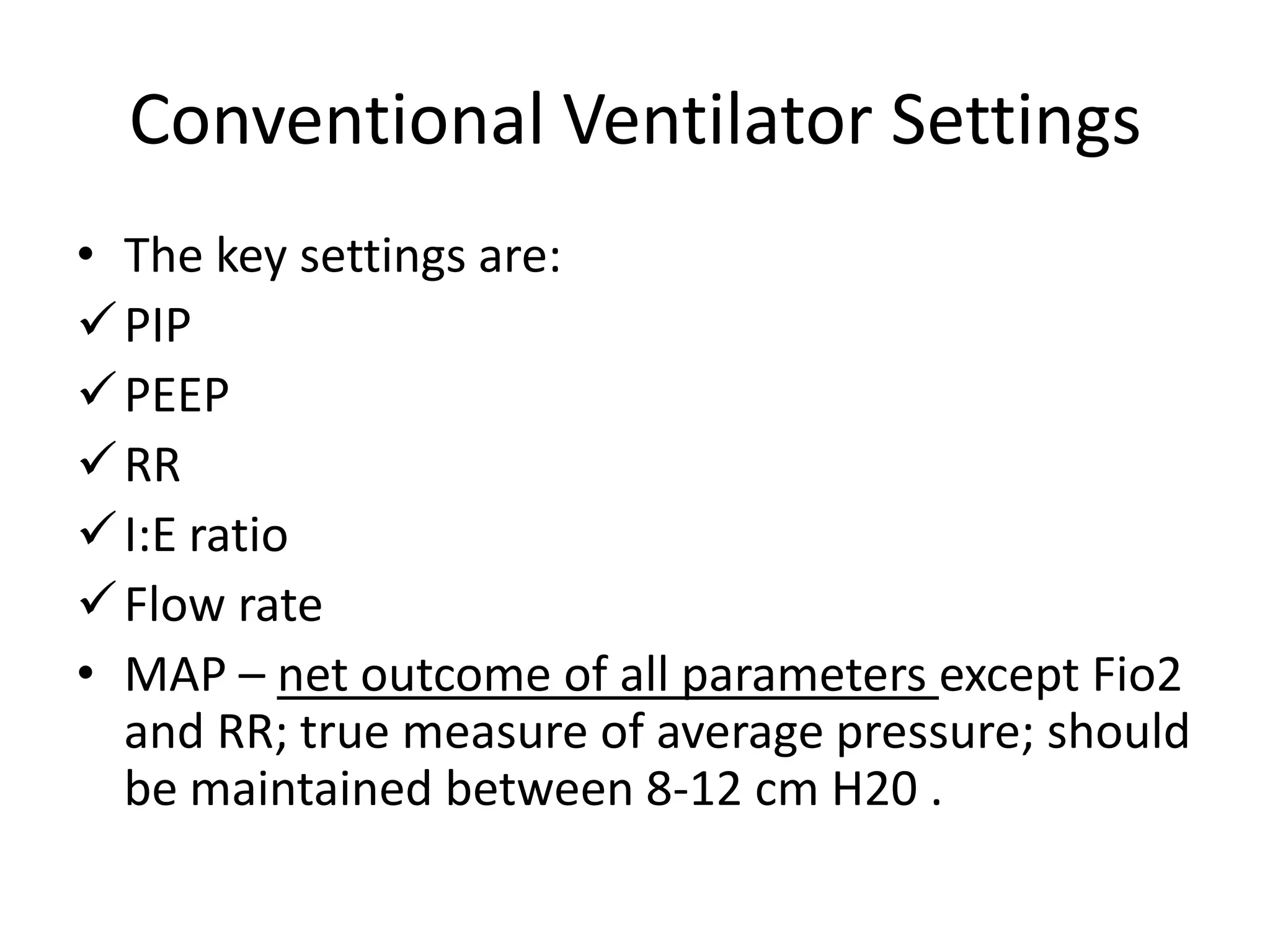
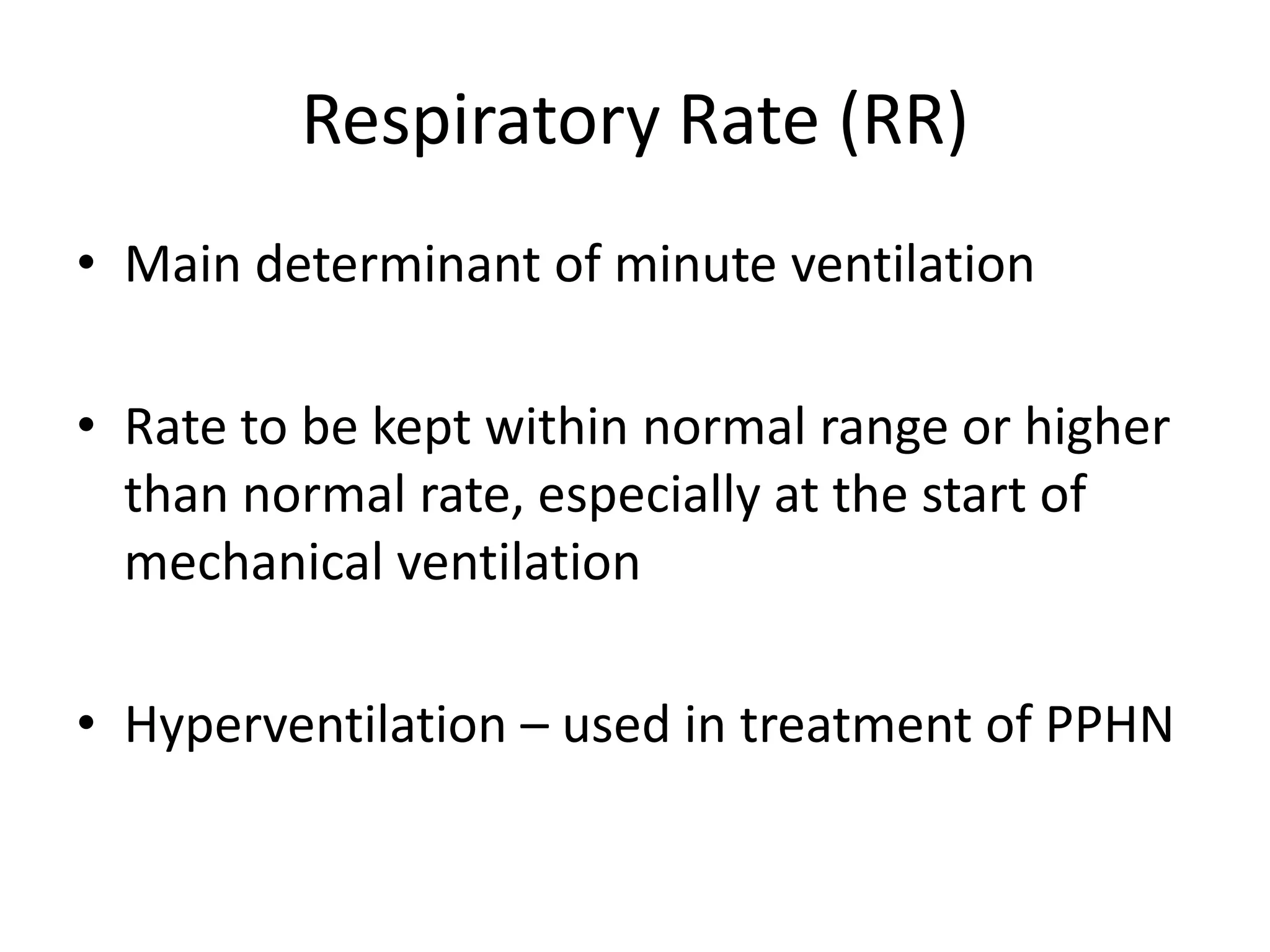
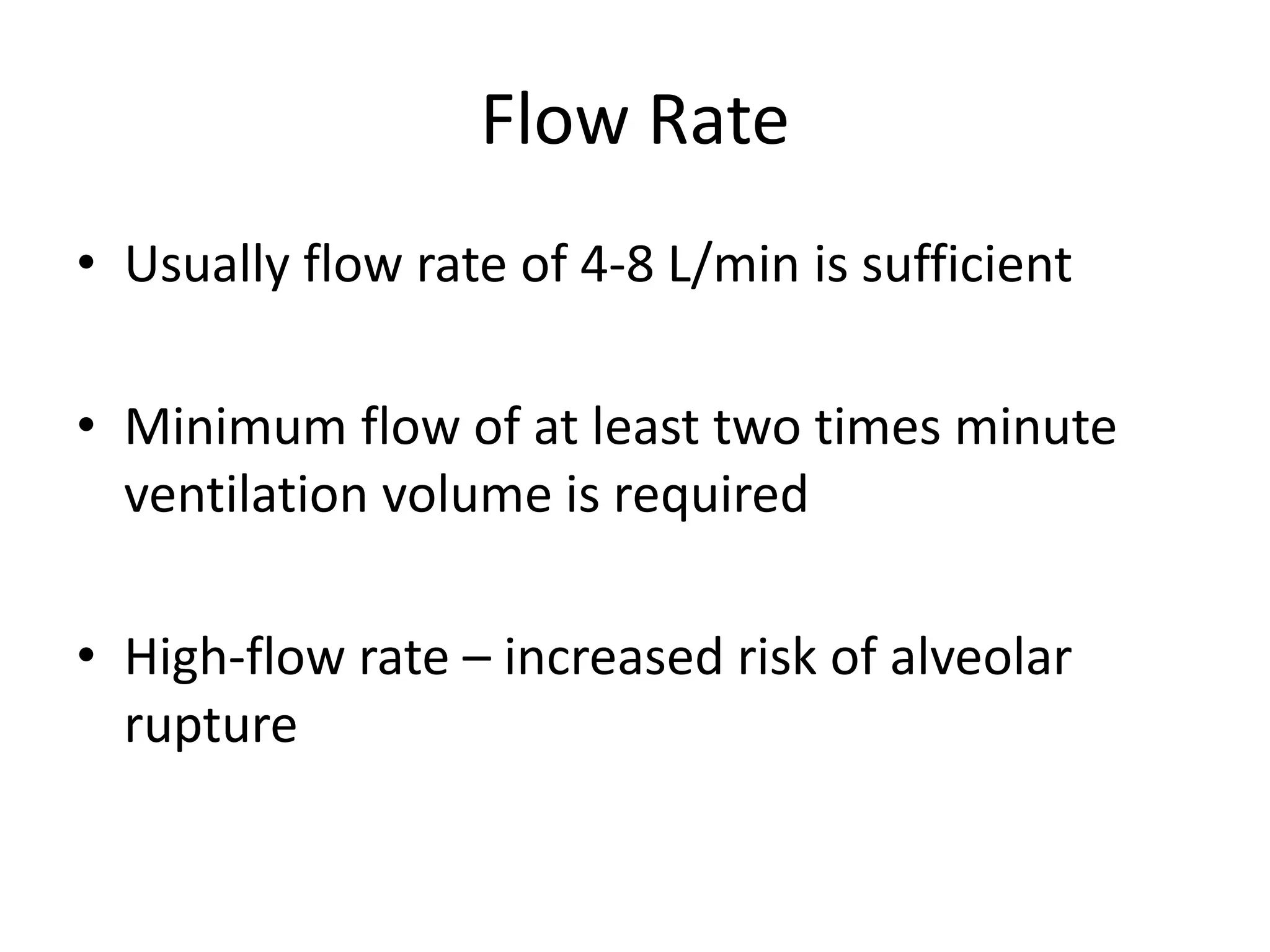
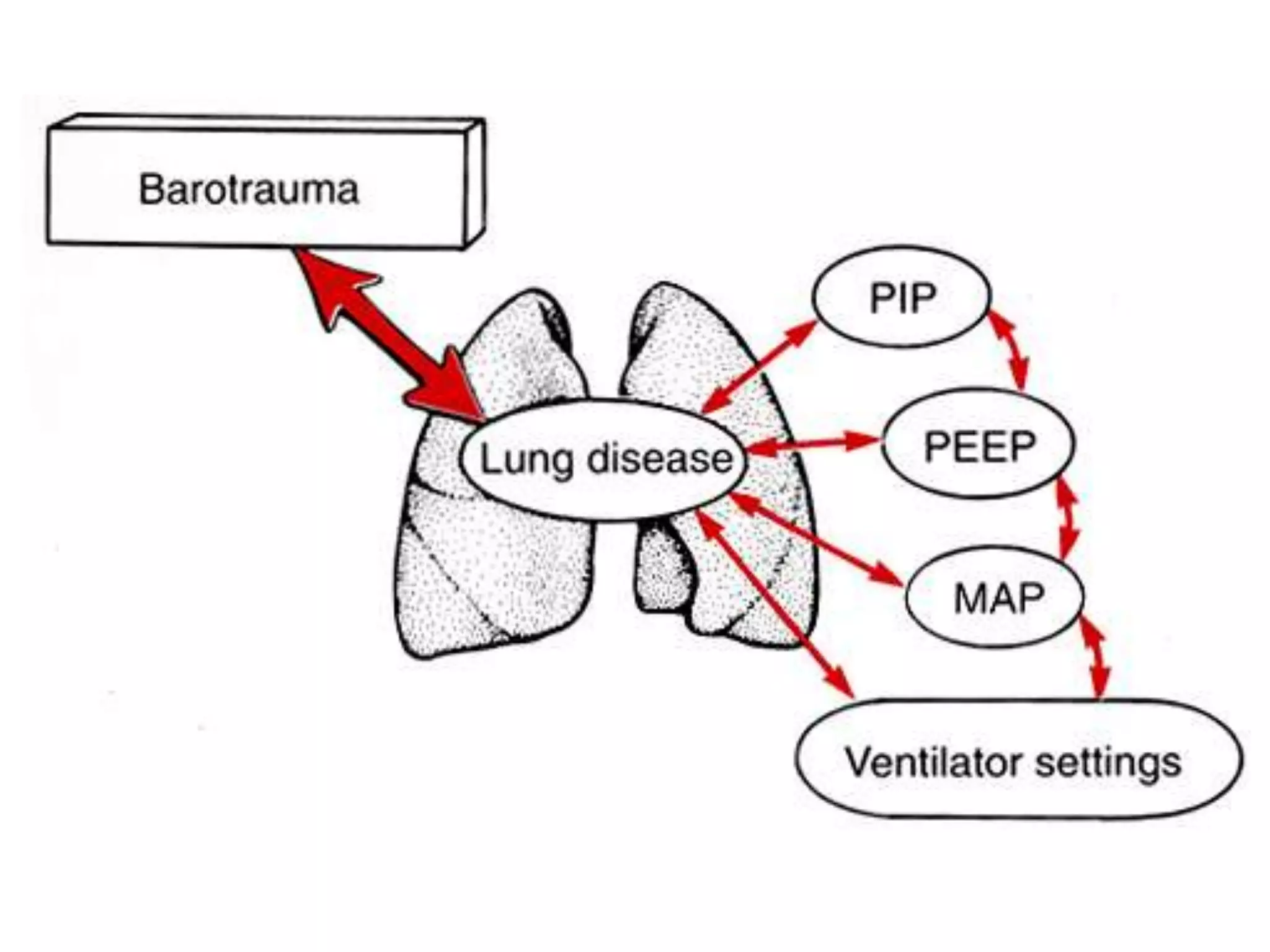
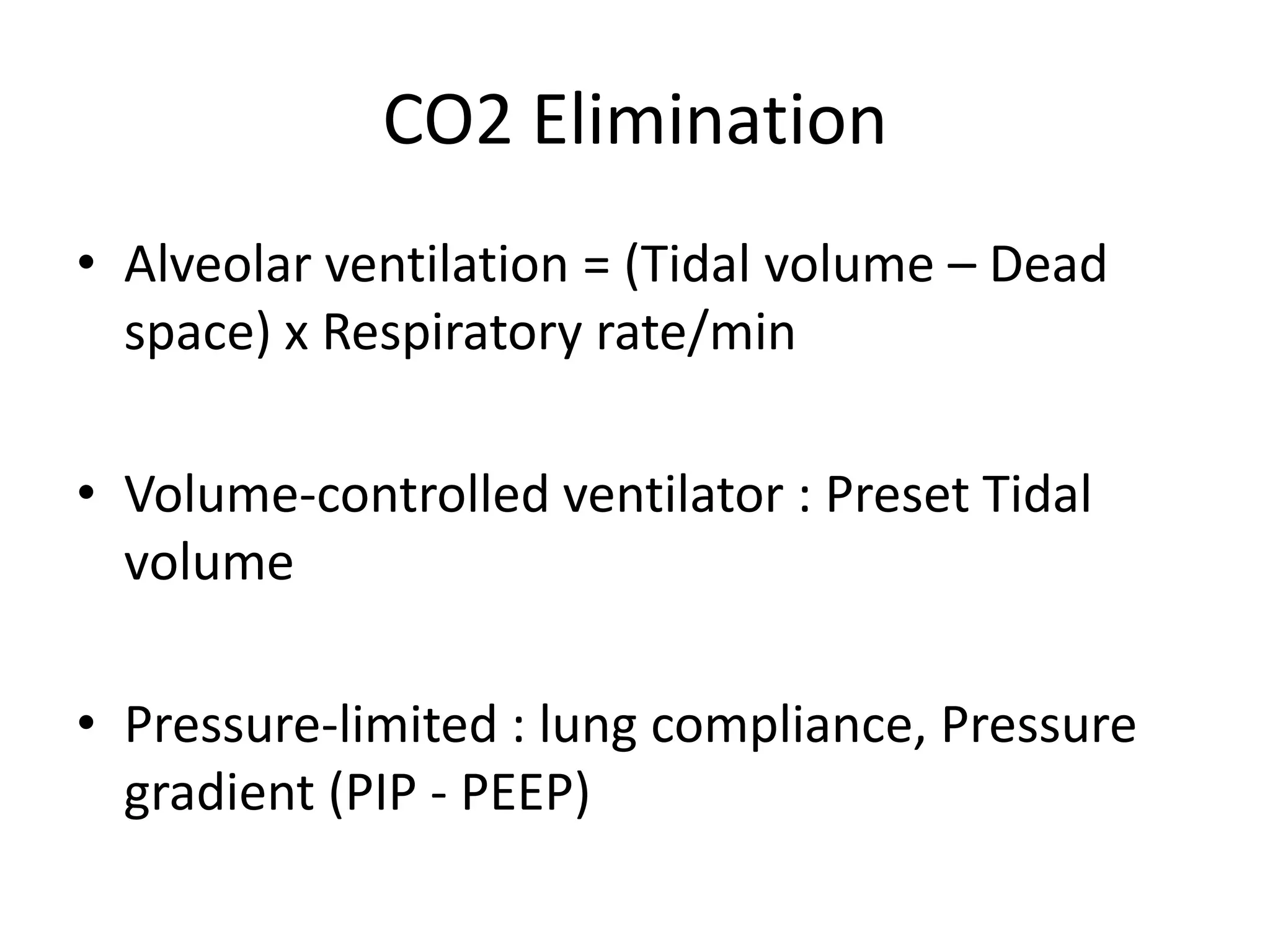
This document provides an overview of basic terminology and parameters related to mechanical ventilation. It discusses factors that influence CO2 elimination and oxygen uptake, such as alveolar ventilation, tidal volume, mean airway pressure, inspiratory flow rate, PIP, PEEP, I:E ratio, and respiratory rate. The key settings on a conventional ventilator are listed as PIP, PEEP, respiratory rate, I:E ratio, and flow rate. Parameters like Fio2, PIP, PEEP, respiratory rate, I:E ratio, and flow rate are explained in terms of their effects and appropriate ranges.

![O2 Uptake
• Depends on Mean Airway pressure (MAP)
• MAP - Area under airway pressure curve
divided by duration of the cycle
• MAP = K (PIP – PEEP) [Ti/(Ti – Te)] + PEEP](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/terminologymechanicalventilation-130925131919-phpapp01/75/Terminology-mechanical-ventilation-3-2048.jpg)