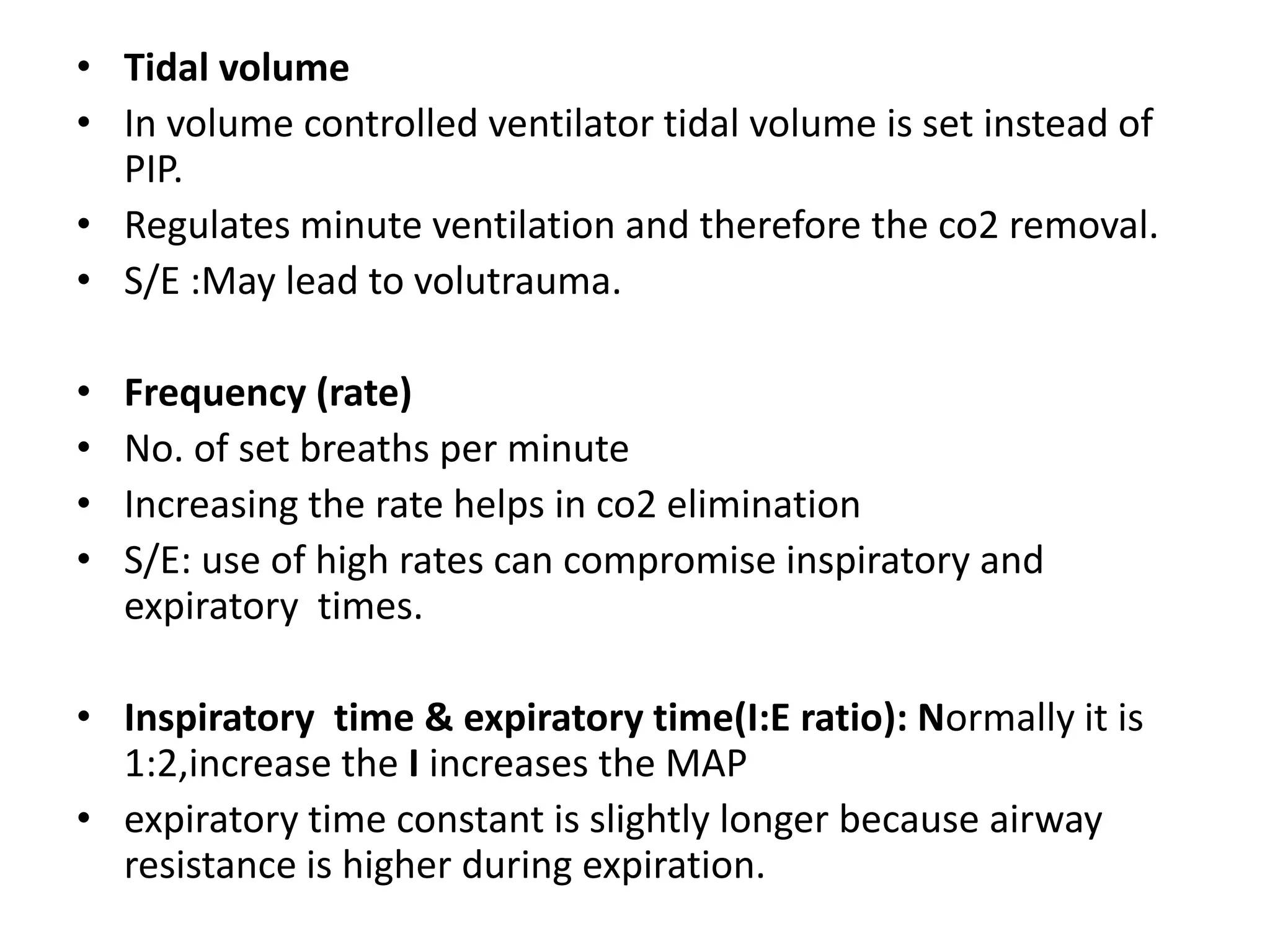
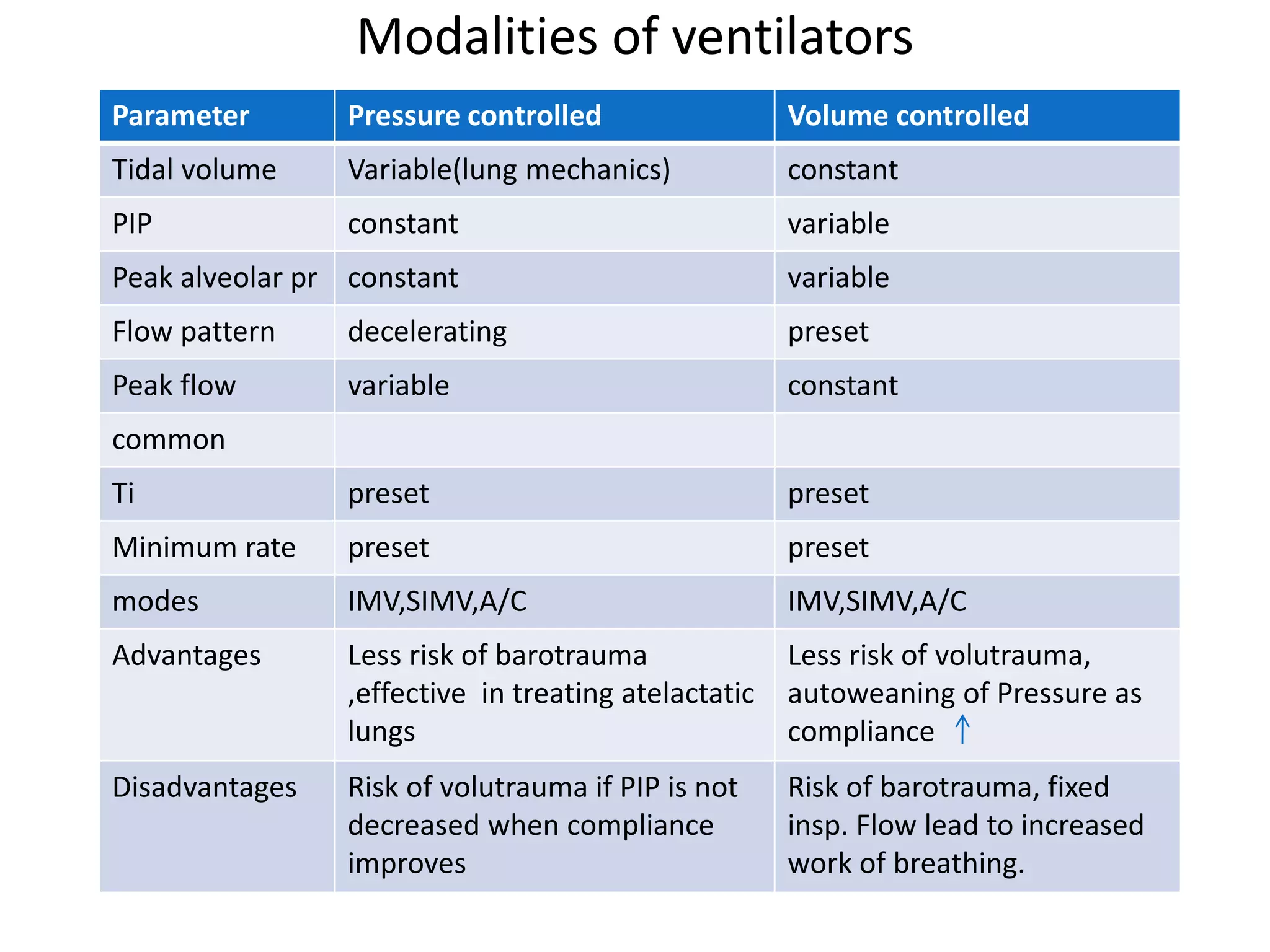
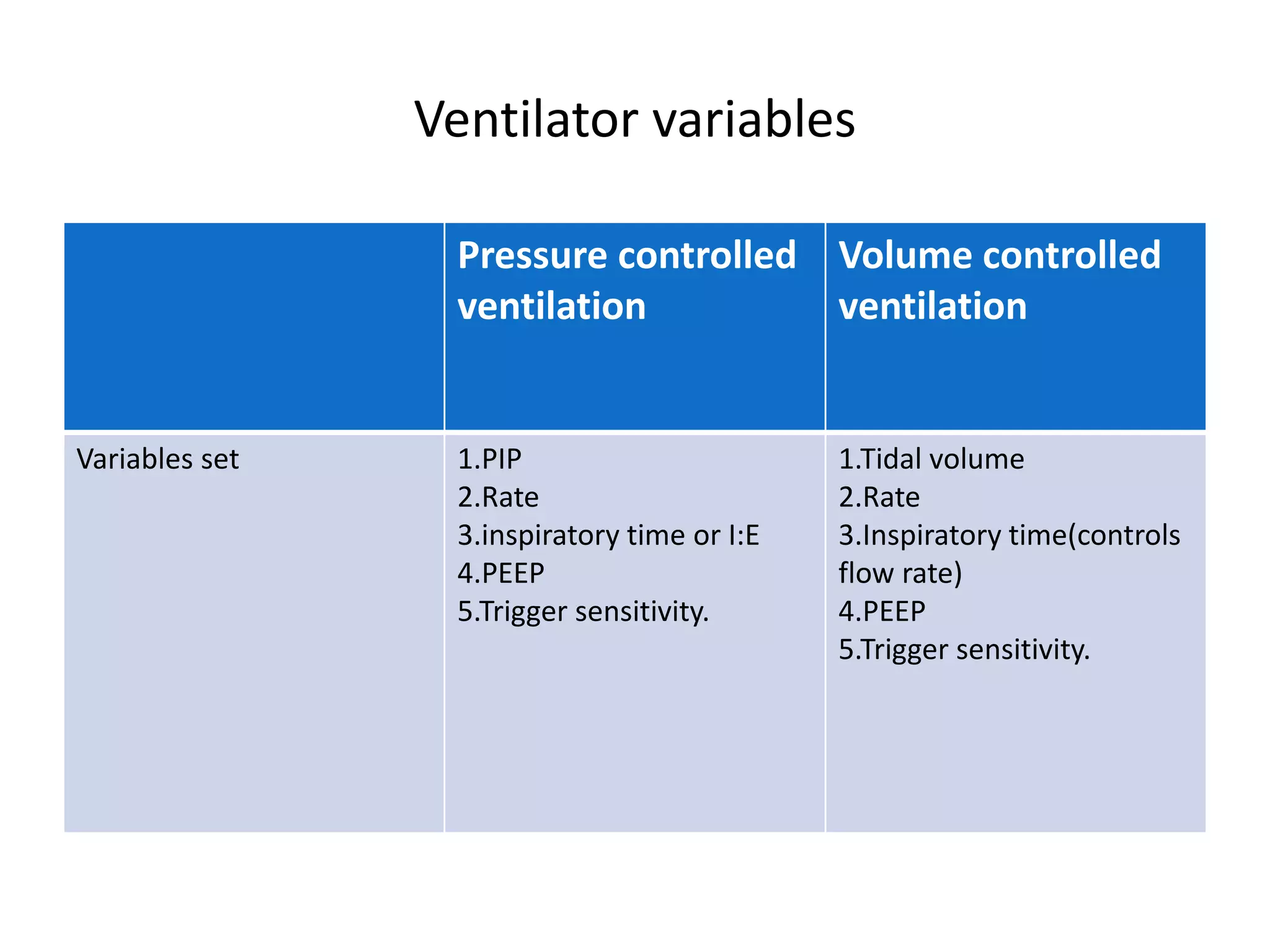
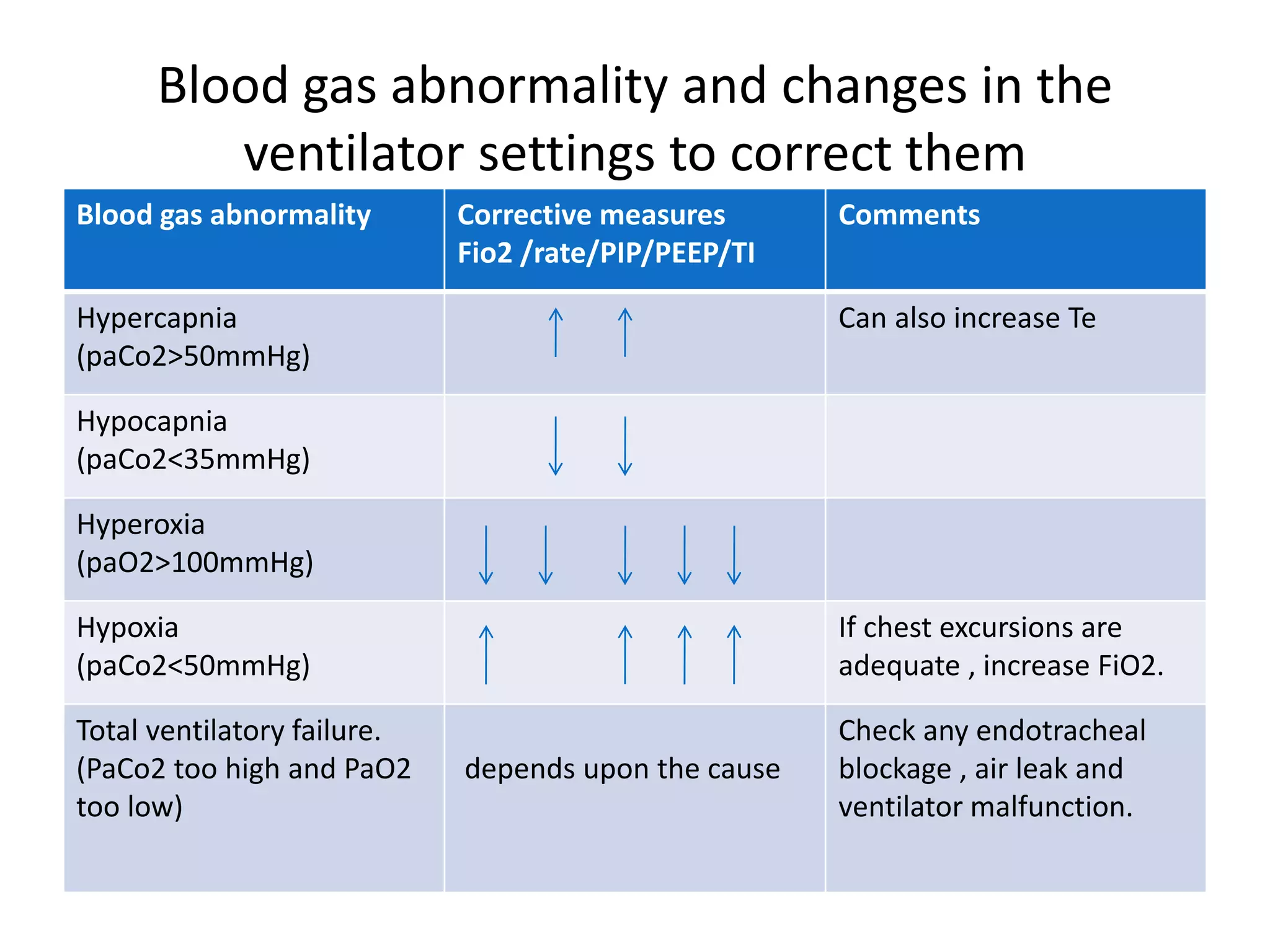
Mechanical ventilation is used to support gas exchange and clinical status in neonates. The goals are to maintain sufficient oxygenation and ventilation until the underlying disease resolves, while protecting the lungs from damage. Modes of ventilation include mandatory, SIMV, assist/control, and pressure support. Parameters like tidal volume, PIP, PEEP, and FiO2 are adjusted based on blood gas levels to optimize oxygenation and ventilation. Ventilator graphics and pulmonary monitoring are used to assess patient-ventilator interaction and guide management.