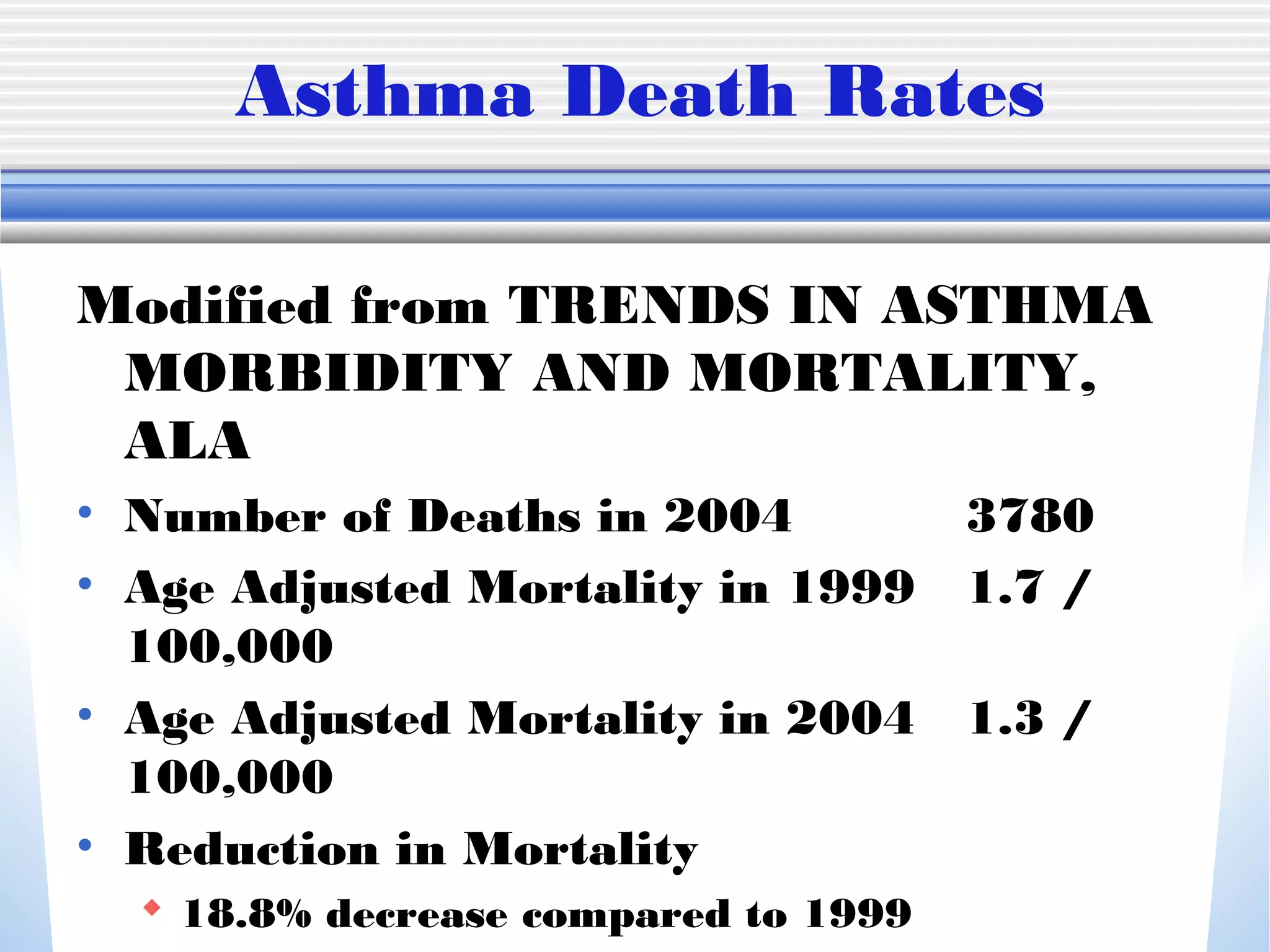
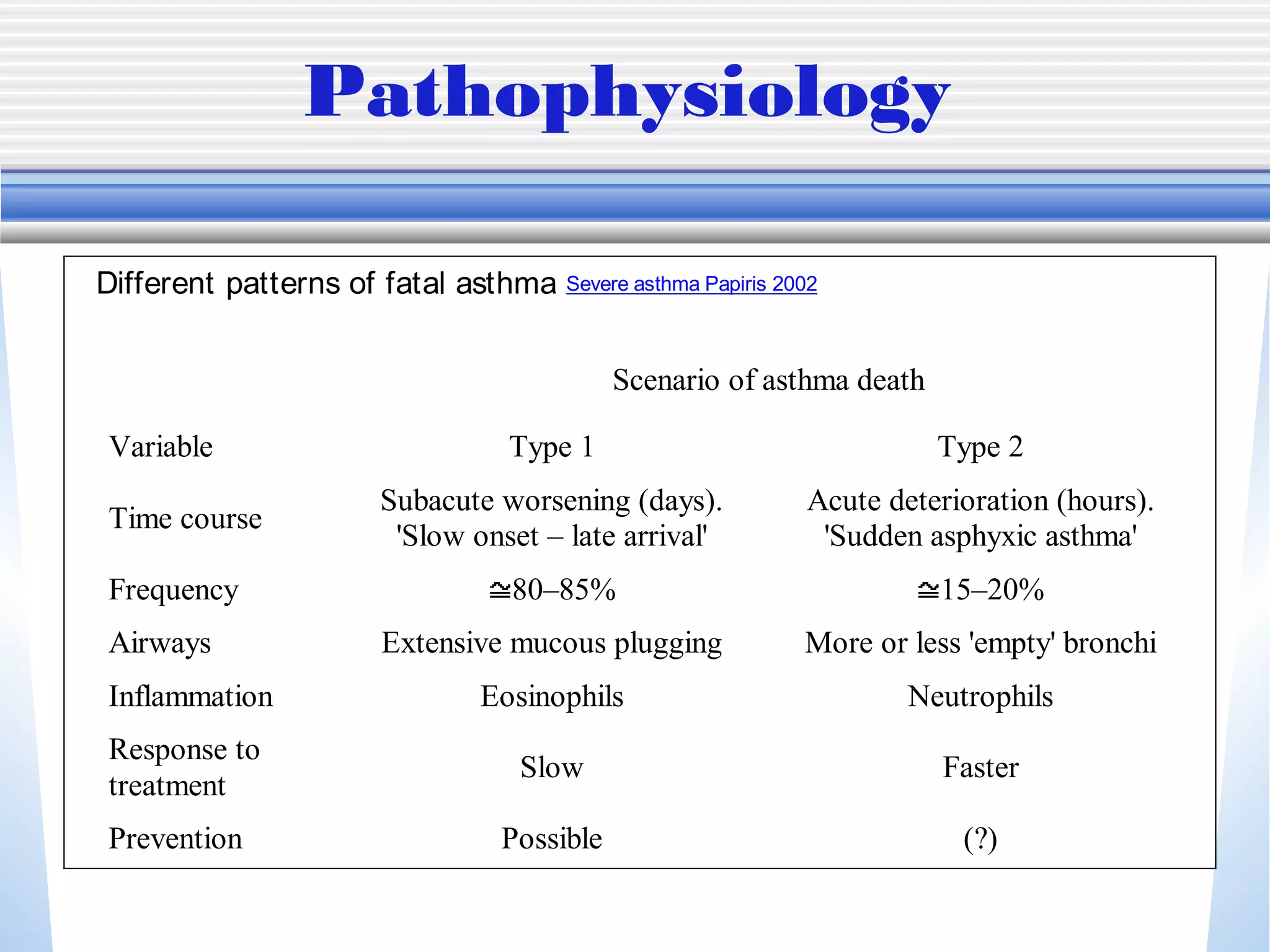
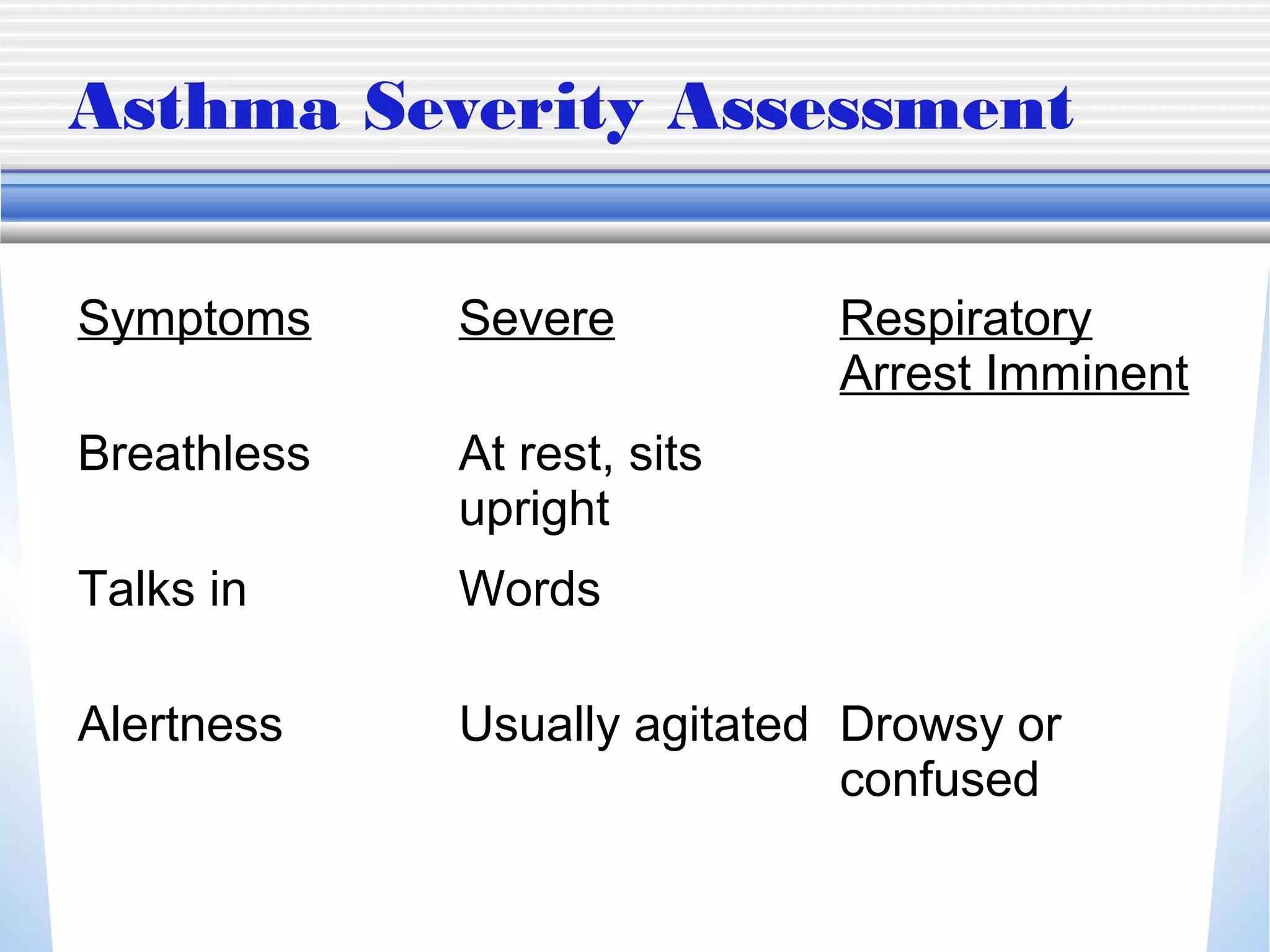
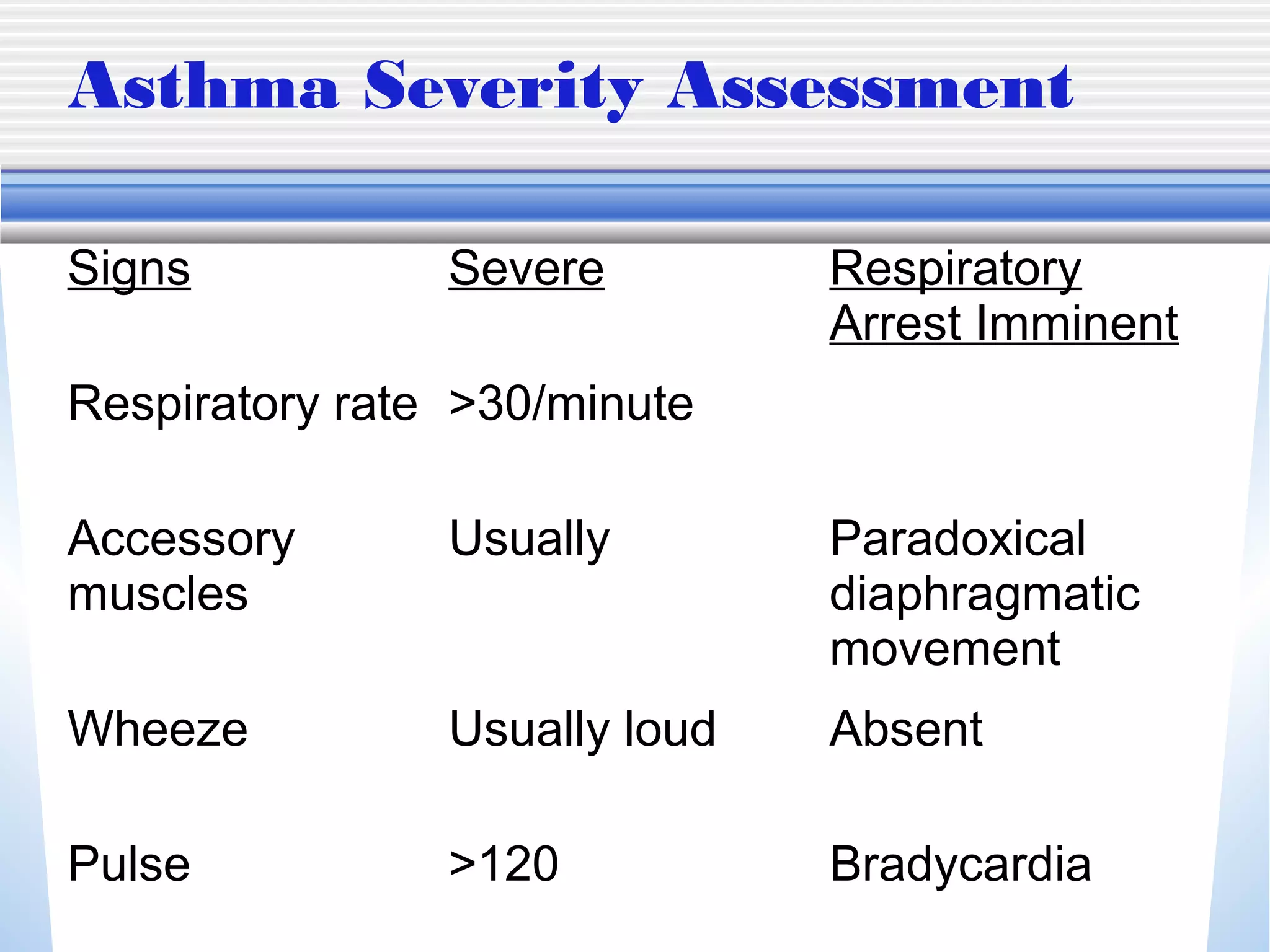
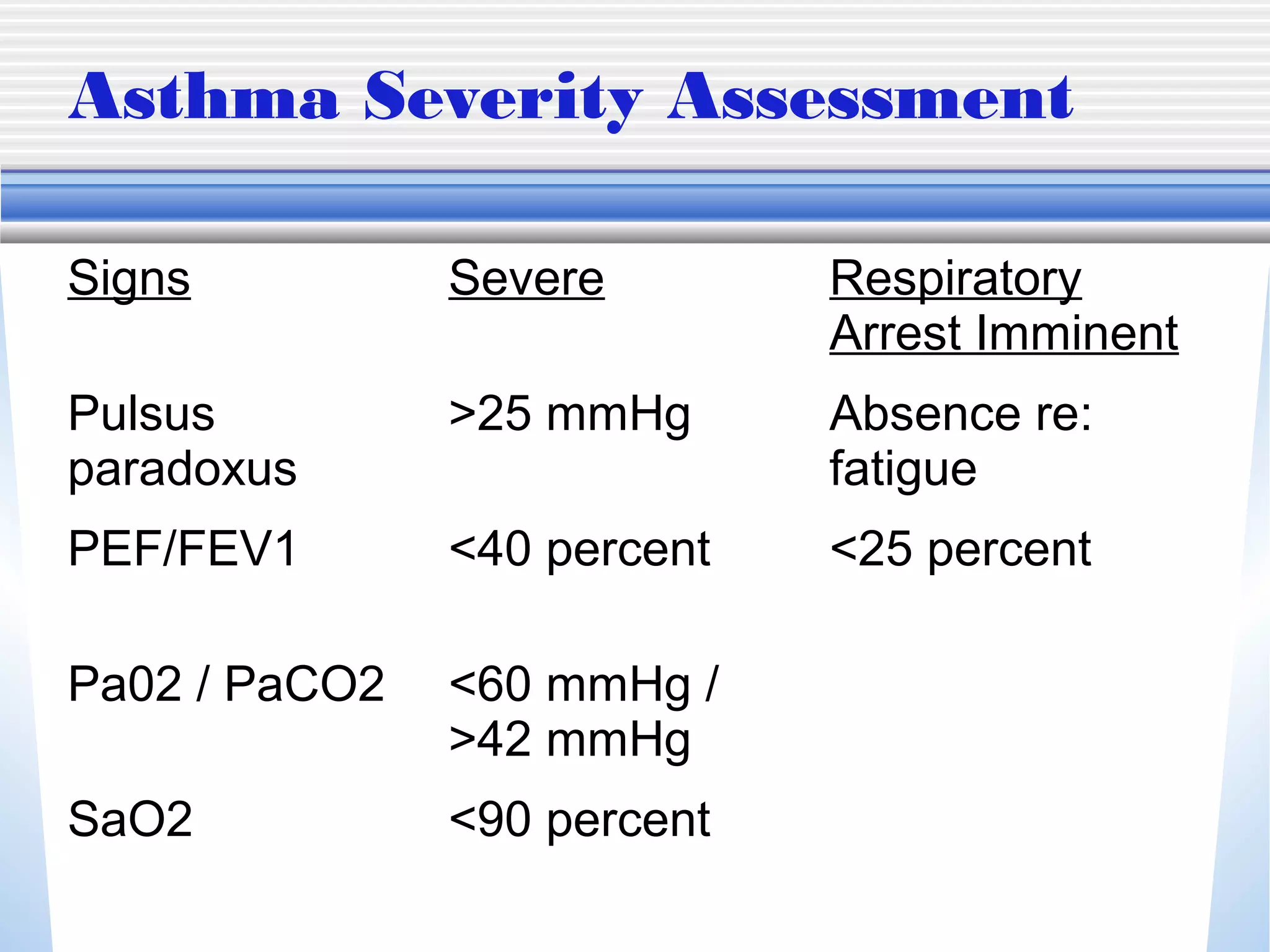
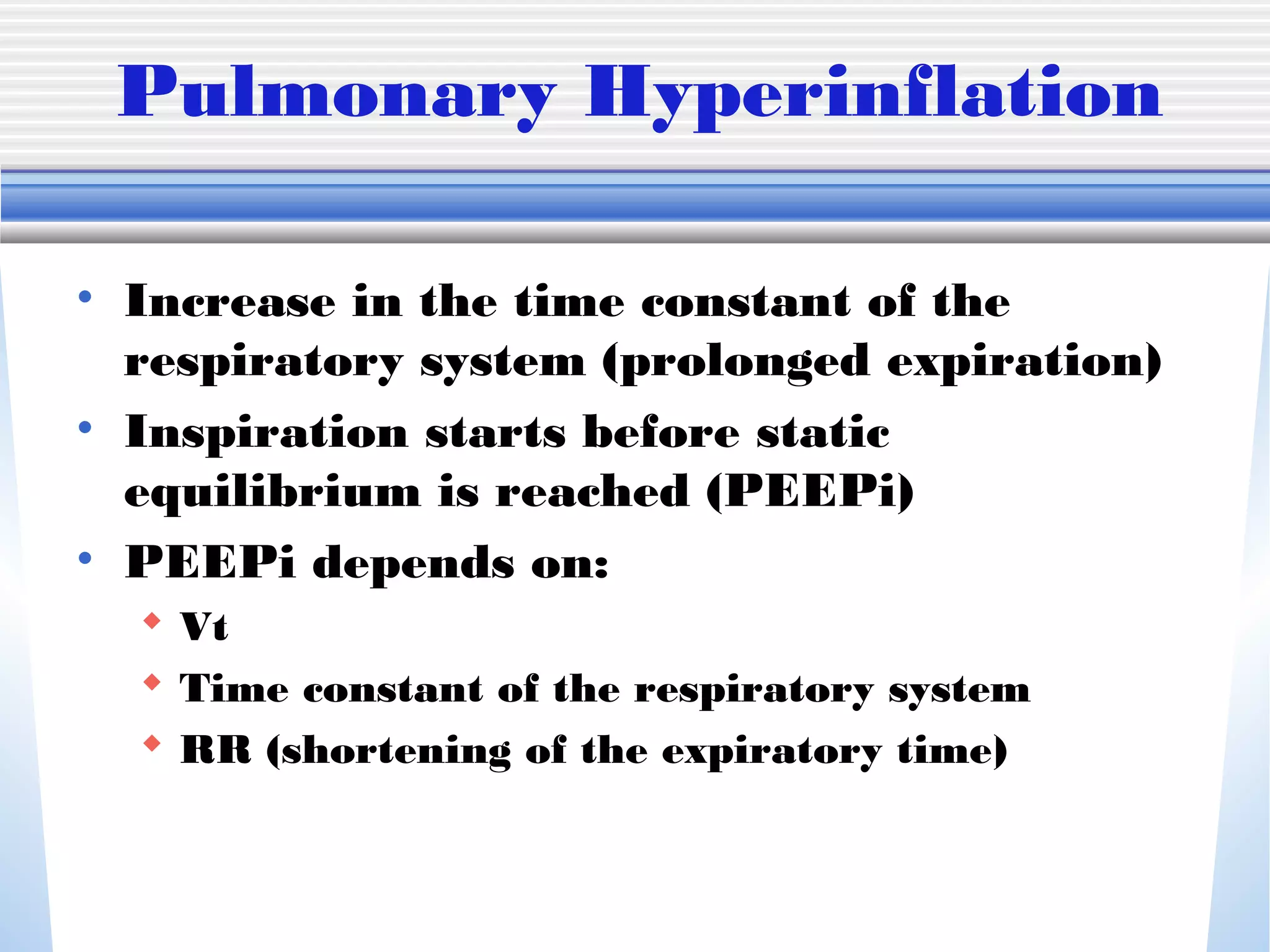
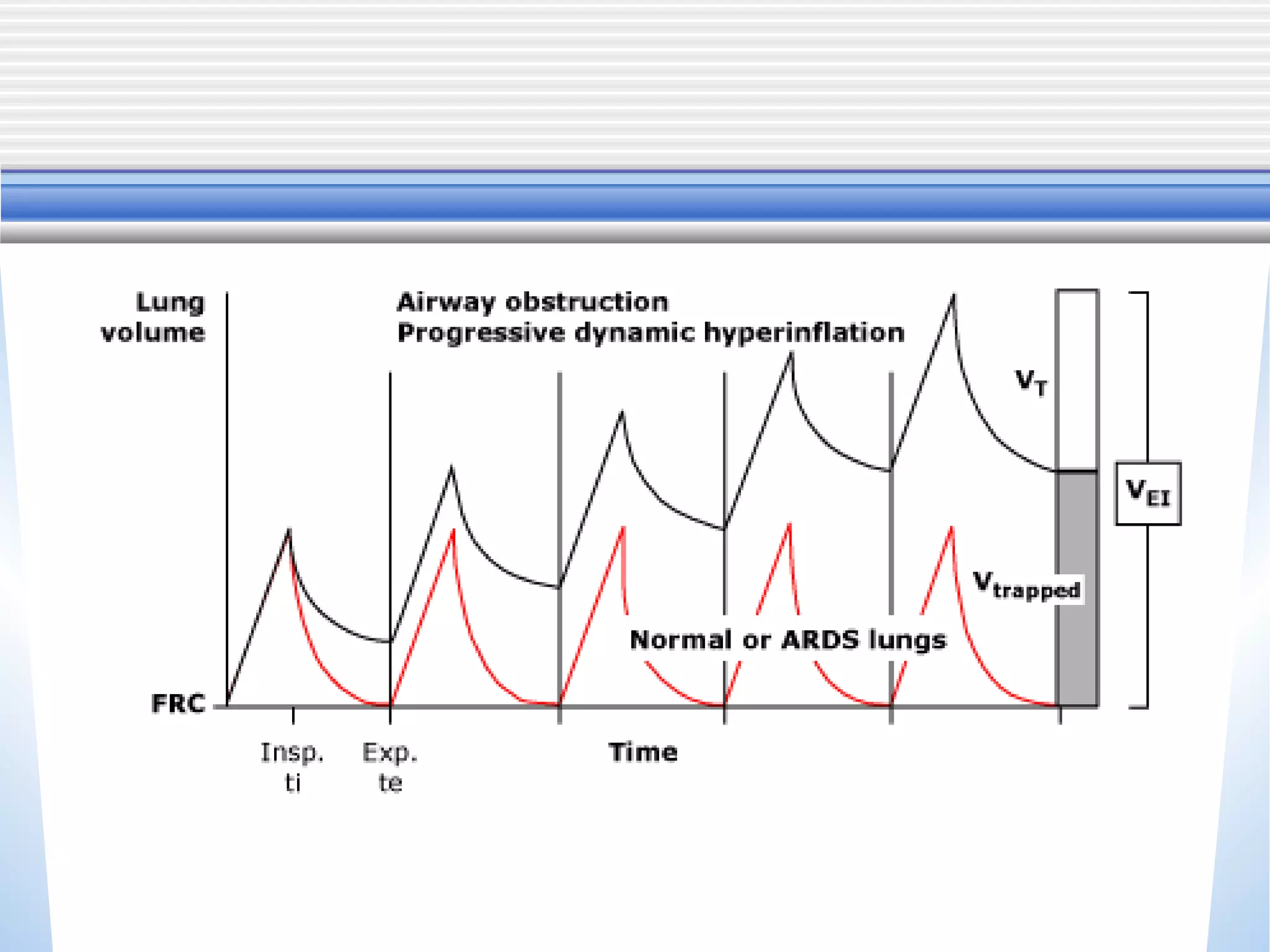
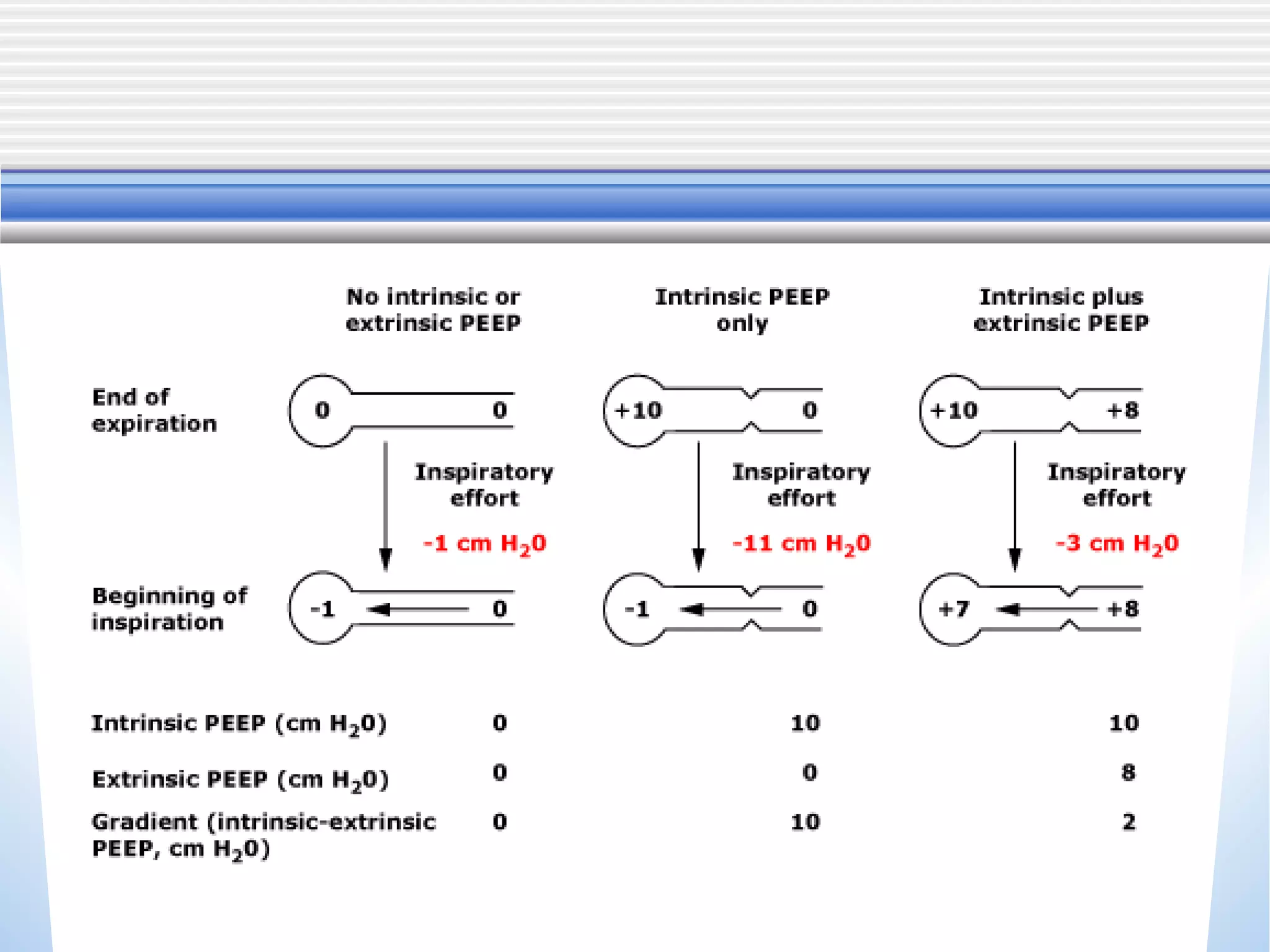
1) Mechanical ventilation may be required for severe, life-threatening asthma to prevent respiratory failure and death. Non-invasive ventilation can be tried initially but intubation may be needed.
2) Permissive hypercapnia is recommended to avoid additional lung injury from mechanical ventilation, allowing CO2 levels up to 90 mmHg if oxygenation is adequate. Sedation and sometimes paralysis are used while ventilating to reduce lung injury.
3) Weaning from mechanical ventilation begins with spontaneous breathing trials once the patient's CO2 levels normalize at a low ventilation rate and airway resistance decreases. Rescue therapies like ECMO may be required in rare cases that do not respond to usual treatments.