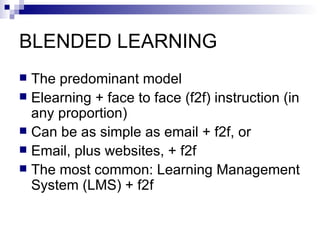
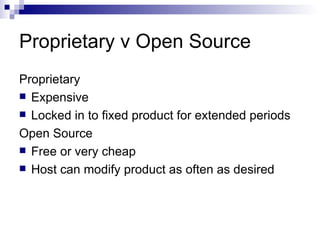
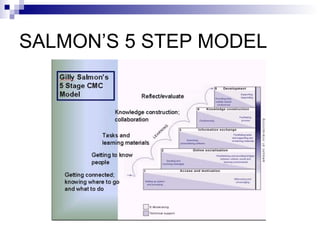
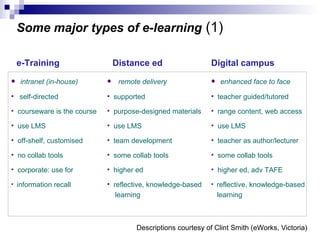
The document discusses the evolution of distance learning from print-based correspondence courses to modern eLearning and mobile learning. It describes blended learning models that combine online and face-to-face instruction, and learning management systems that provide course content and communication tools. The document also covers social software and networking approaches like eLearning 2.0 that enable user-generated content and interactions beyond traditional courses.











![Michael Coghlan [email_address]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/elearning-the-big-picture-7121/85/eLearning-The-BIG-Picture-21-320.jpg)