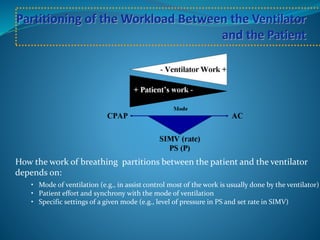
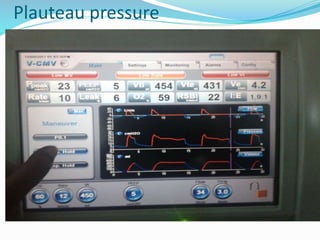
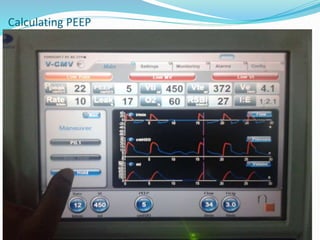
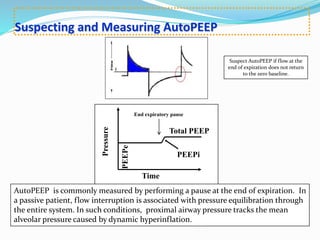
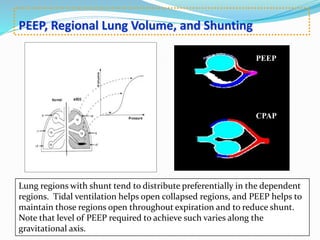
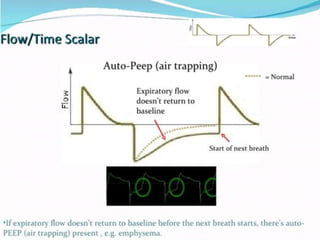
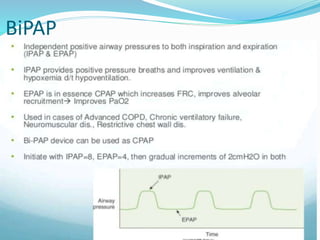
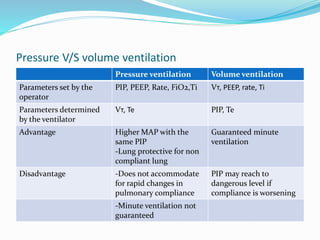
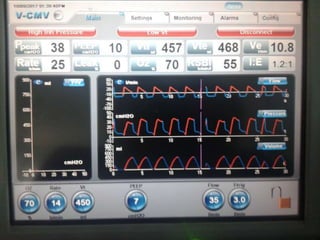
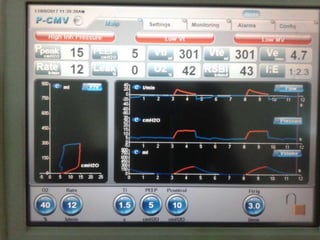
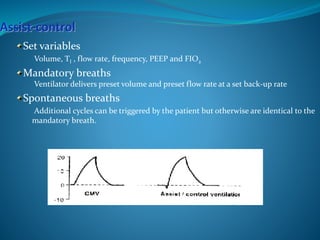
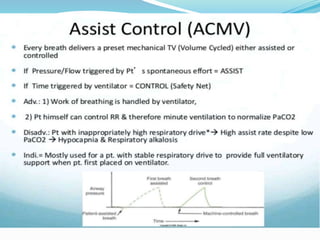
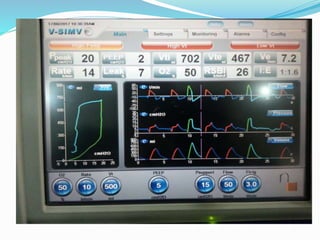
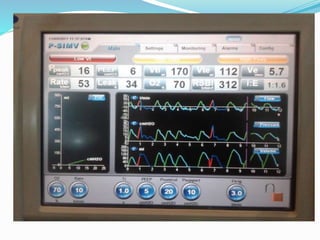
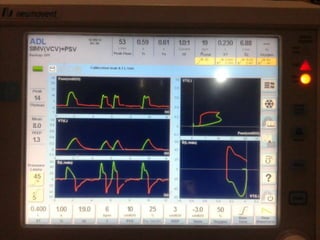
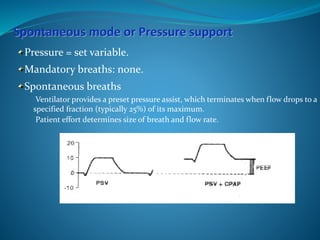
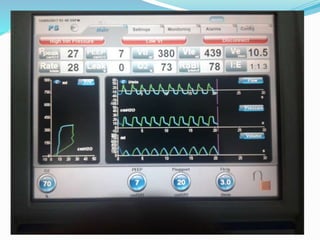
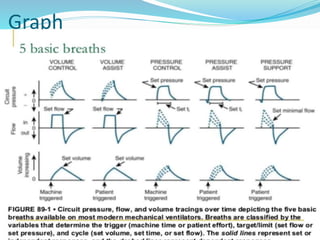
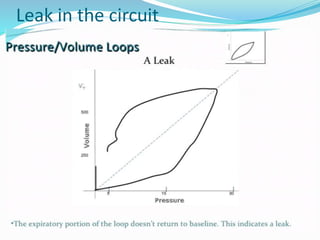
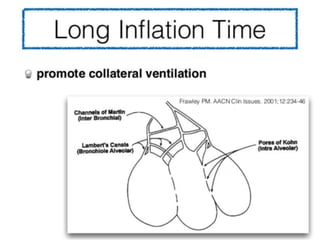
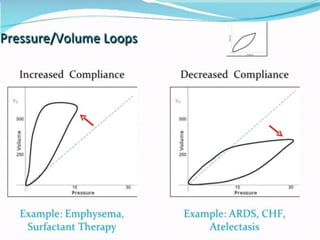
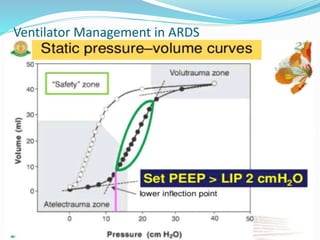
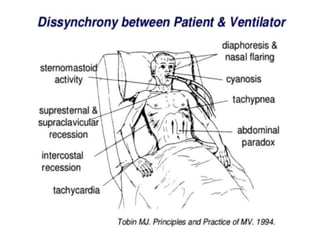
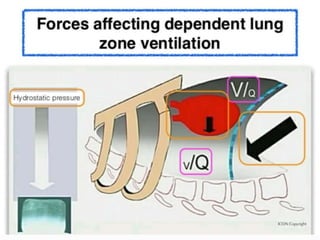
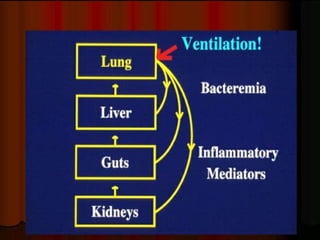
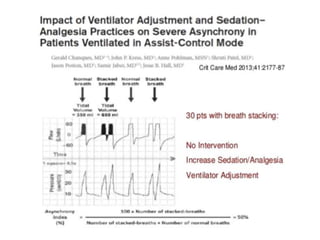
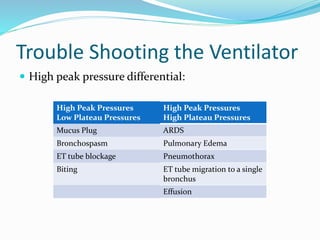
This document provides an overview of mechanical ventilation including definitions, modes, settings, and management. It discusses non-invasive ventilation techniques like CPAP and BiPAP as well as various modes of invasive ventilation such as CMV, SIMV, and pressure support. Key variables, advantages, and disadvantages of different modes are explained. Graphs are presented to illustrate concepts like PEEP, auto-PEEP, and the relationship between pressure and volume ventilation. Management considerations for various disease states are also covered.