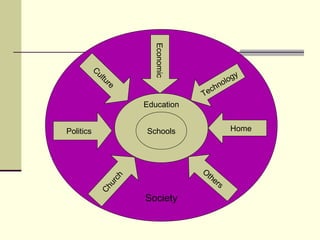
Sociology is the study of social beings and encompasses human behavior in groups, social structures, and interrelations. The document emphasizes that education is influenced by societal issues, including changes in social structure, culture transmission, and economic factors, and it highlights the role of schools in shaping students' social values and skills. It concludes that education is inherently a social process essential for developing democratic values and addressing societal needs.