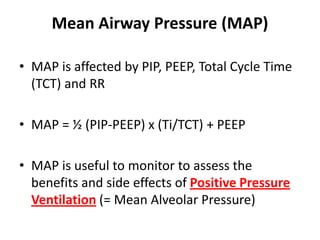
Monitoring of mechanical ventilation involves assessing pressure, flow, volume, and calculated and measured parameters. Calculated parameters include compliance, resistance, and time constants. Waveform analysis uses pressure, flow, and volume waveforms. Loops such as pressure-volume and flow-volume can be used to evaluate lung mechanics. Monitoring compliance, resistance, and loops can help determine the condition of the lungs.