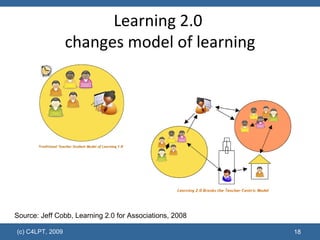
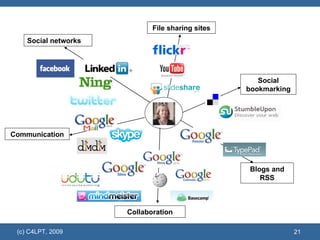
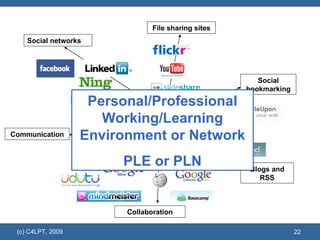
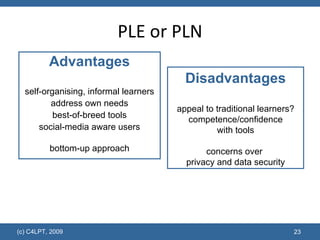
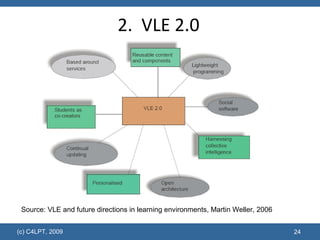
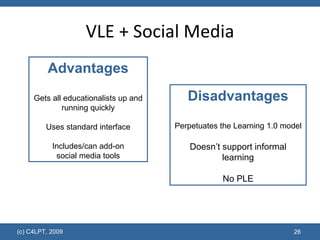
The document discusses the evolution of educational technology and online learning from the late 1980s to the present. It covers the early web-based learning in universities in the 1990s, the rise of e-learning and virtual learning environments, and the emergence of Web 2.0 and social learning approaches. It proposes several models to support the new "Learning 2.0" paradigm, including personal learning environments, VLE 2.0 platforms, social learning environments, and social learning networks.