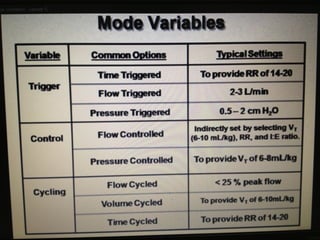
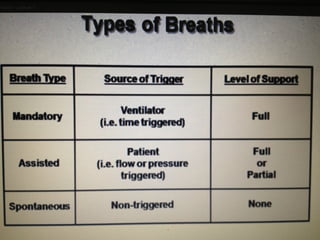
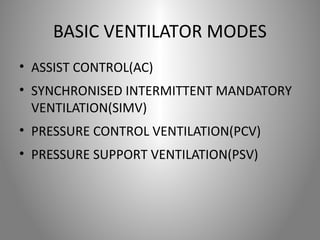
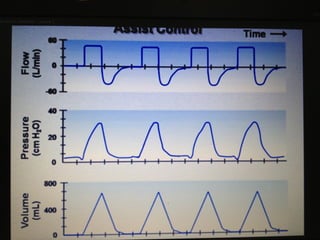
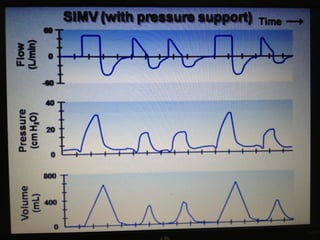
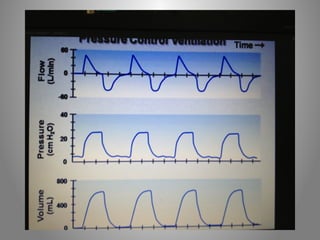
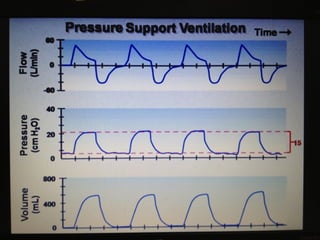
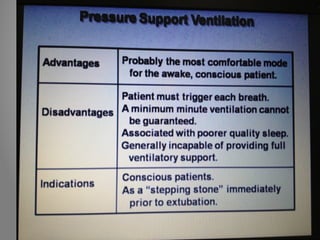
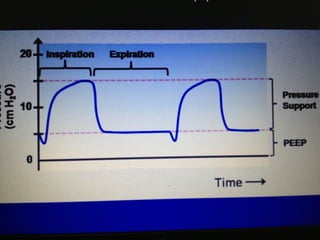
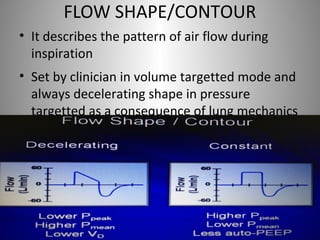
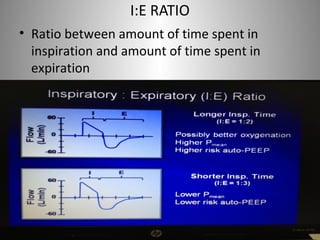
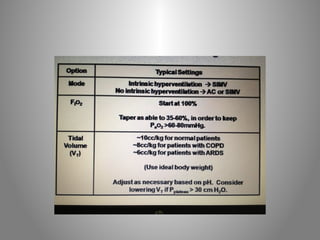
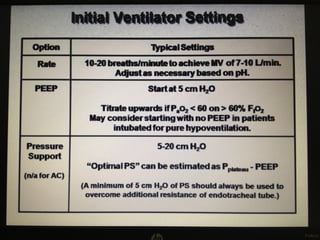
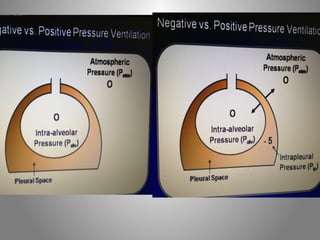
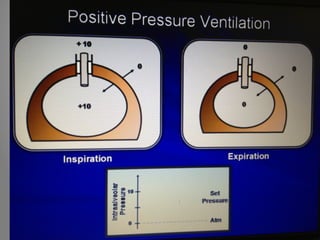
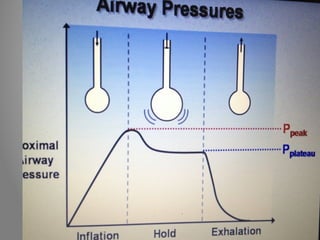
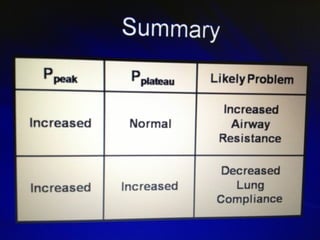
Mechanical ventilation is a therapeutic method that uses physical devices to assist or replace spontaneous breathing. There are two main types: negative pressure ventilation which applies pressure lower than atmospheric to the chest, and positive pressure ventilation which applies pressure higher than atmospheric to the lungs. Positive pressure ventilation is more commonly used today. It is important to carefully monitor patients on mechanical ventilation to optimize ventilation and prevent lung injury, through monitoring pressures, volumes, oxygen levels and CO2 levels. The goals are to provide adequate gas exchange while applying the lowest possible pressures and volumes to the lungs.













![Normal gas exchange
• Most important is to calculate (A-a)gradient
• It measure how effectively oxygen moves
from the alveoli into pulmonary vasculature
• Normal (A-a)gradient=[age/4]+4
• When there is increase in(A-a)gradient the
possible causes](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/mechanicalventilation-141014225754-conversion-gate02/85/Mechanical-ventilation-ppt-21-320.jpg)