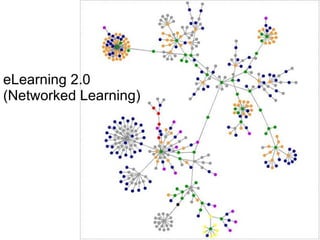
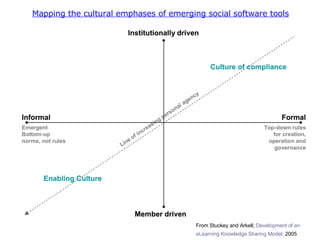
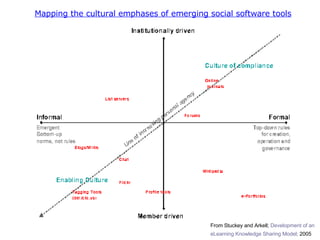
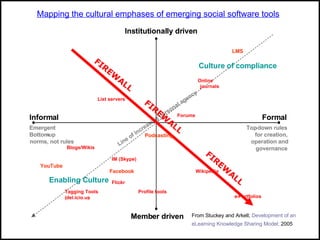
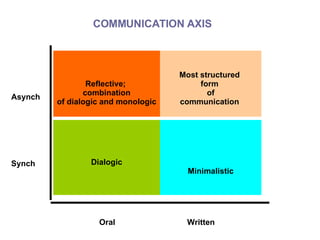
The document discusses various topics related to elearning including different types of elearning models, the role of Web 2.0 and social software, challenges of keeping content up to date and students engaged, and how other educational institutions are incorporating new technologies like wikis, podcasting and virtual worlds into their programs.