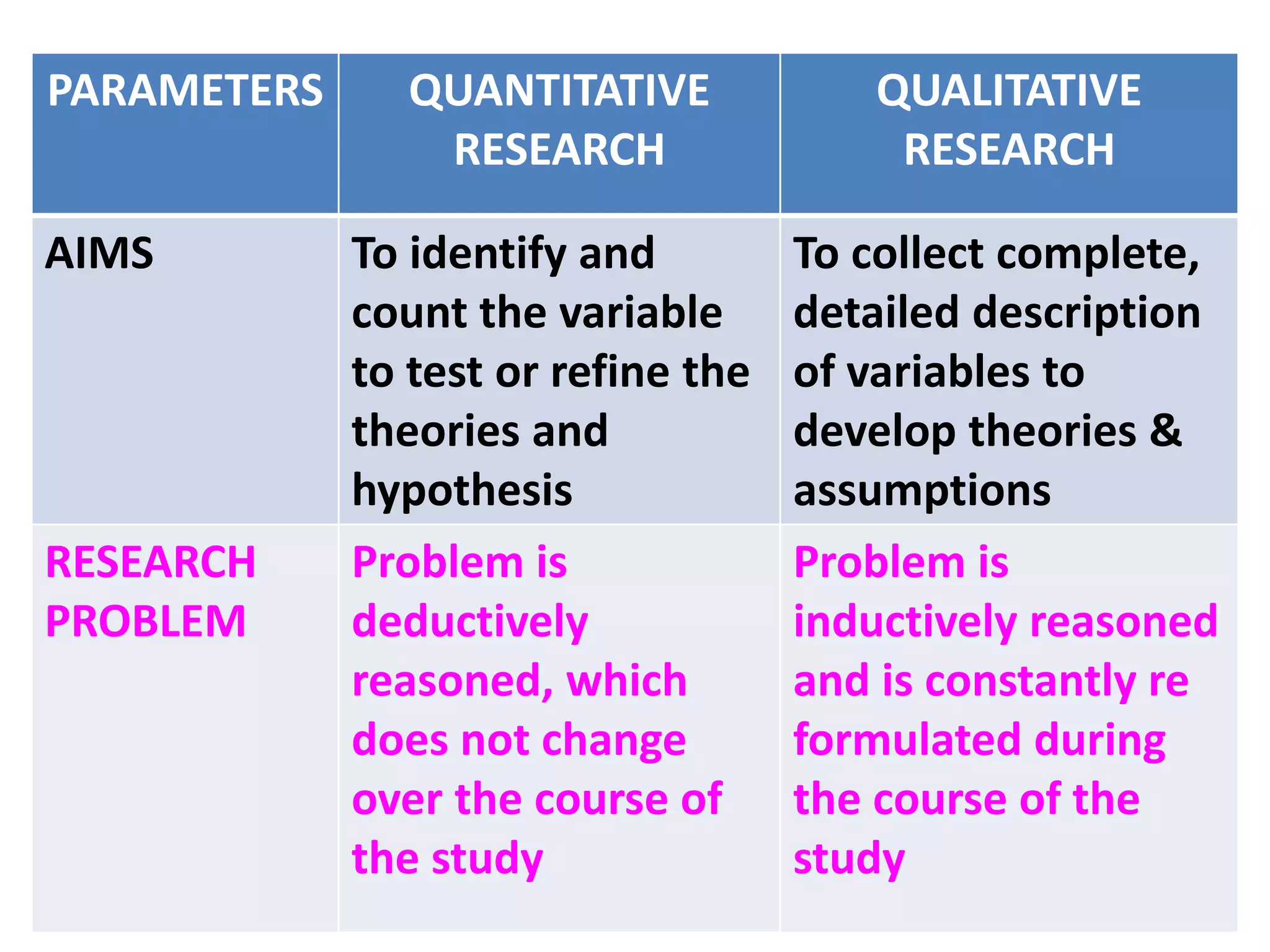
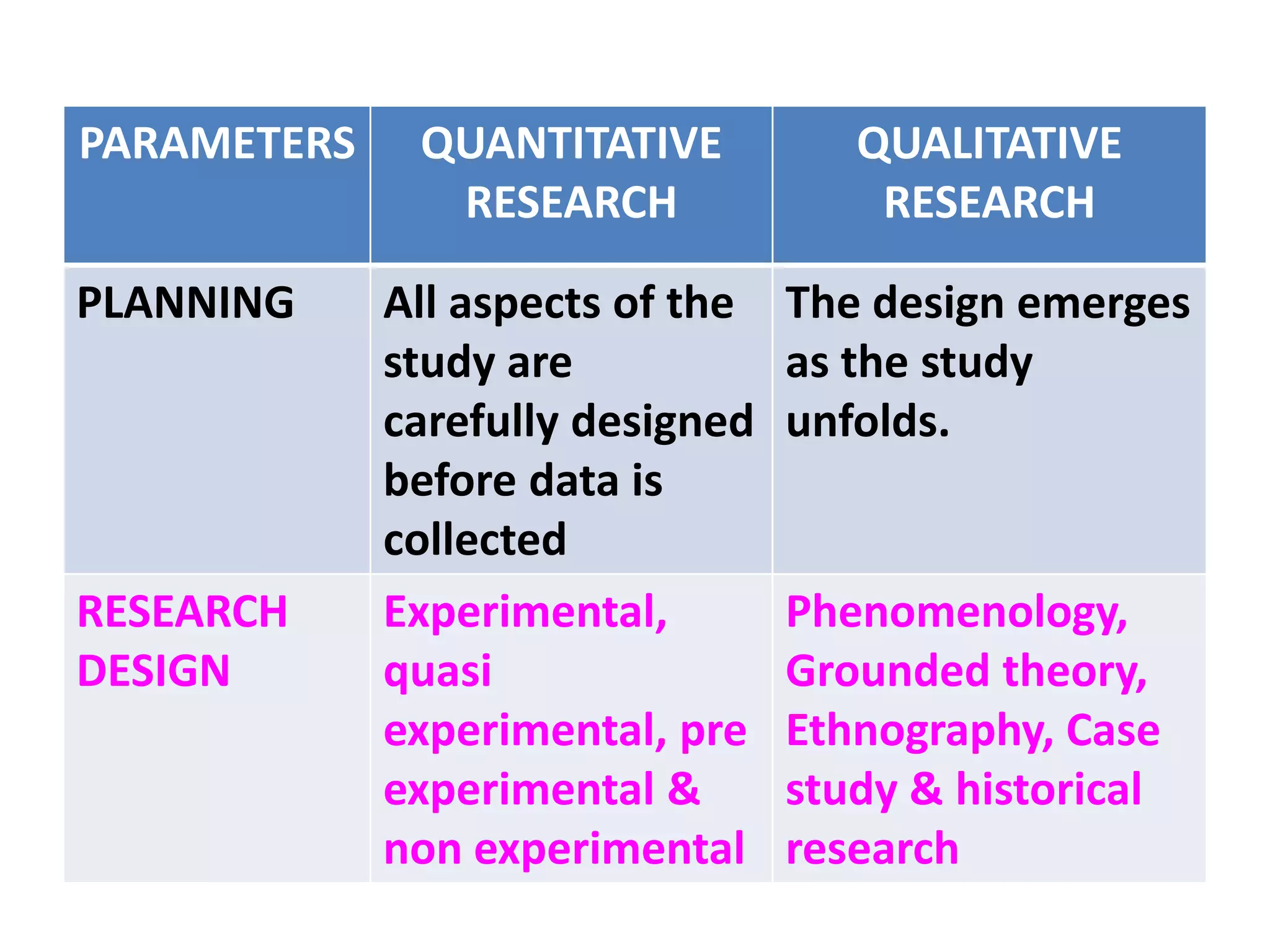
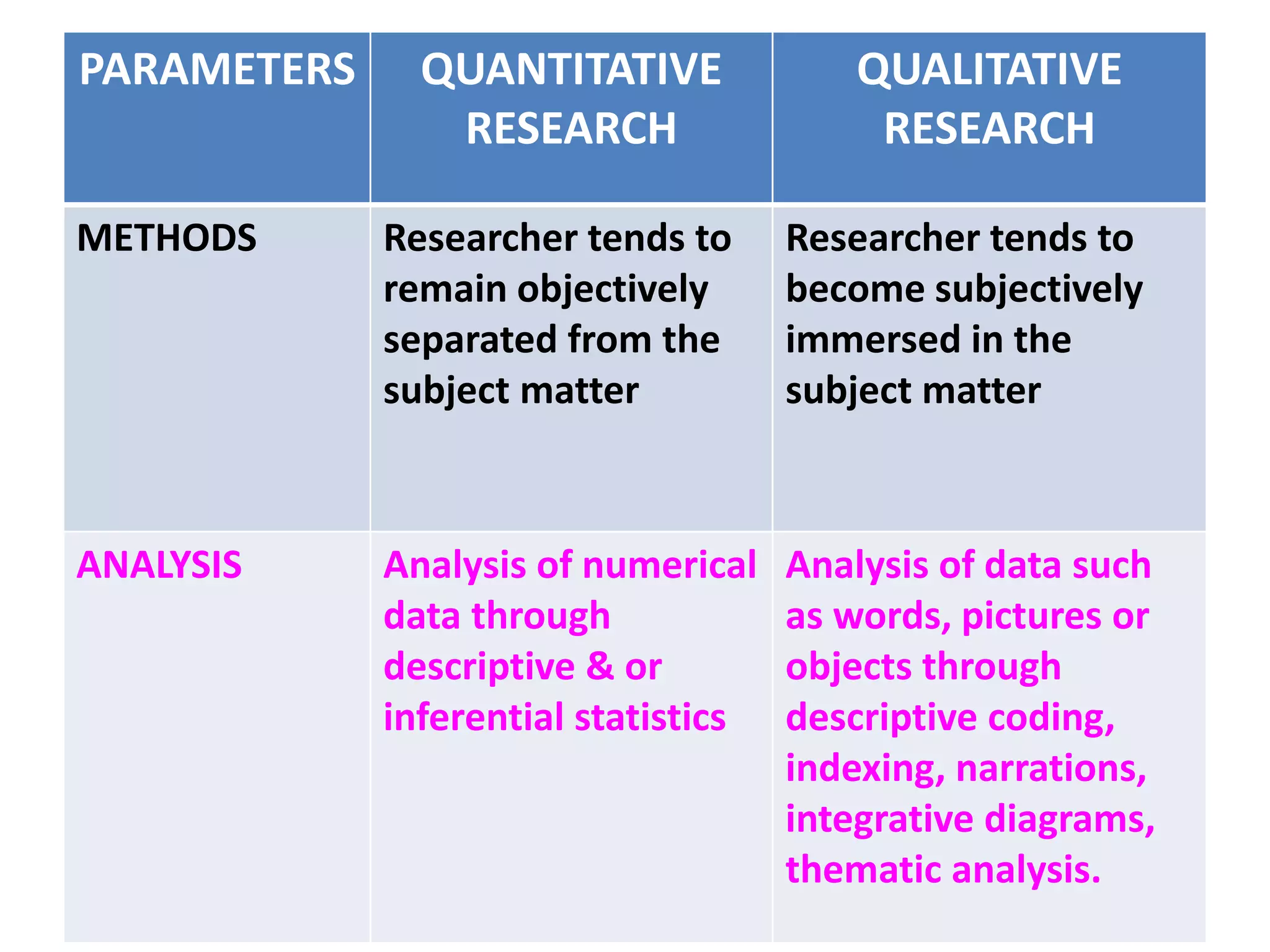
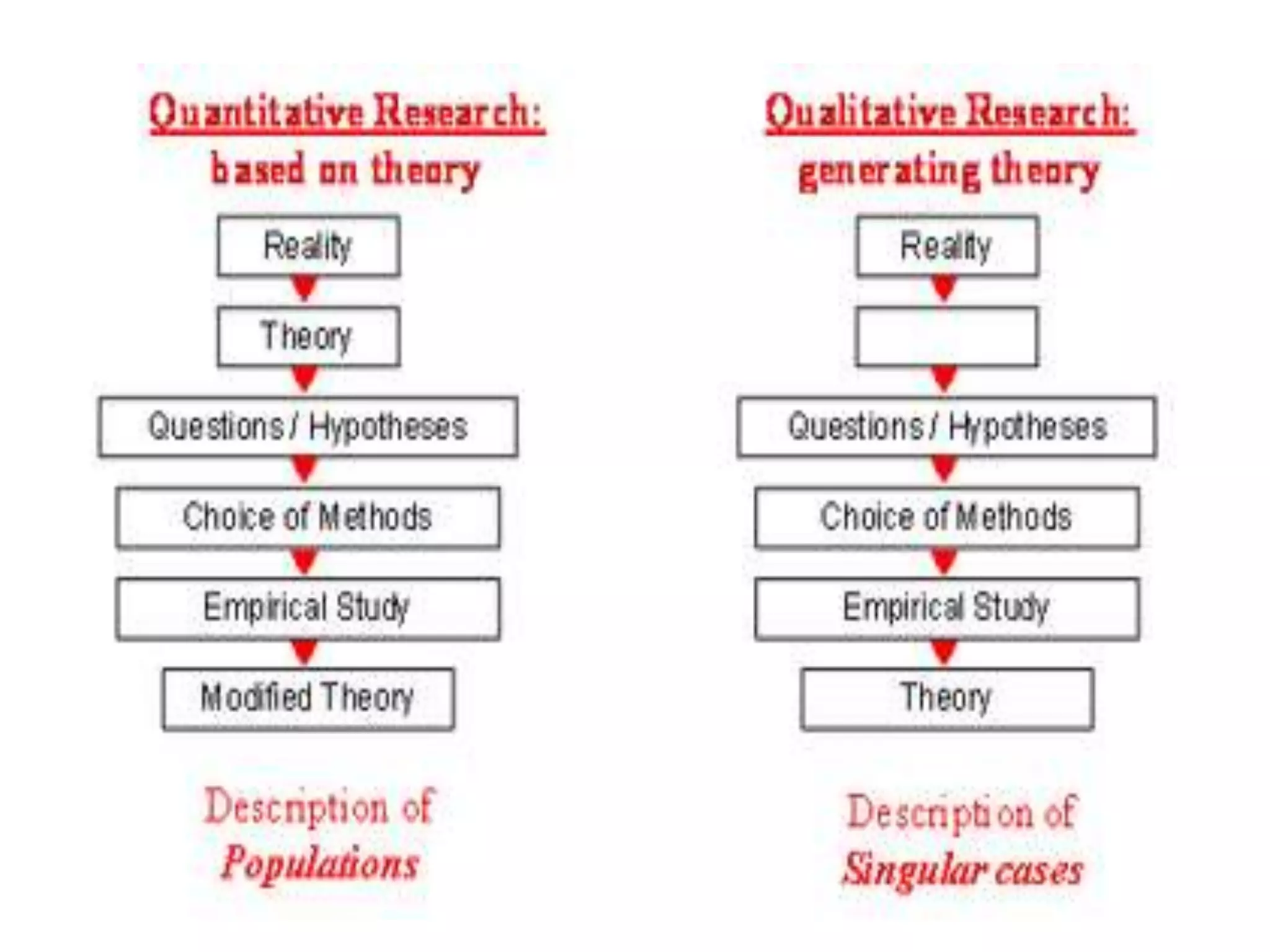
This document compares and contrasts quantitative and qualitative research. Quantitative research aims to precisely measure and test hypotheses using experimental, quasi-experimental, or non-experimental designs with large sample sizes. The variables are clearly defined, the problem is deductively reasoned, and all aspects are carefully planned. Qualitative research seeks an in-depth understanding of human behavior using small sample sizes in phenomenological, grounded theory, ethnographic, or case study designs. The problem is inductively reasoned and emerges during the study, while variables are loosely defined. It collects rich narrative data through immersion in the subject matter to develop theories rather than test them.