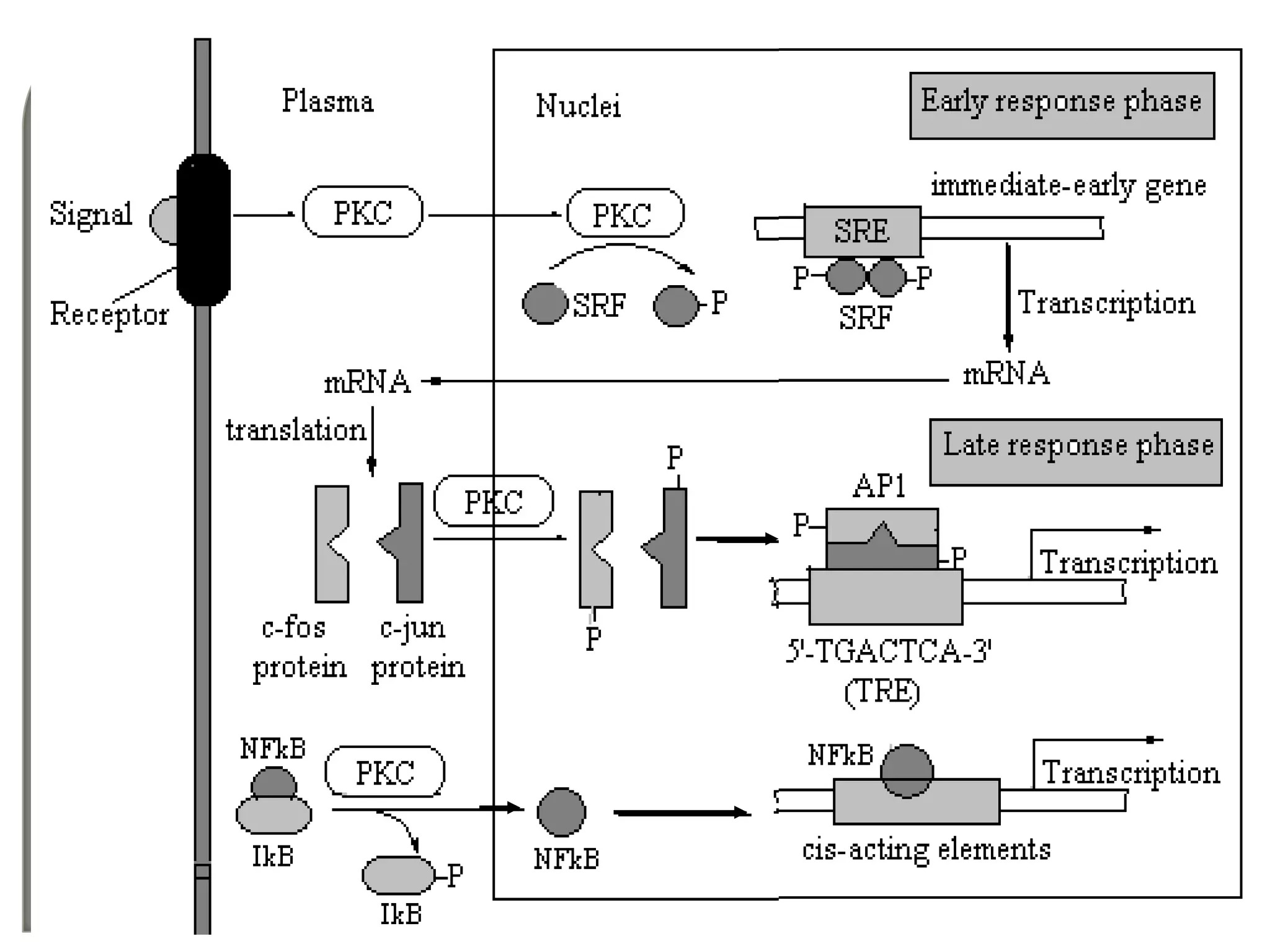
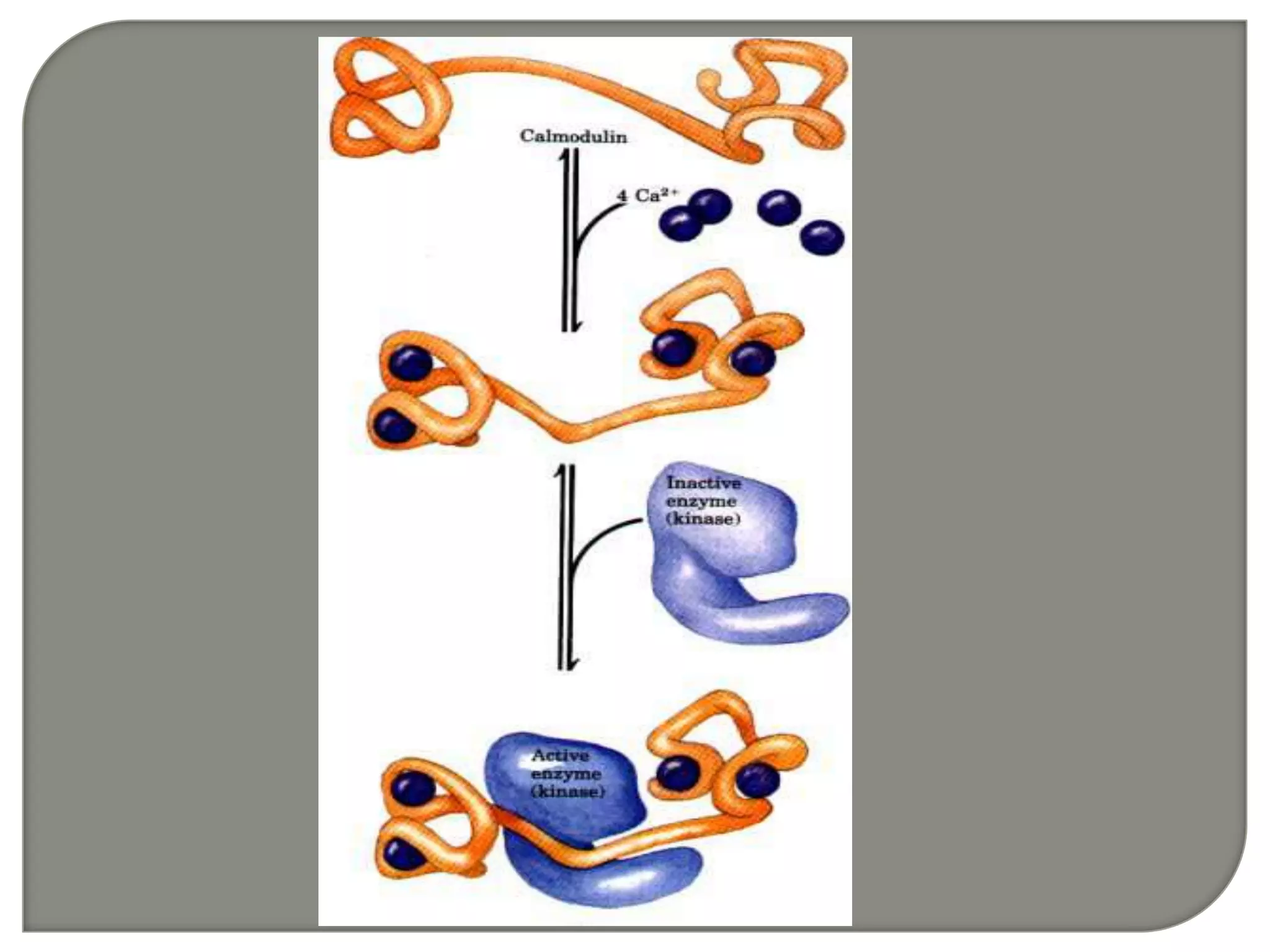
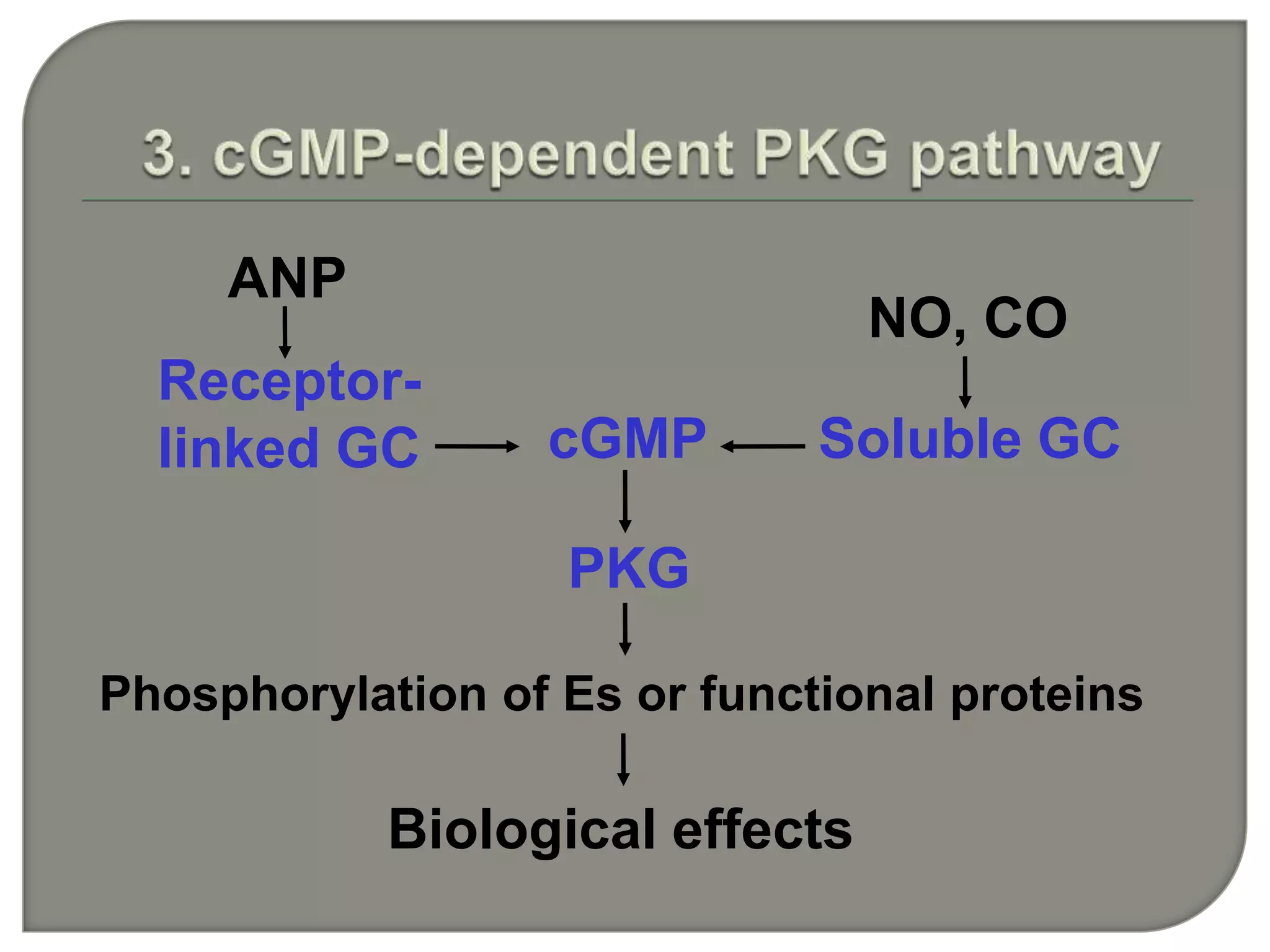
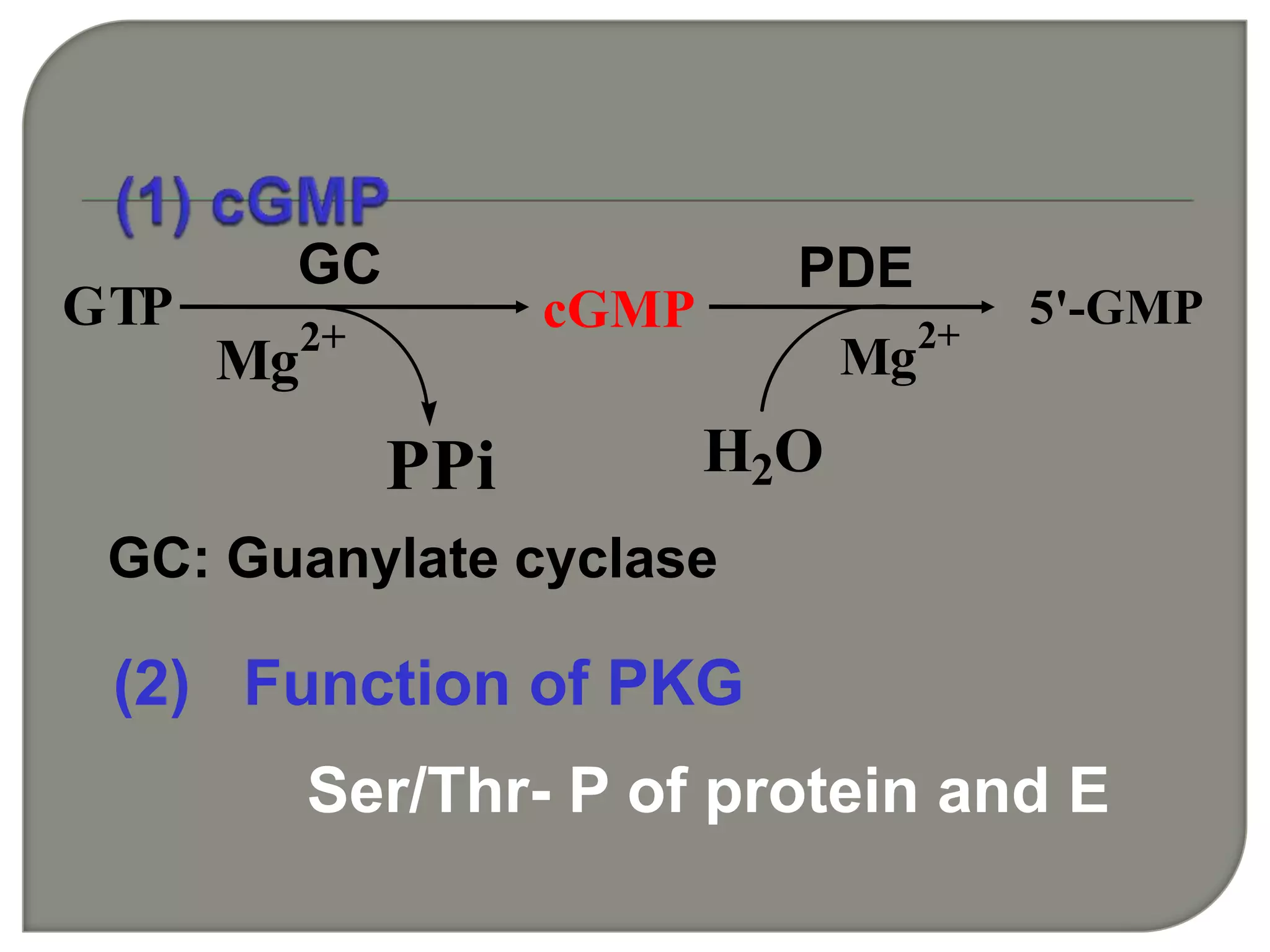
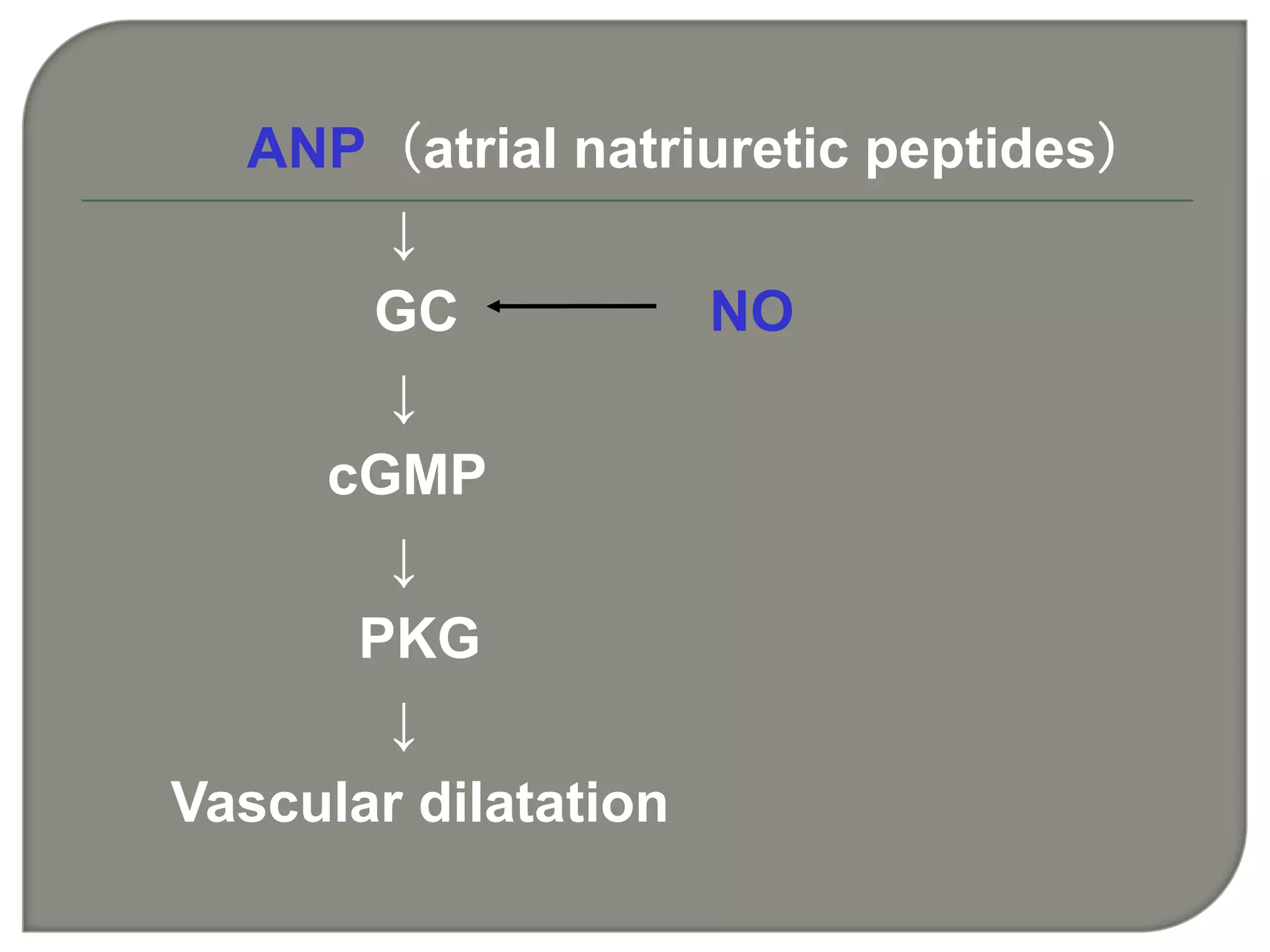
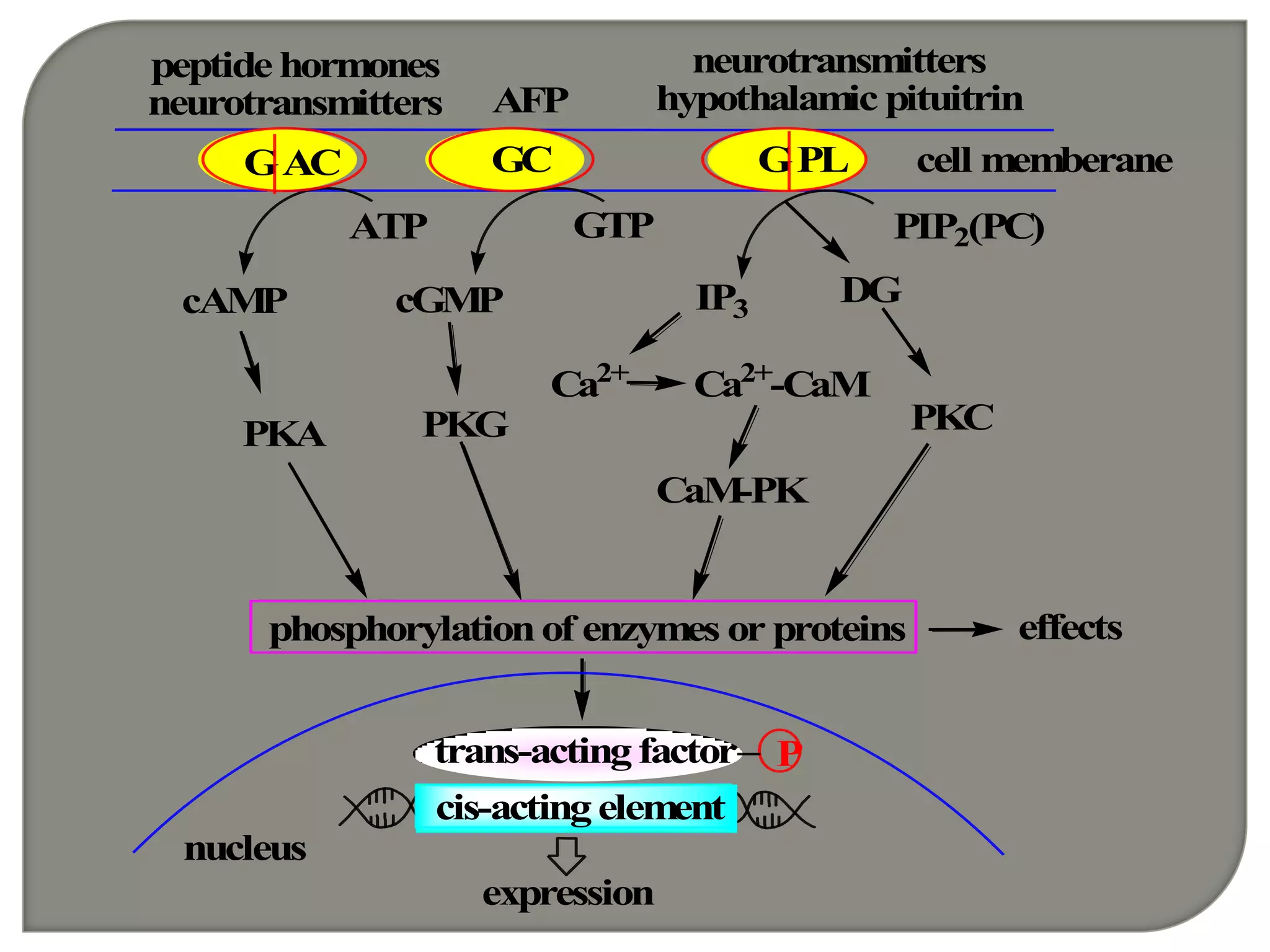
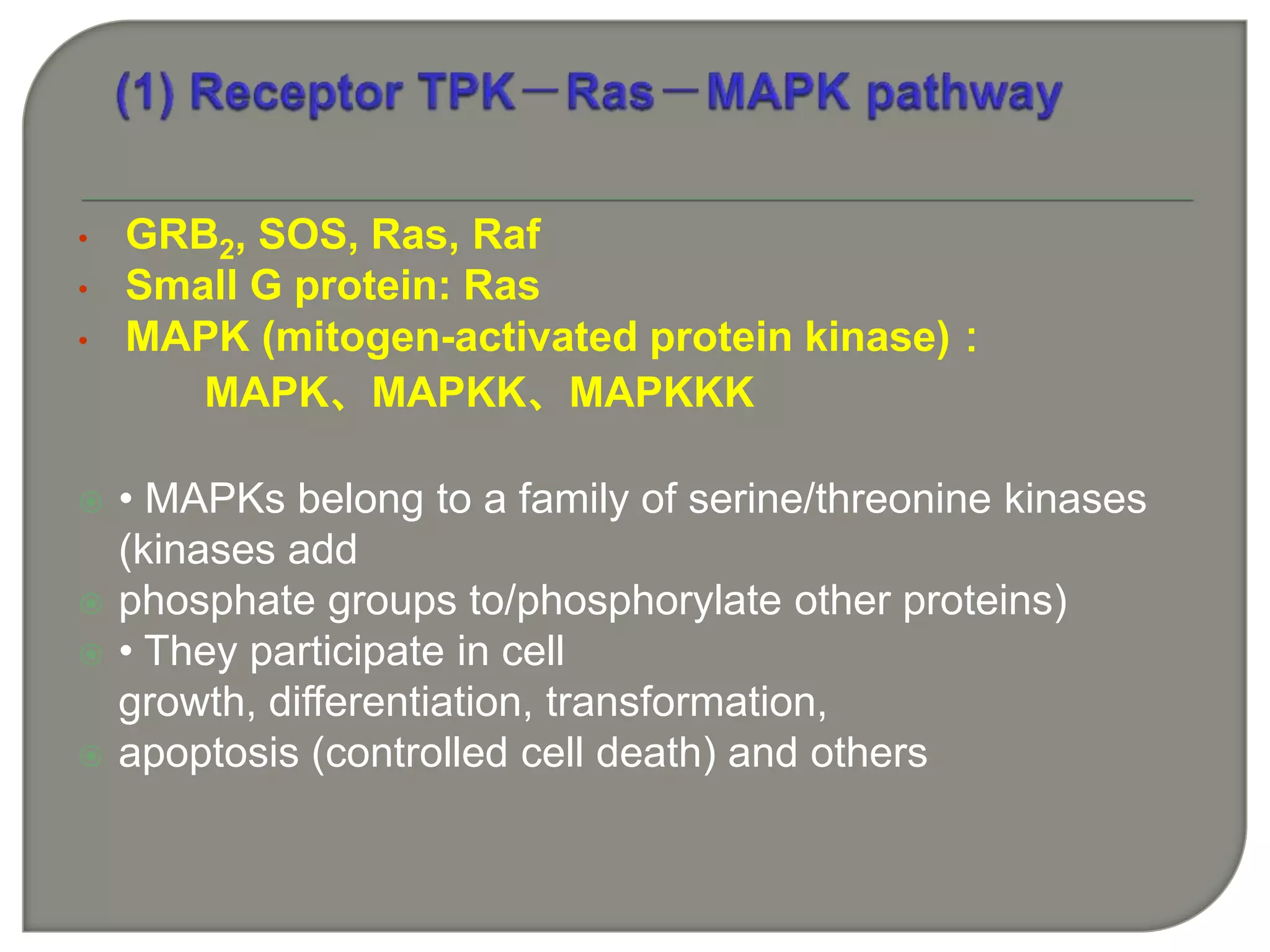
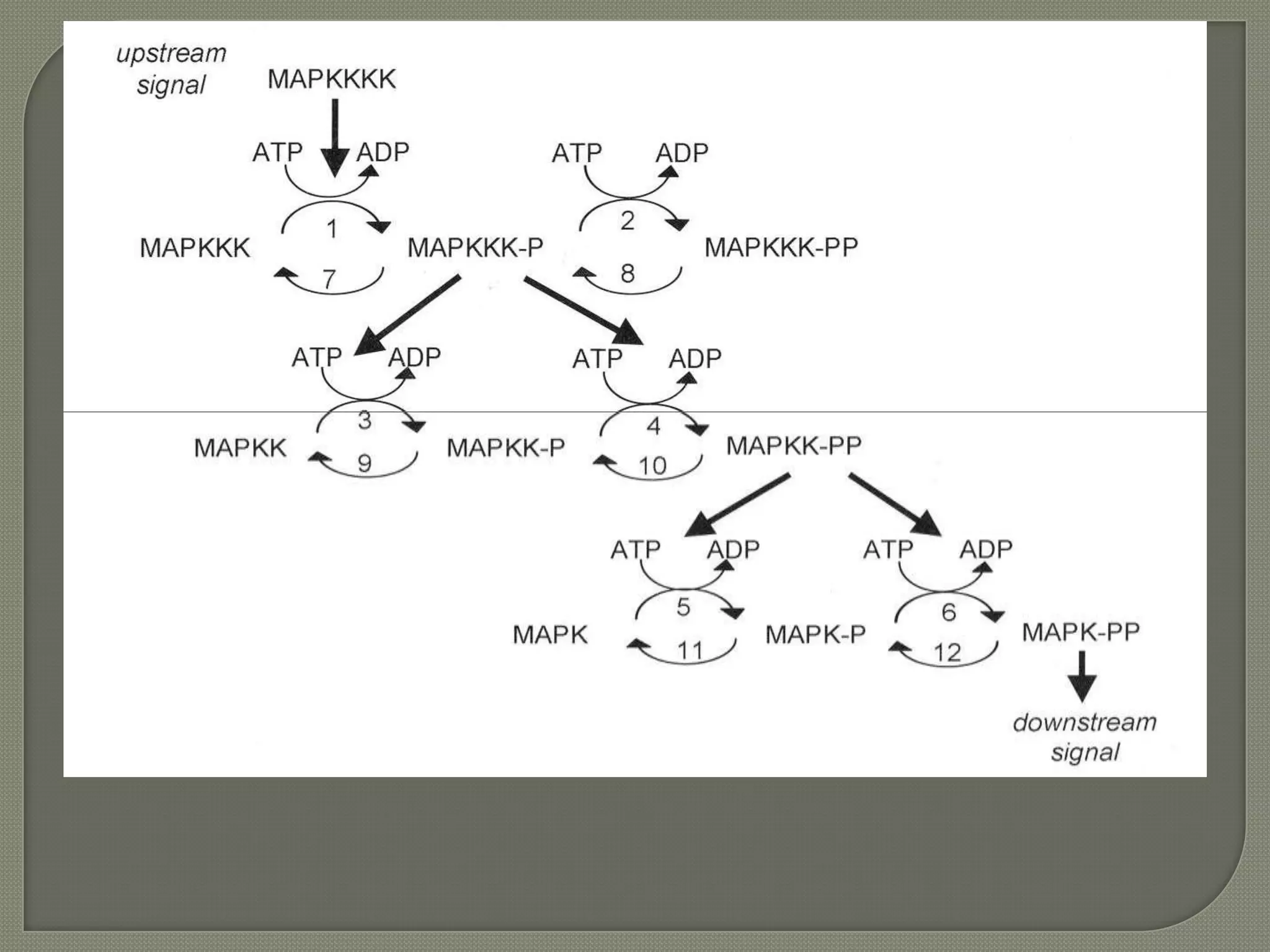
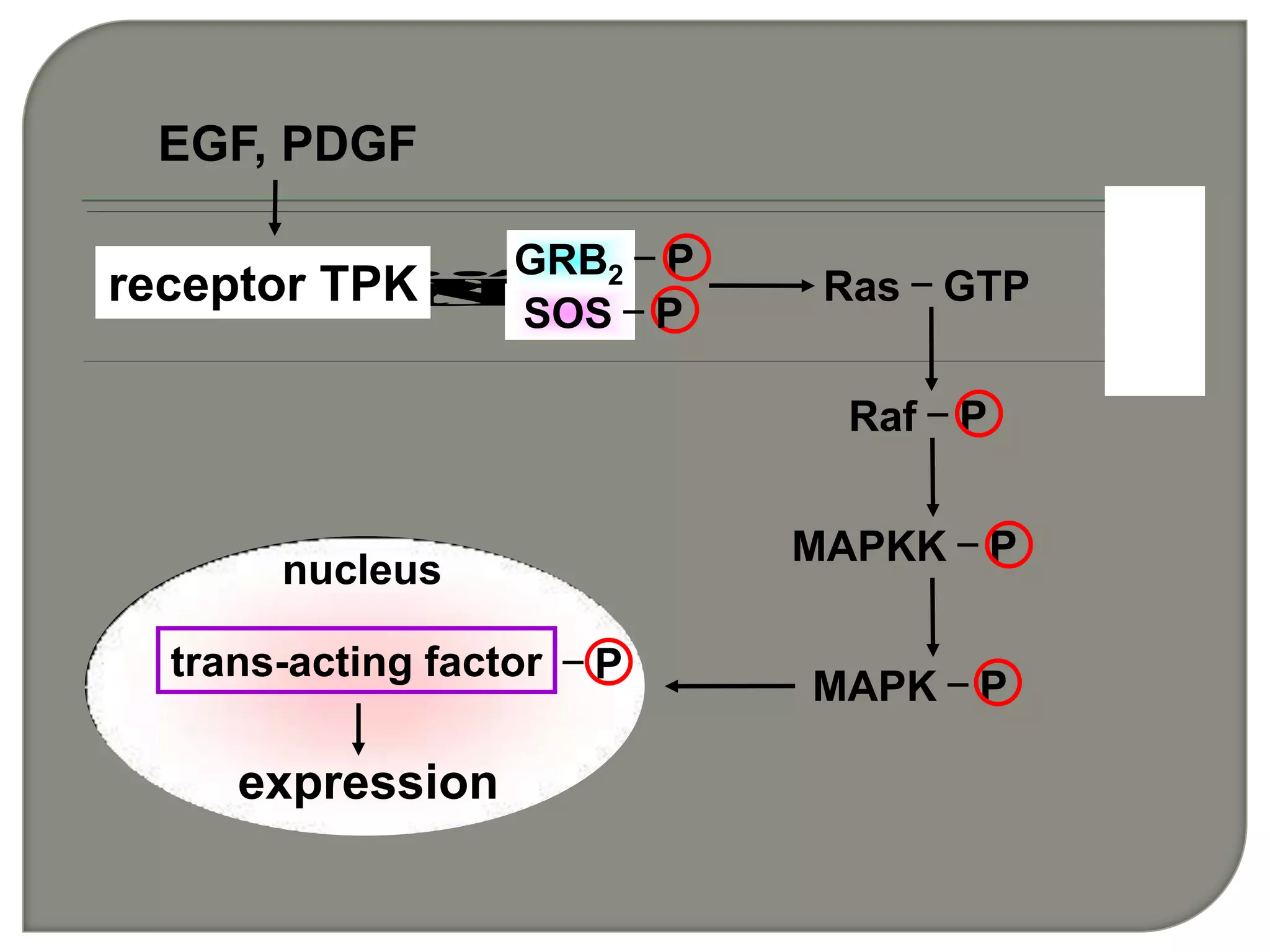
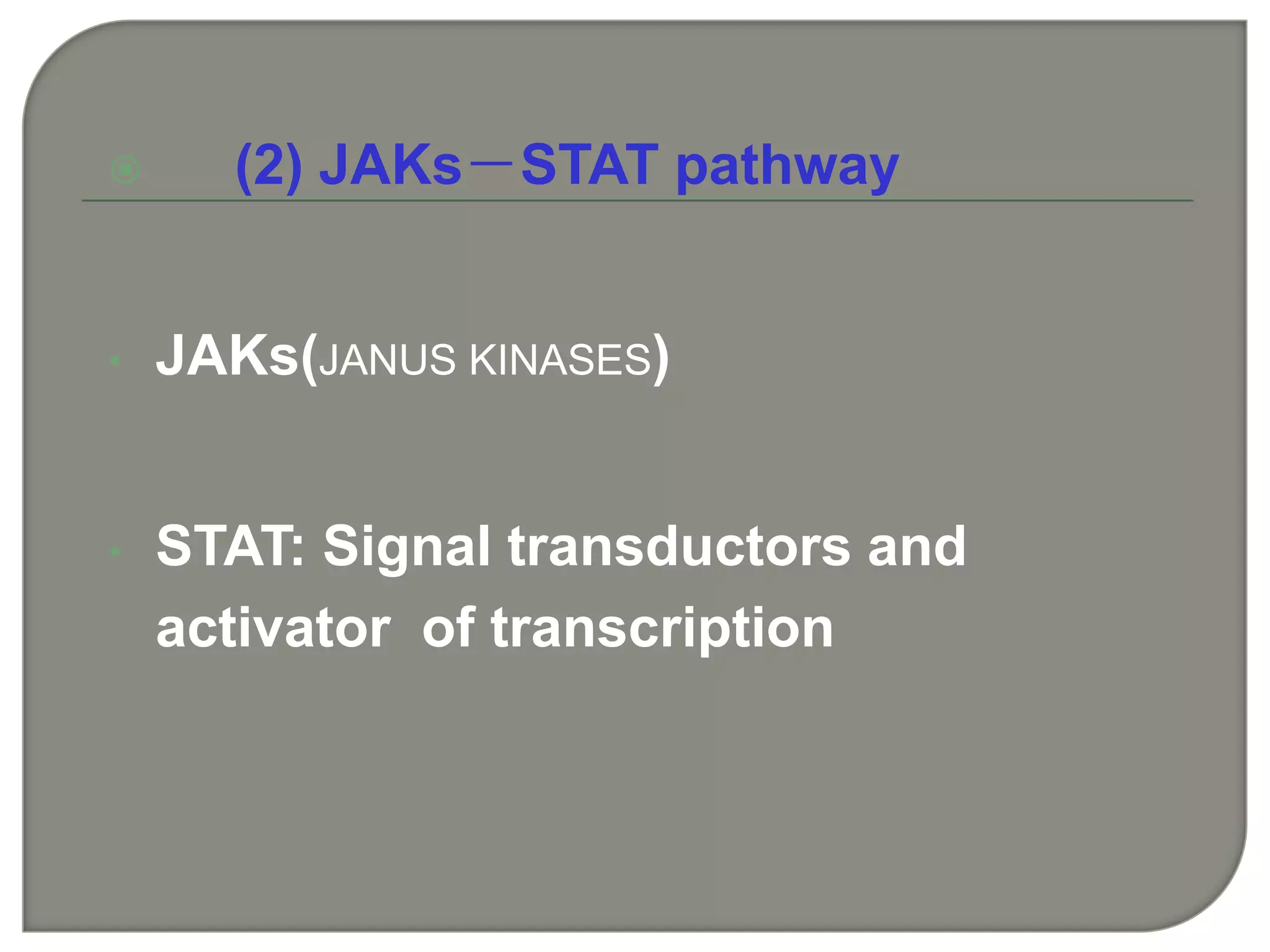
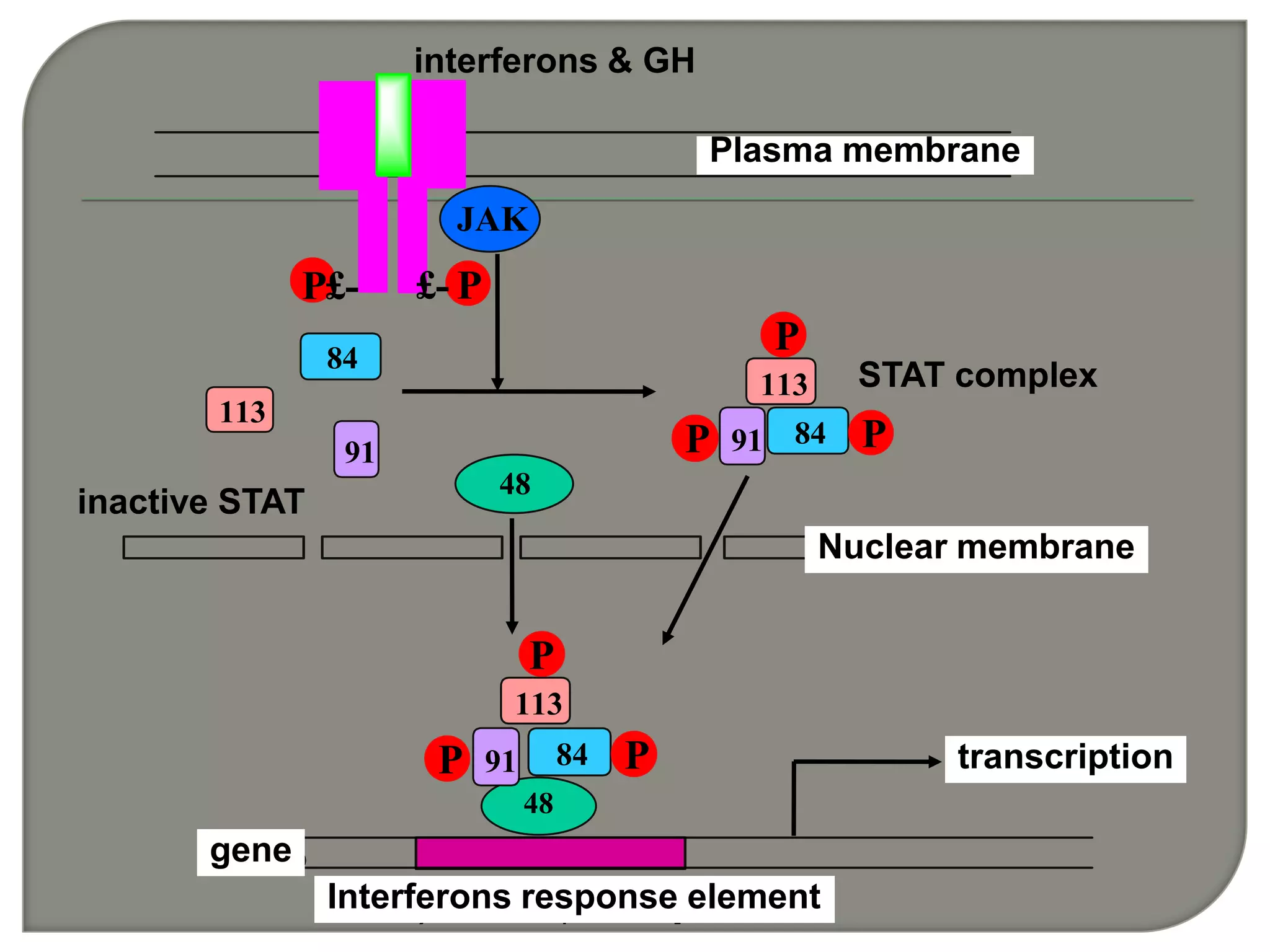
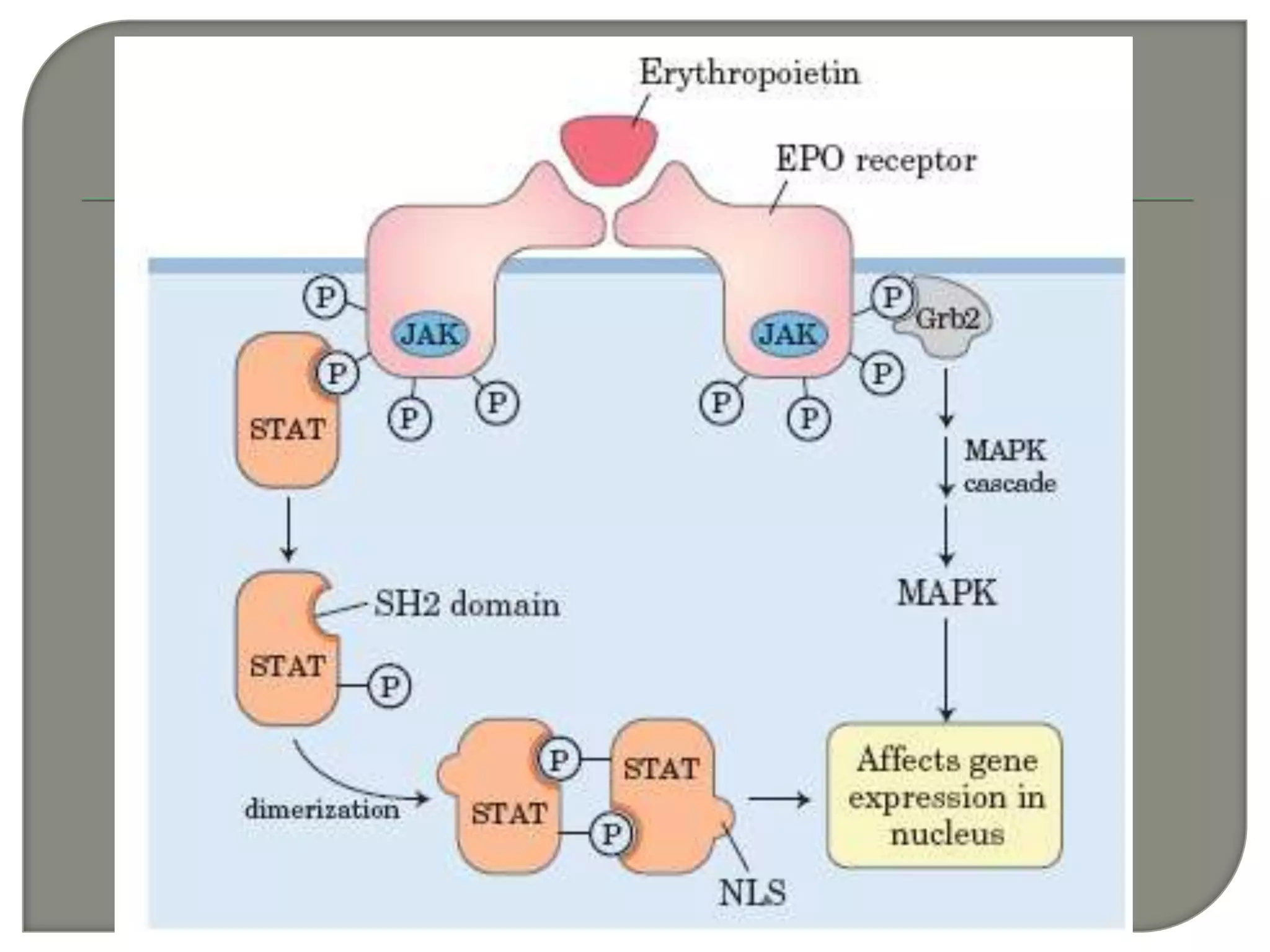
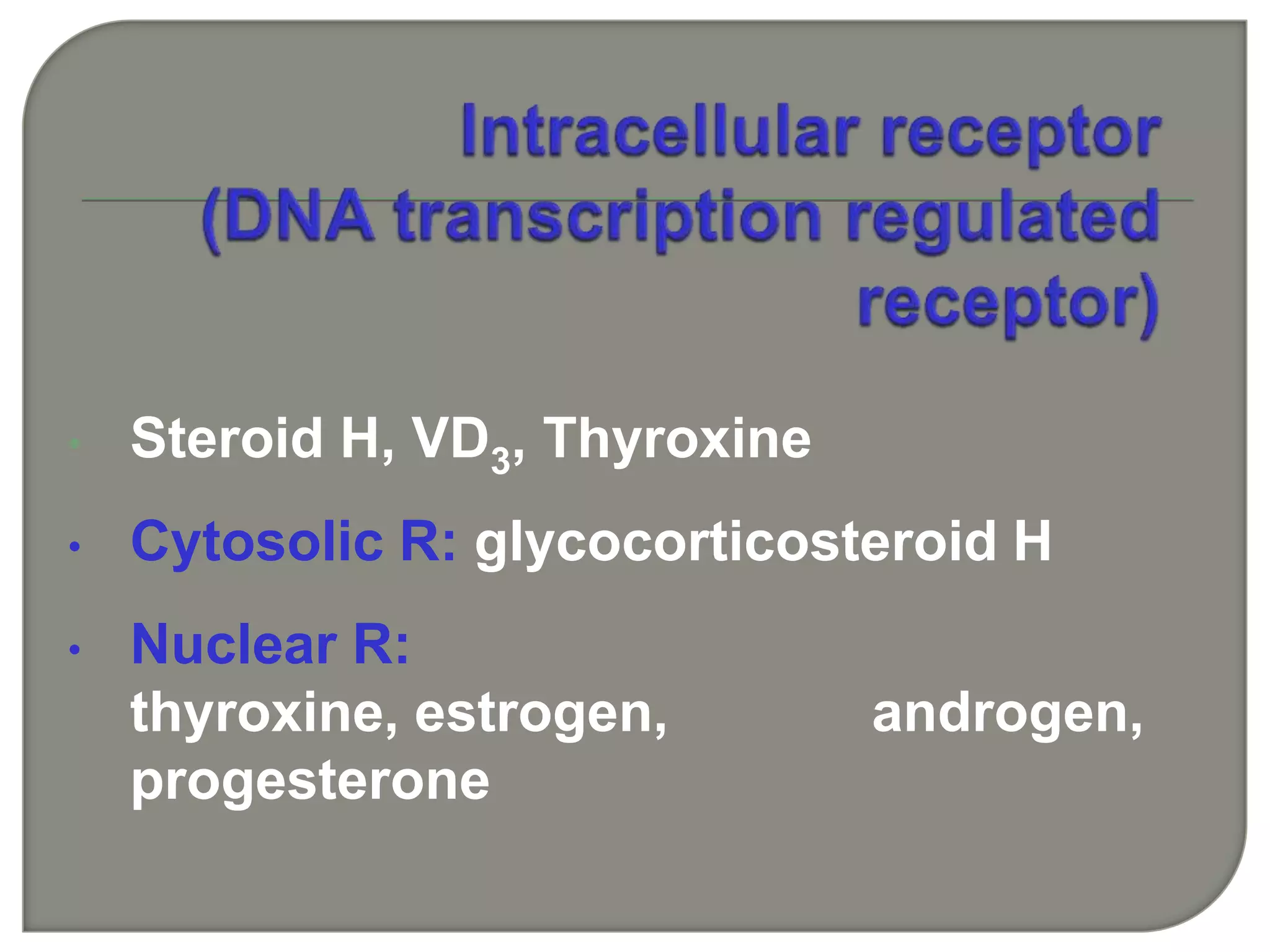
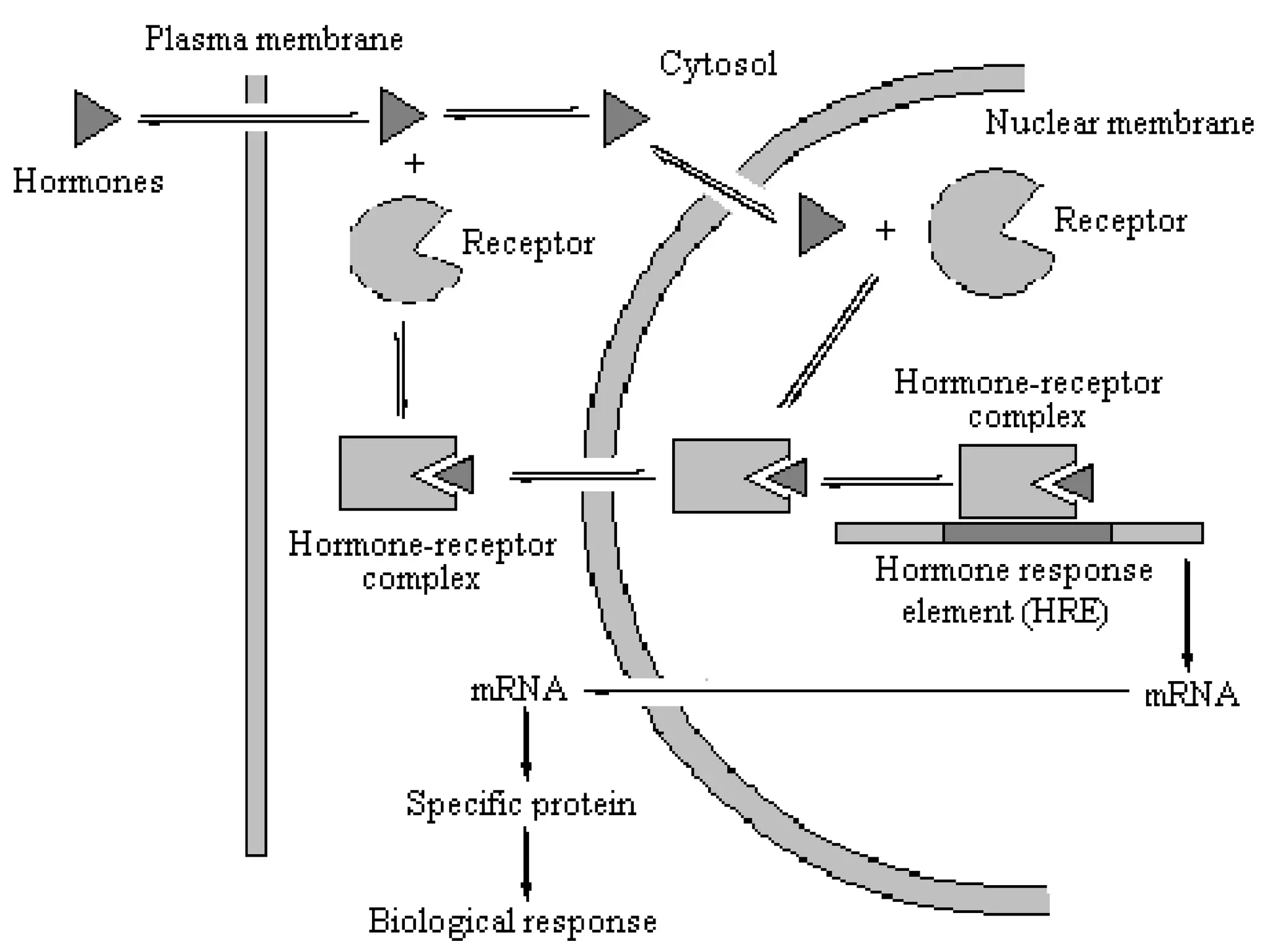
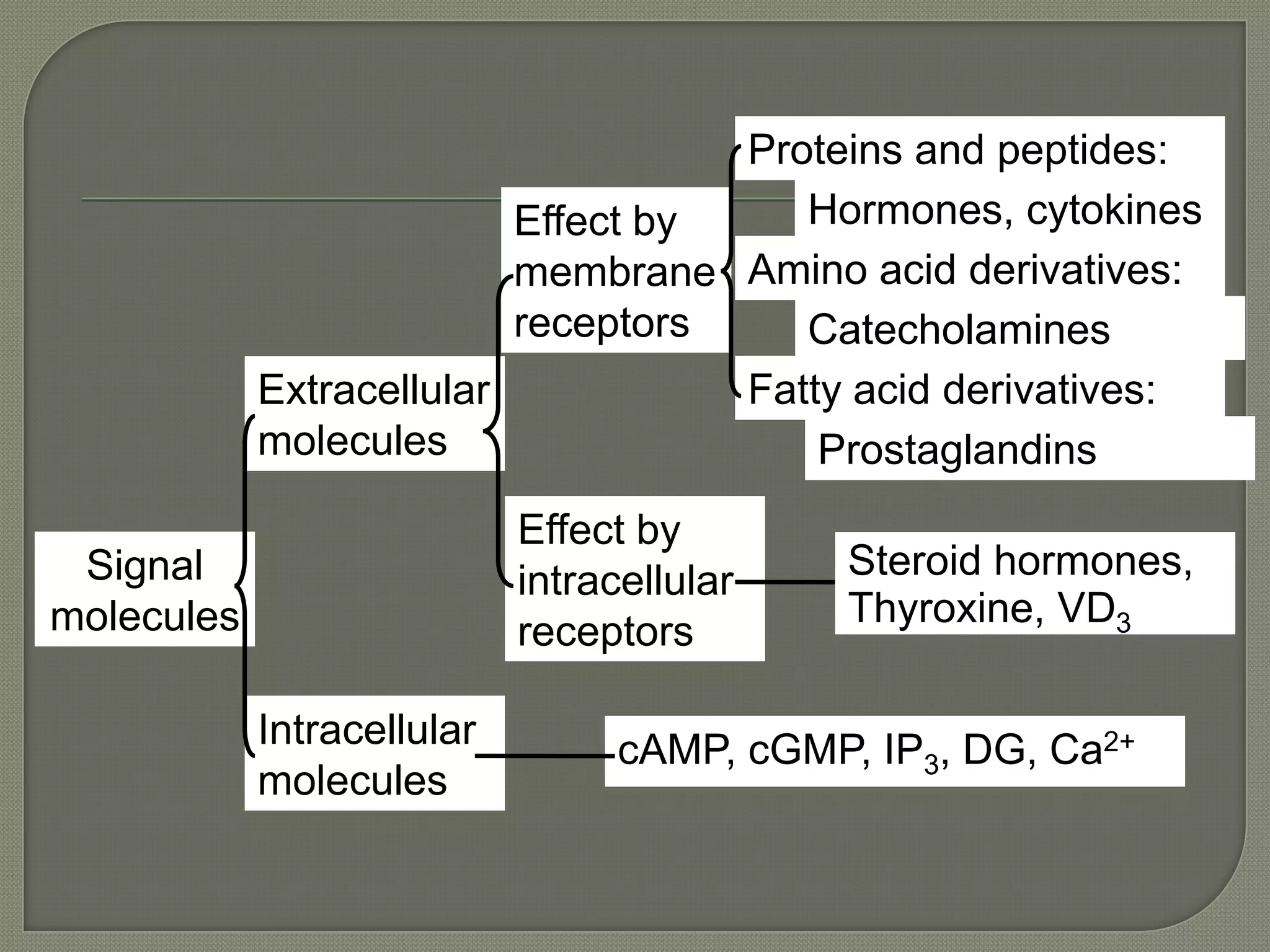
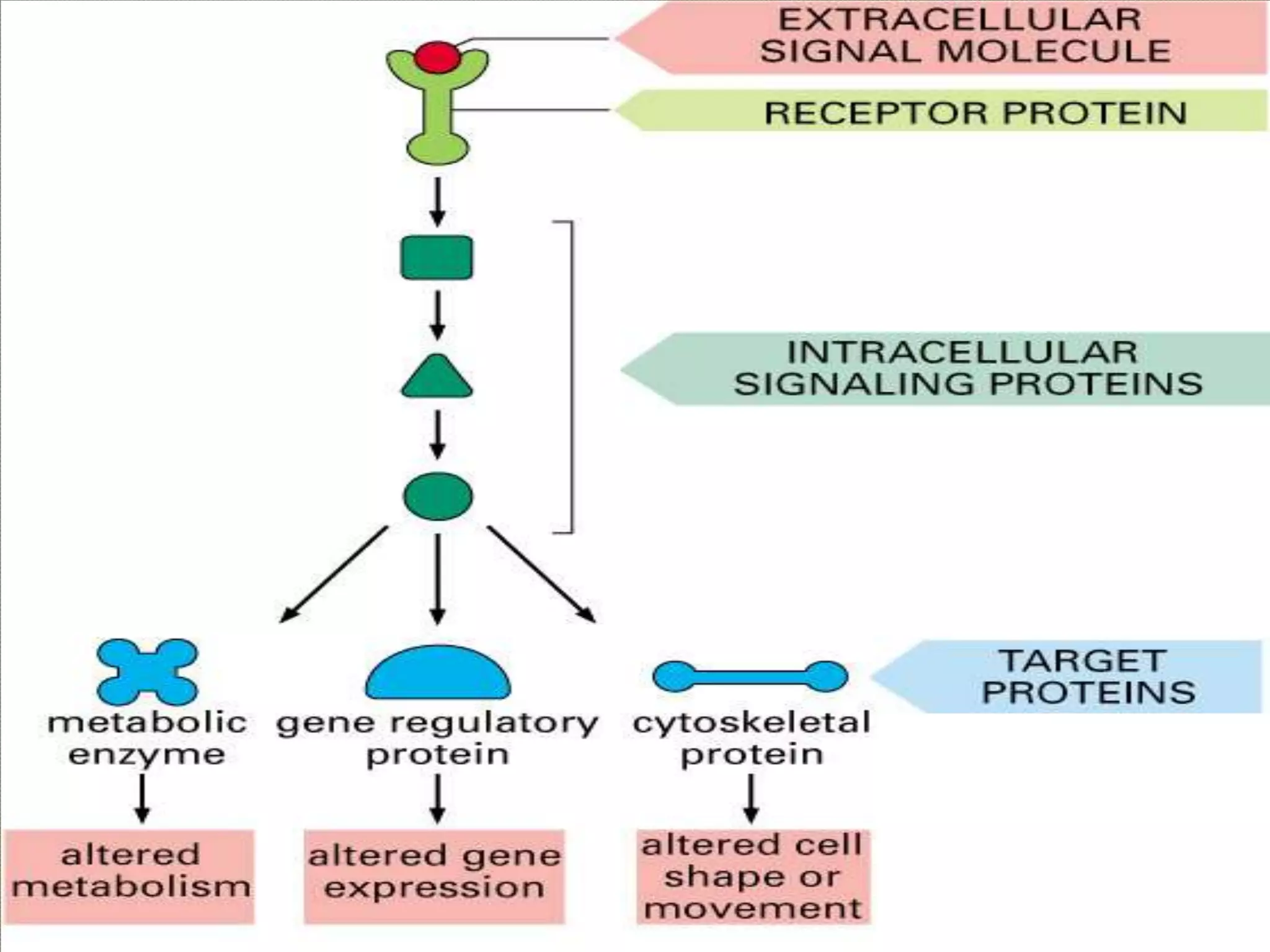
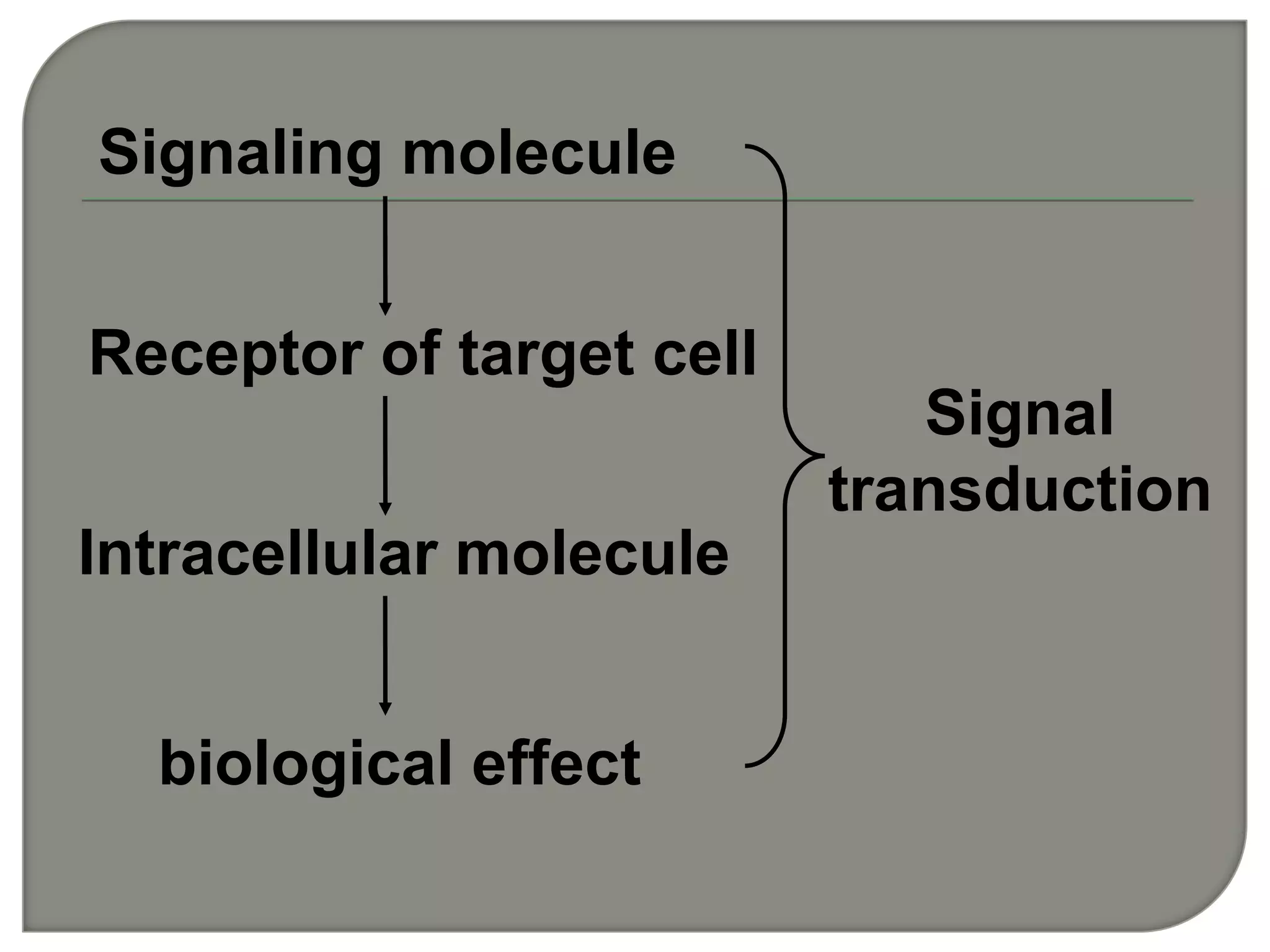
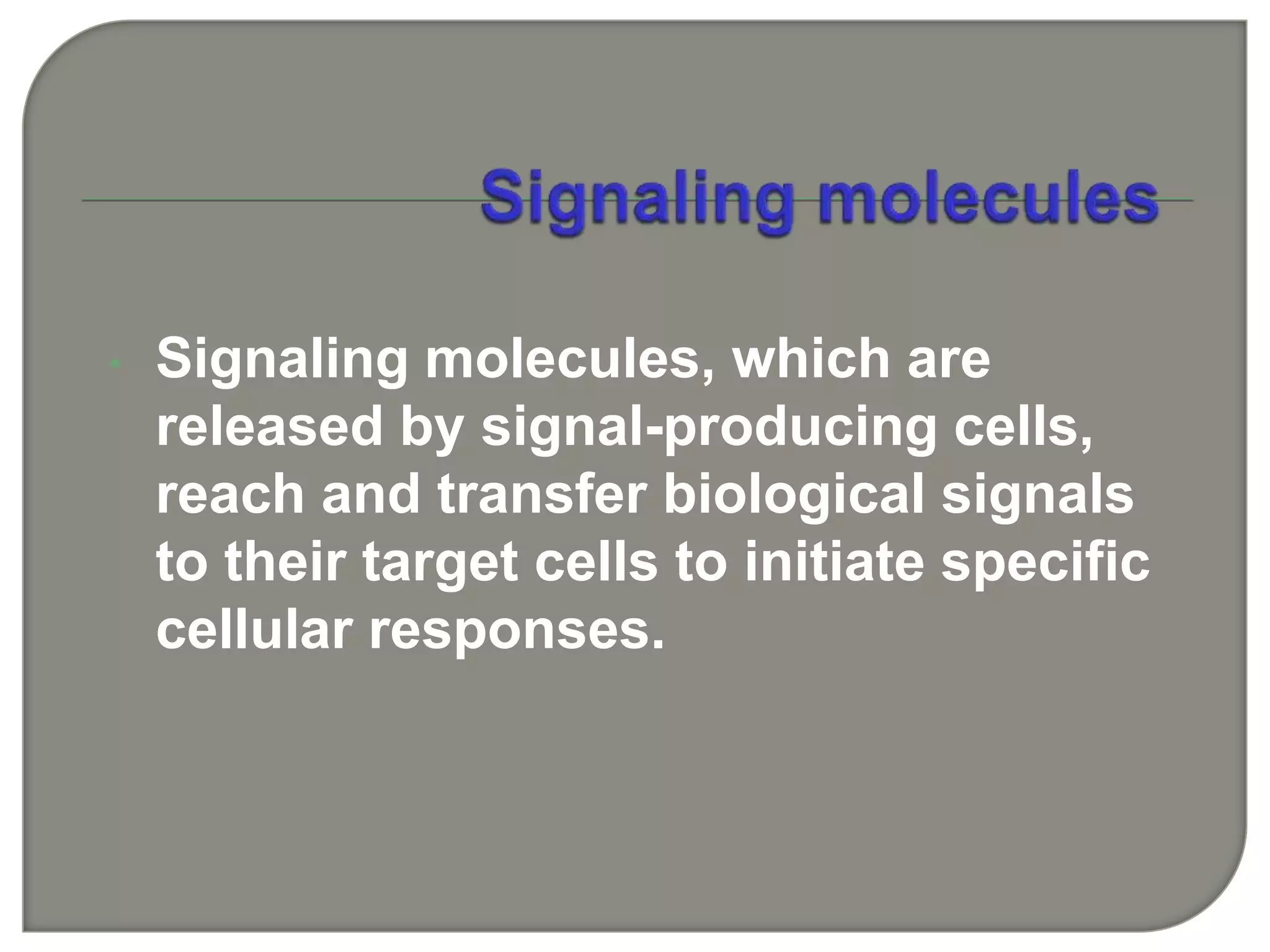
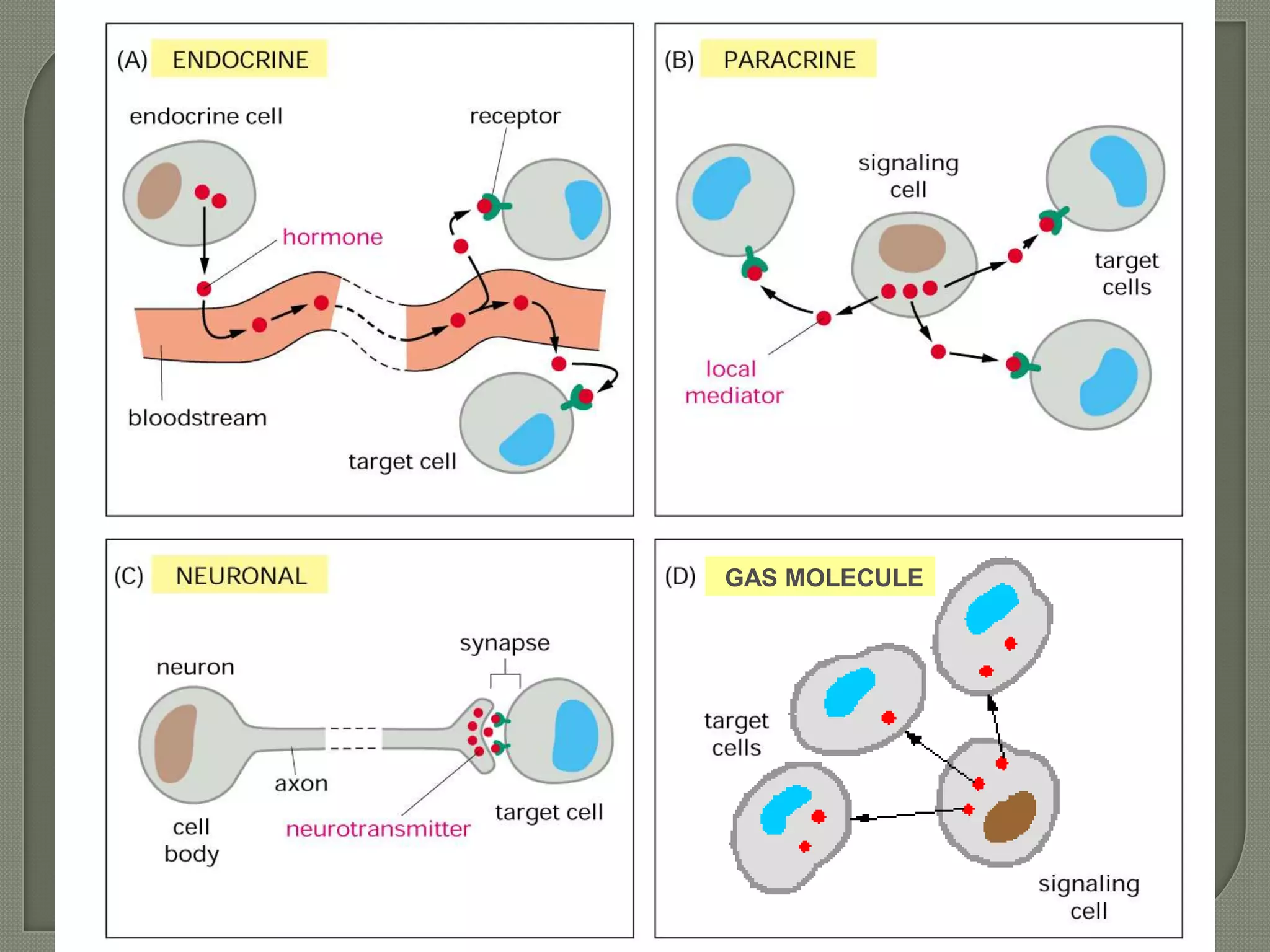
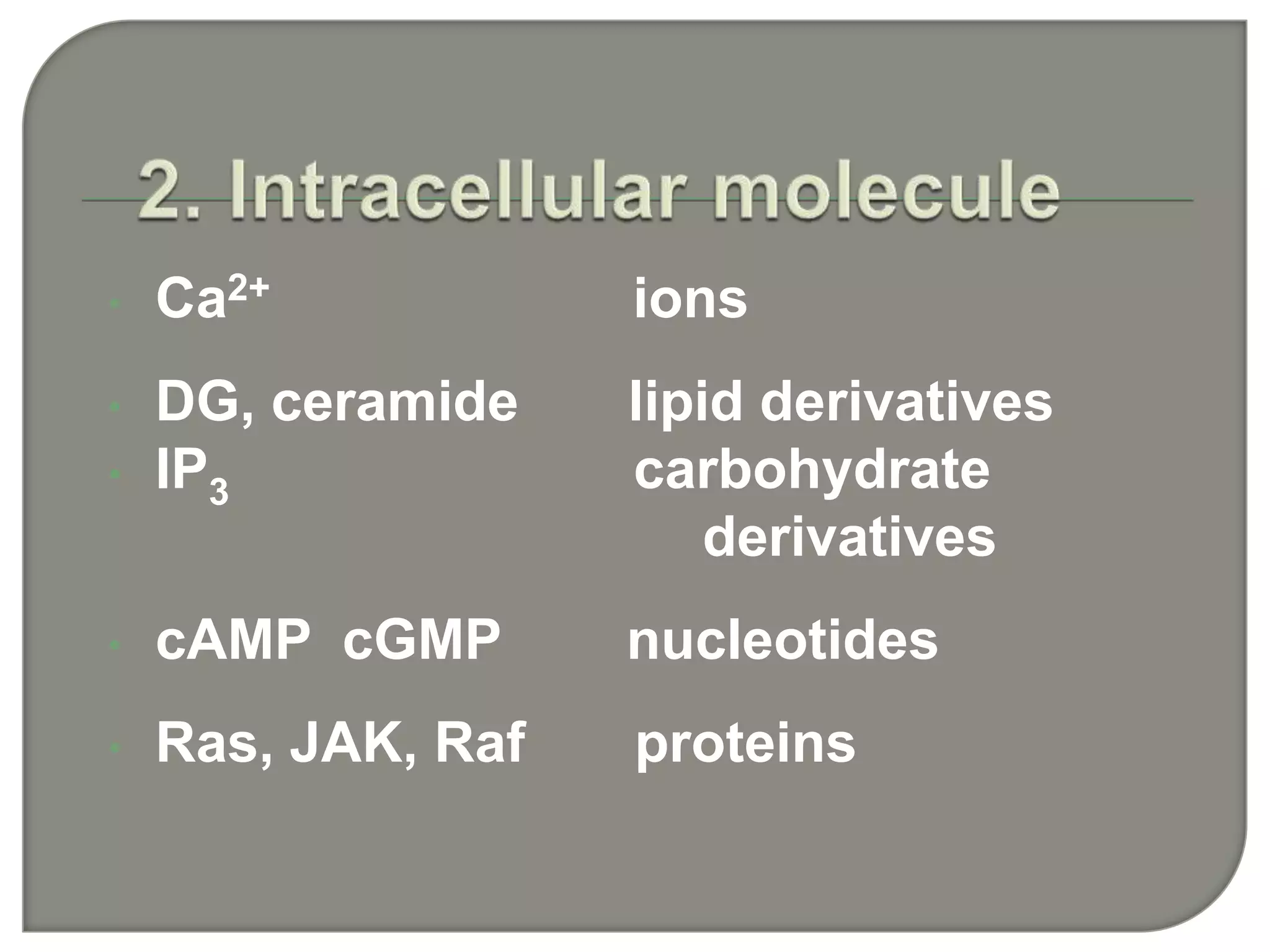
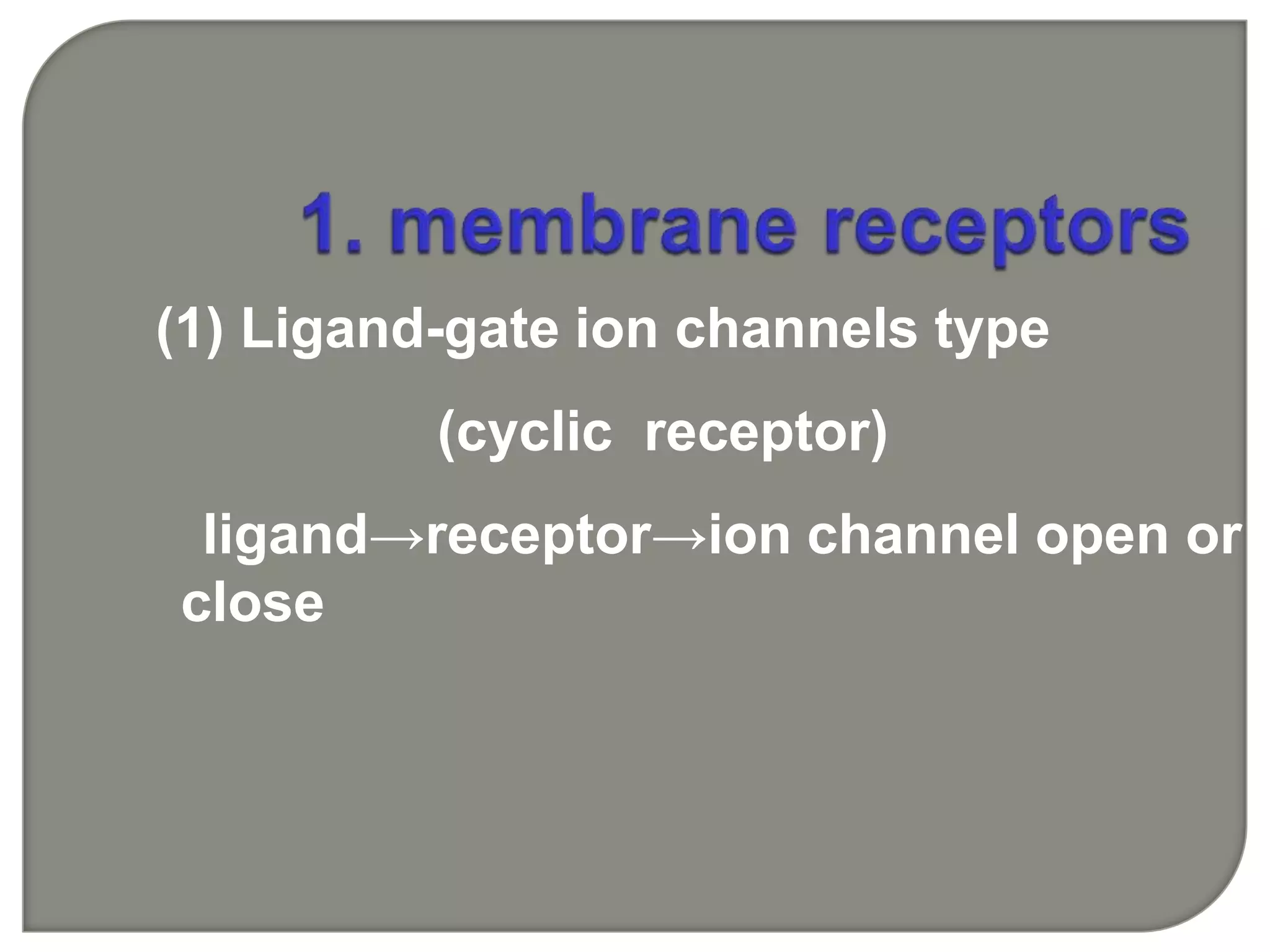
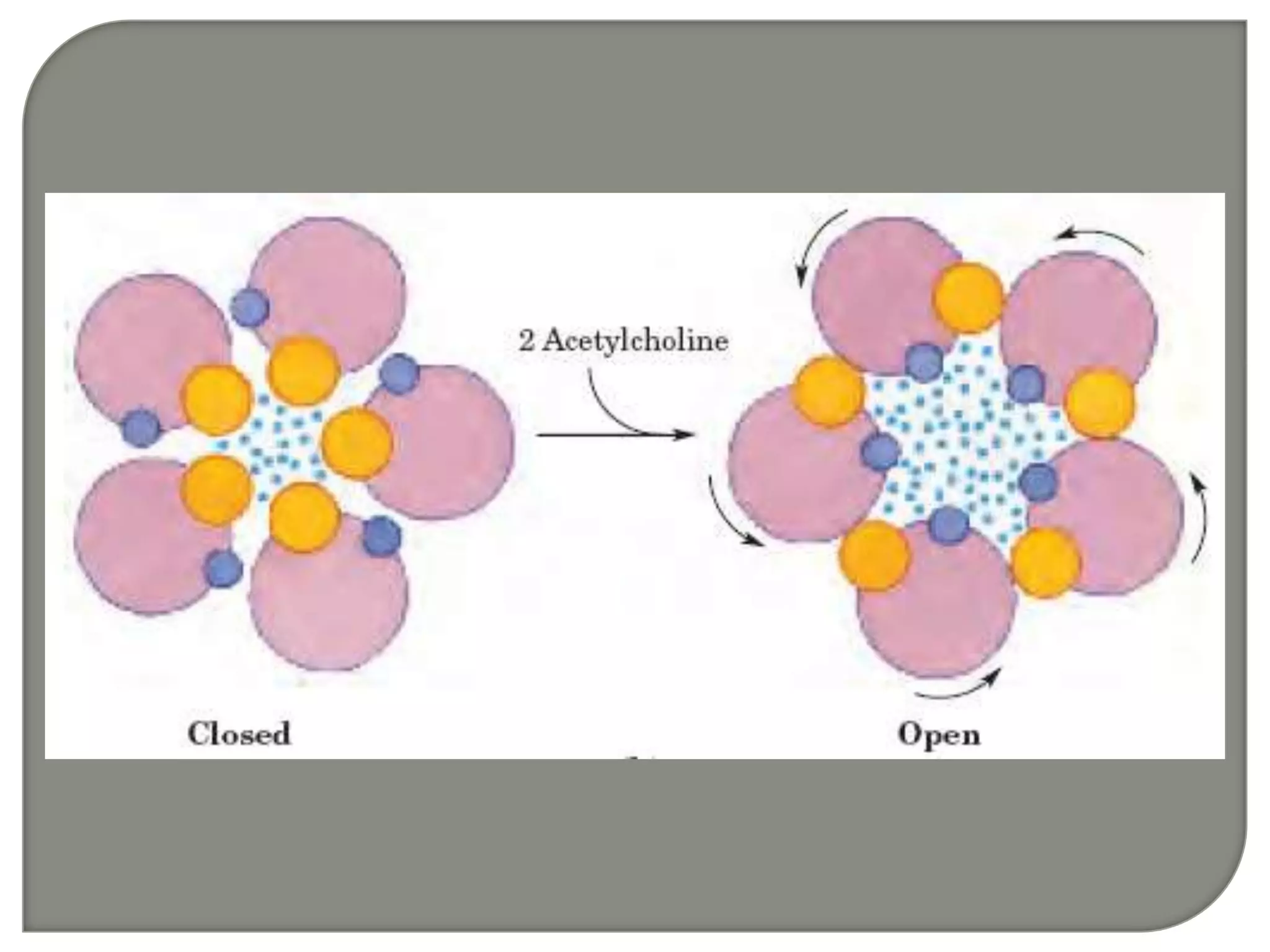
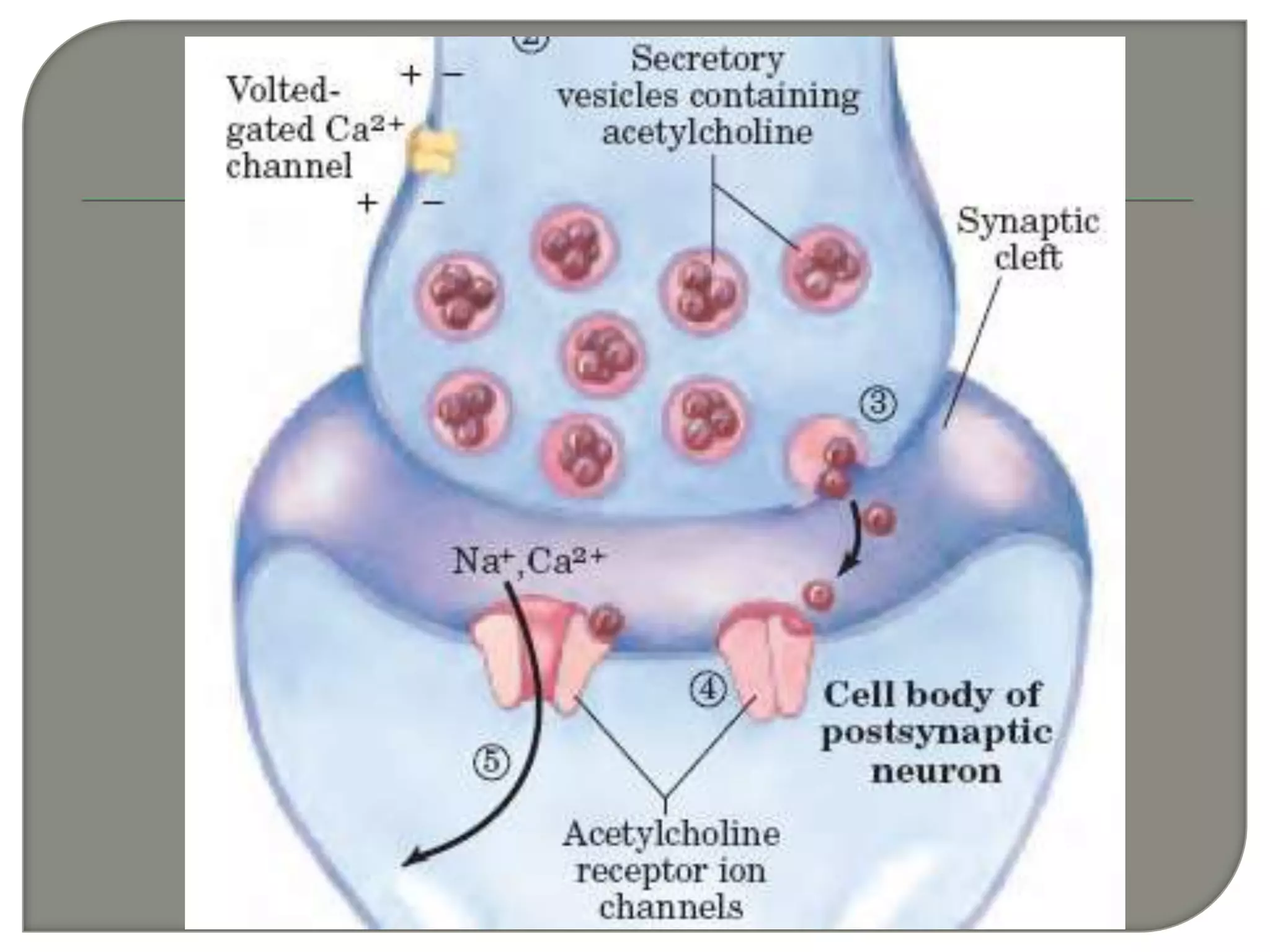
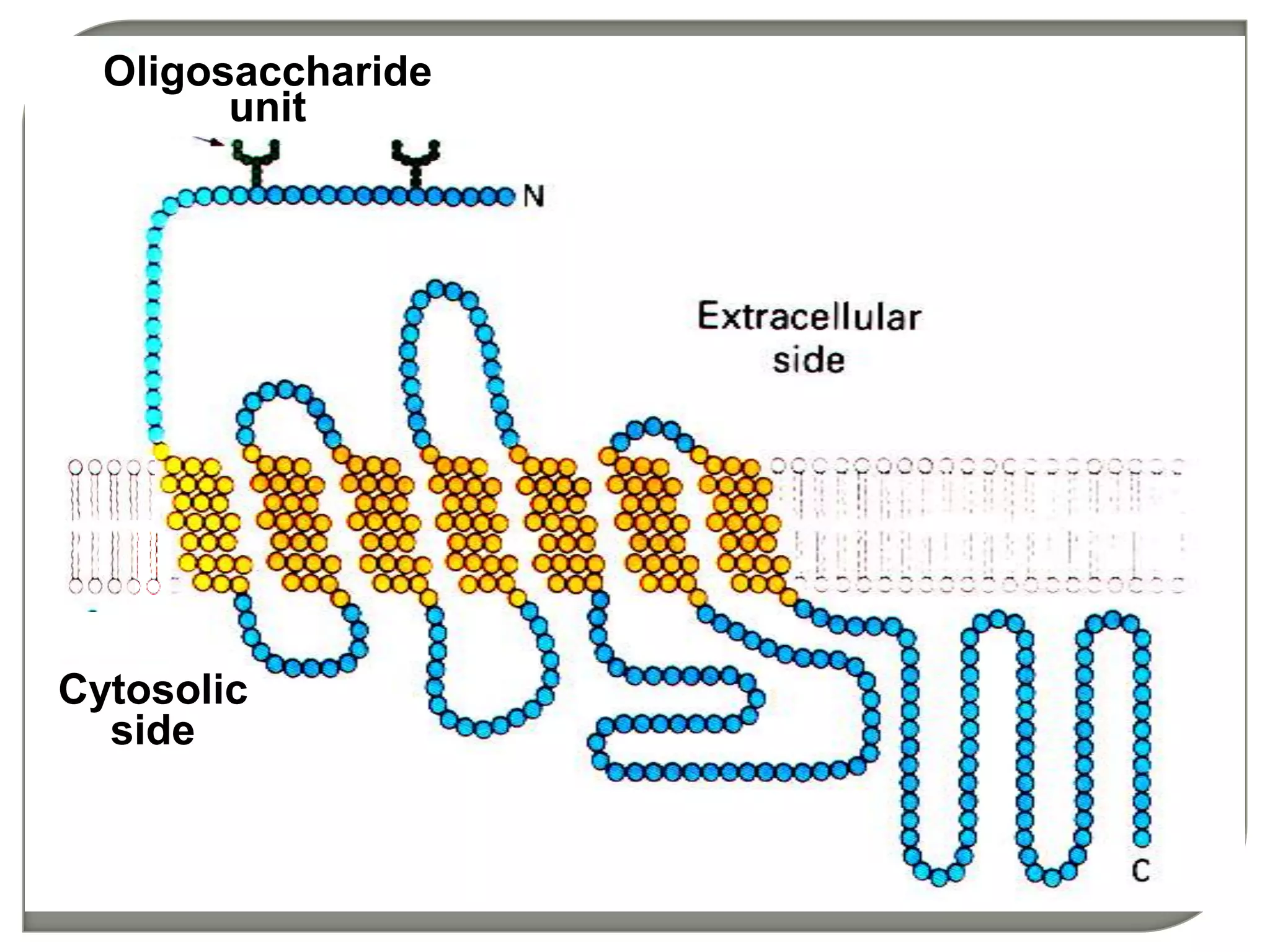
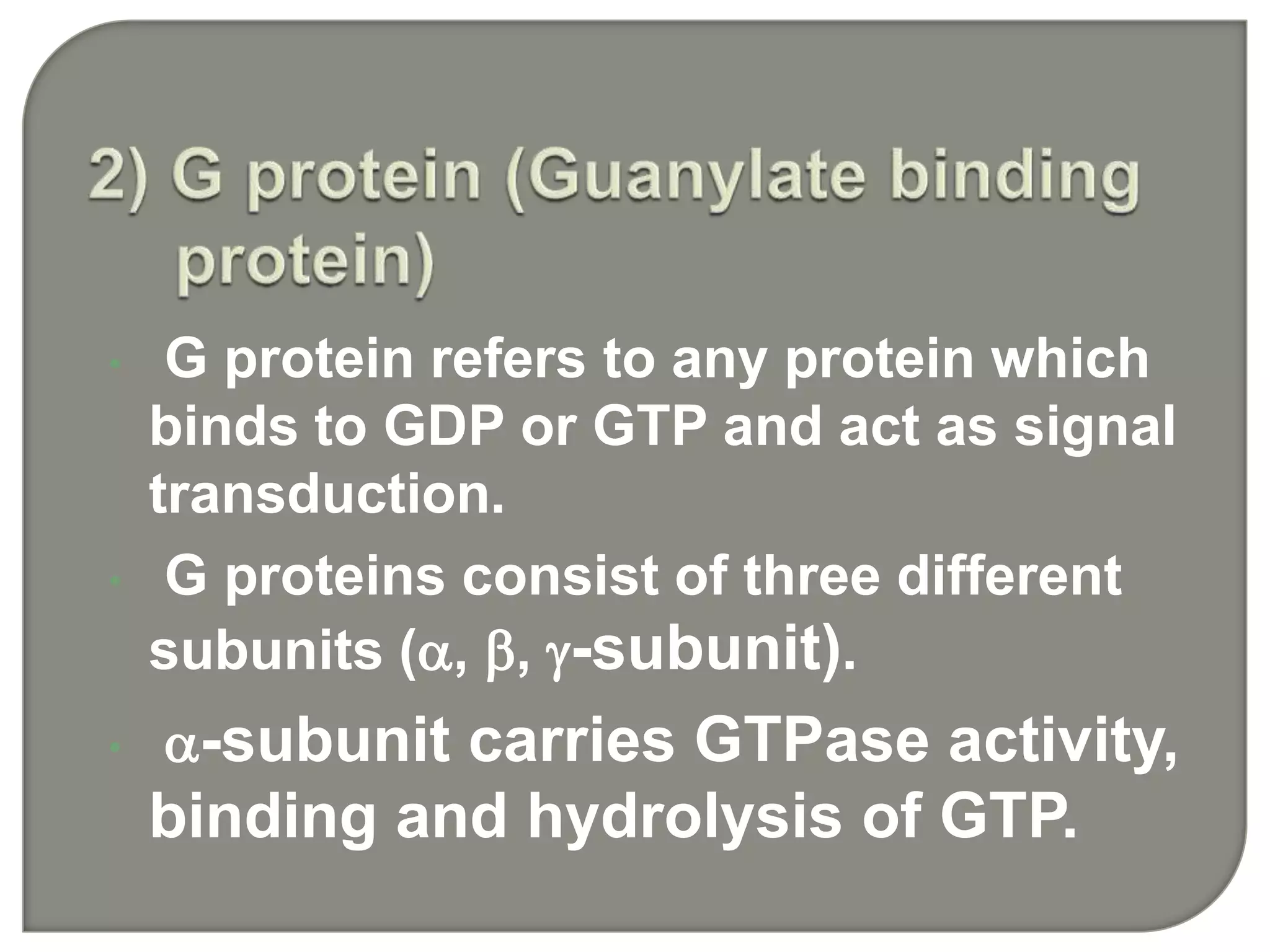
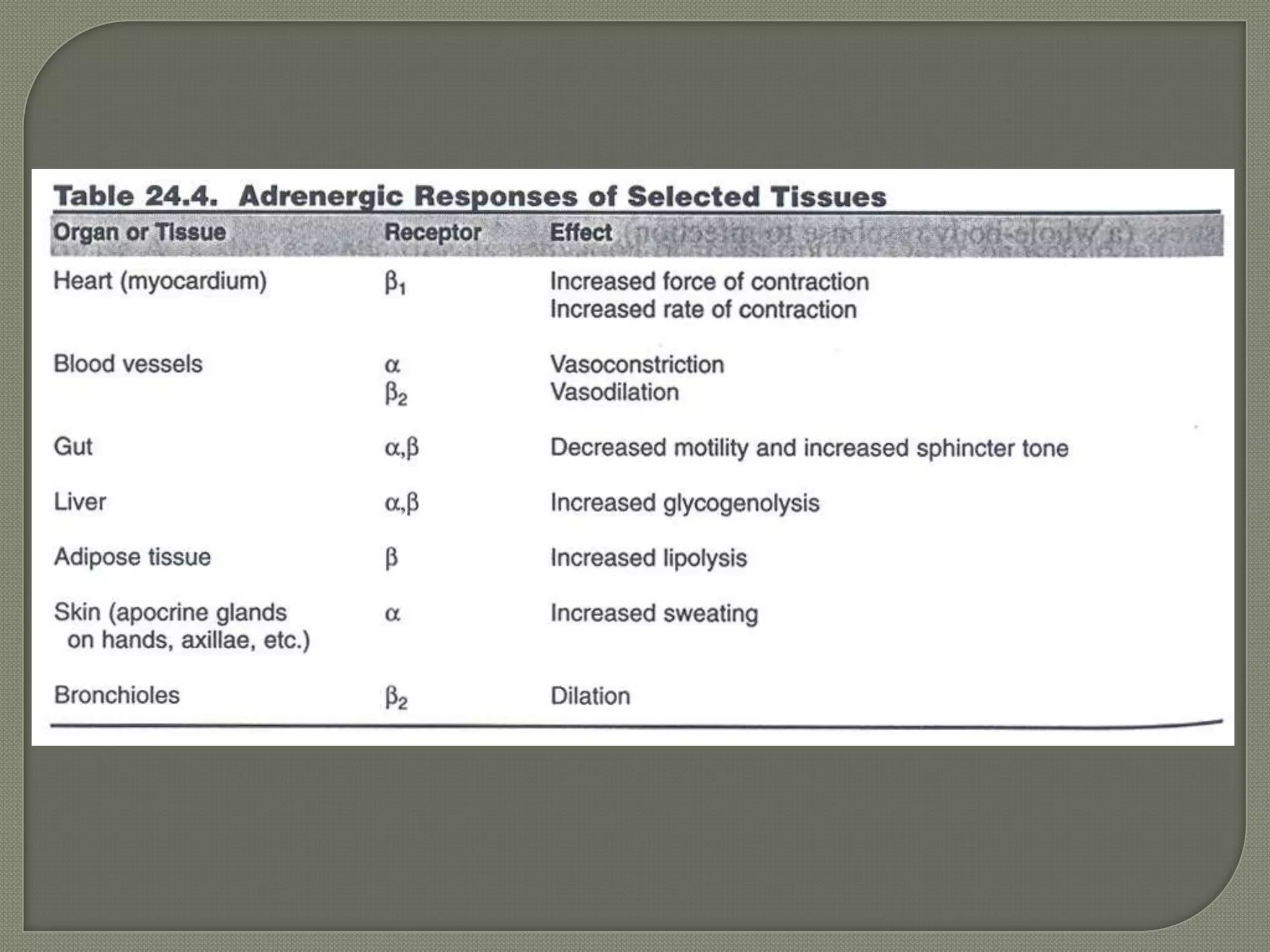
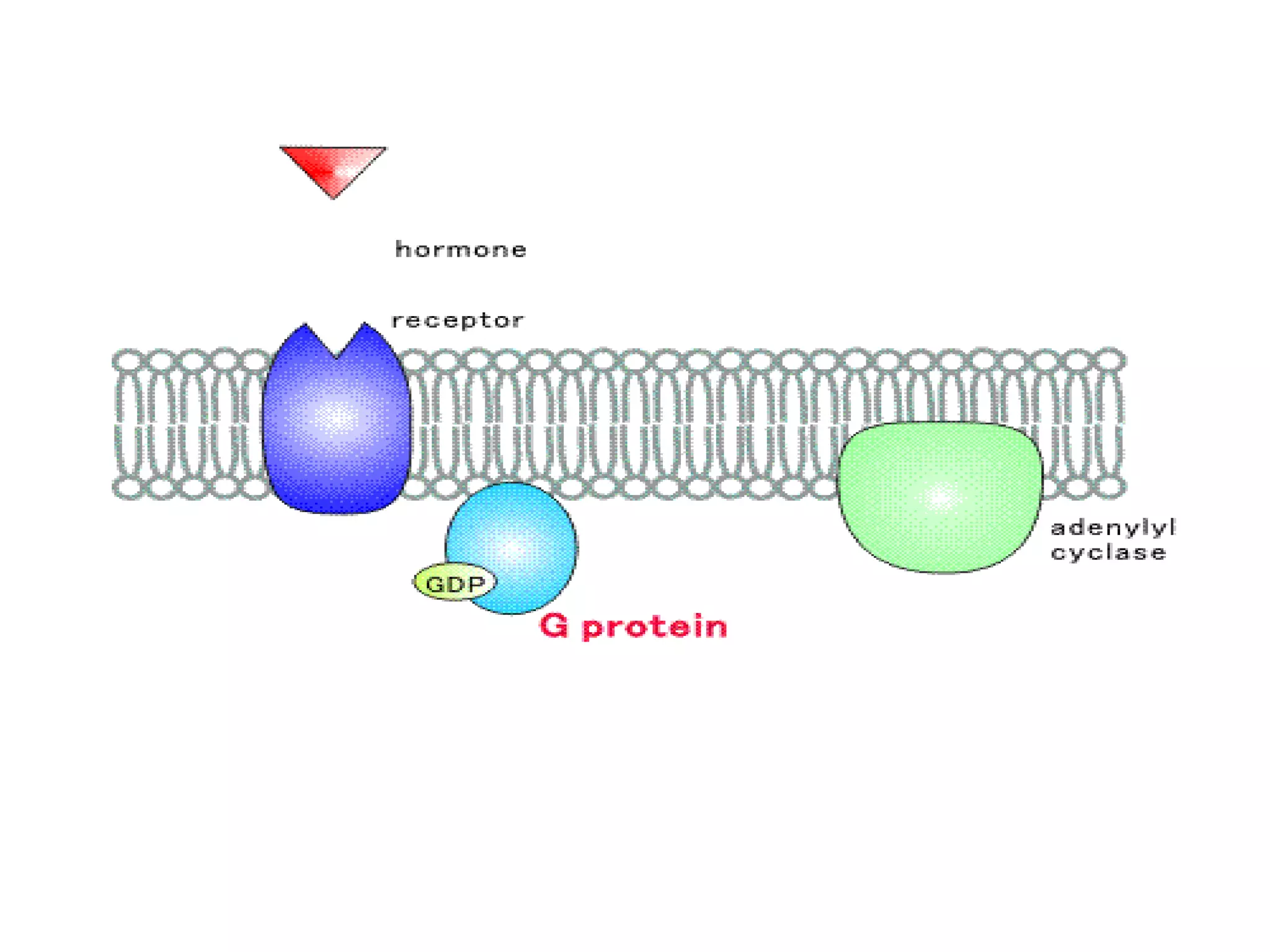
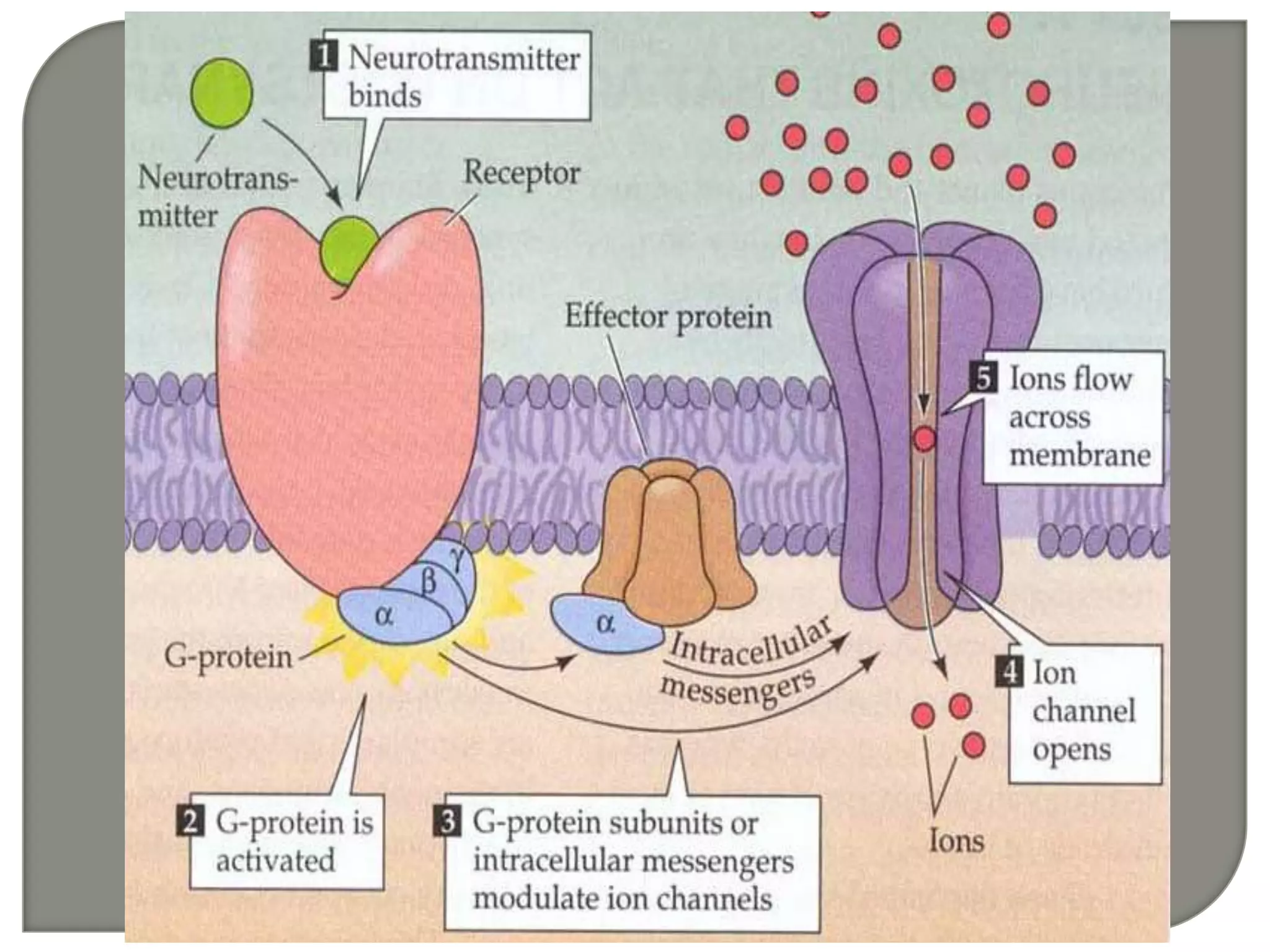
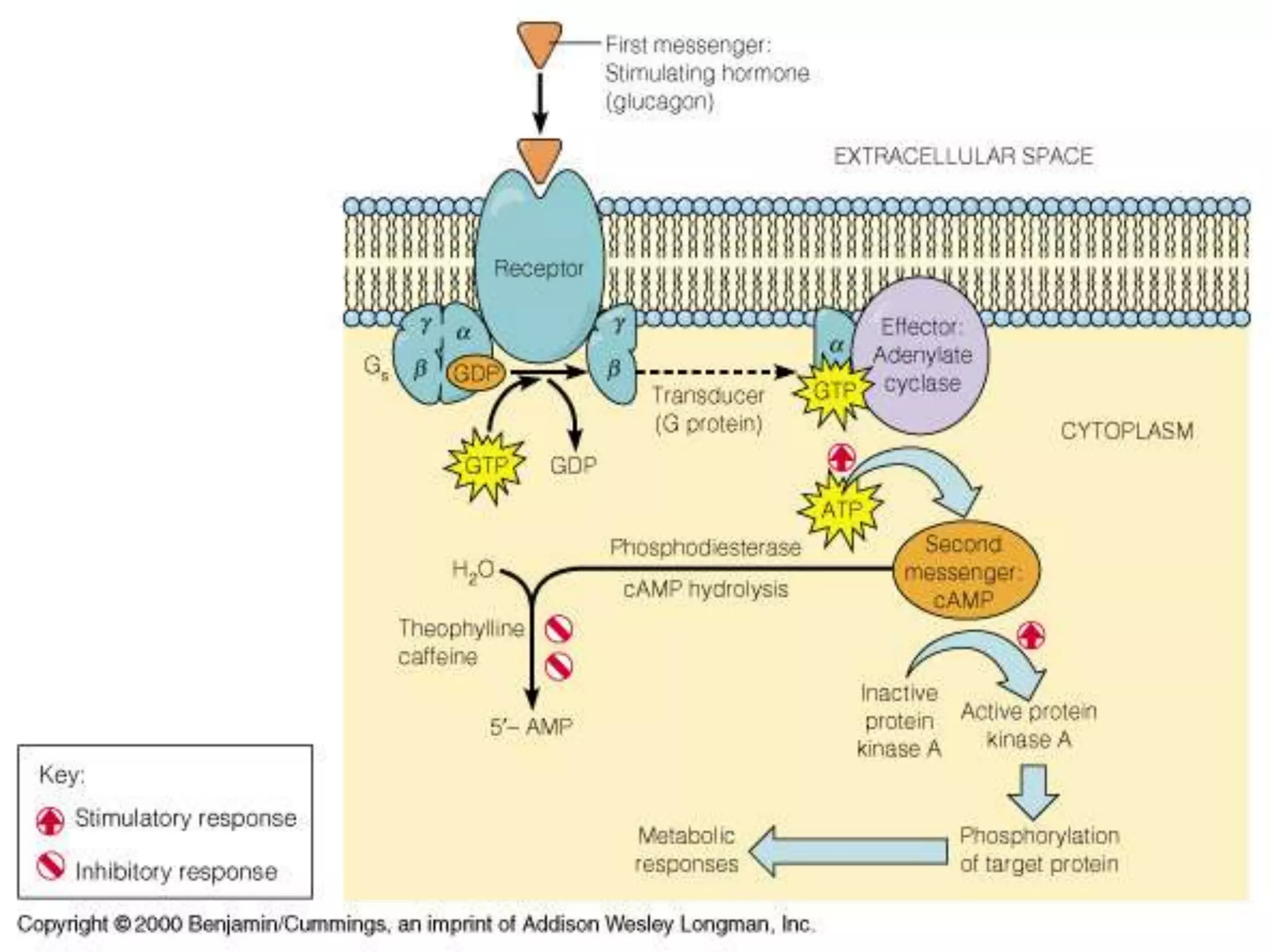
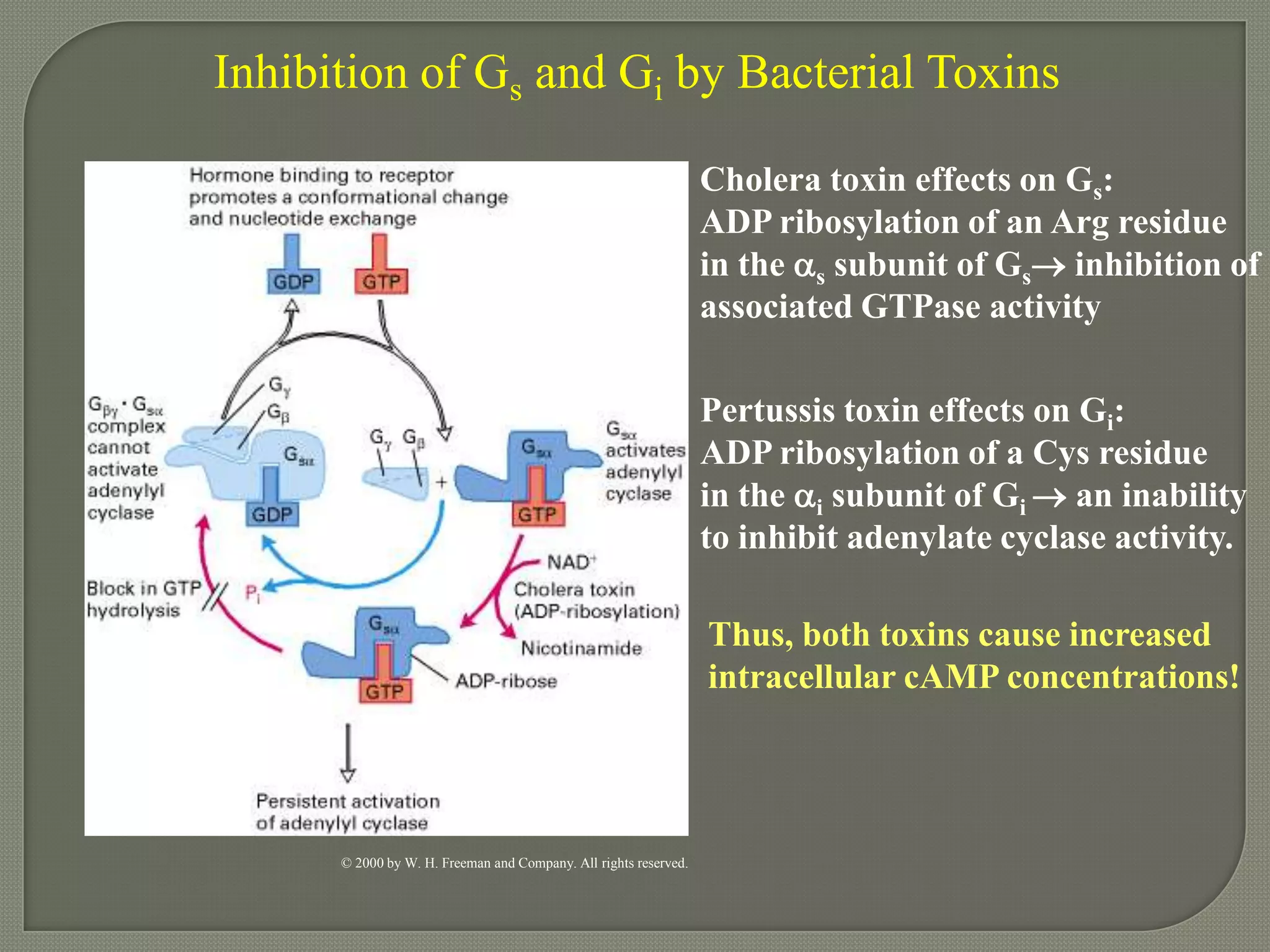
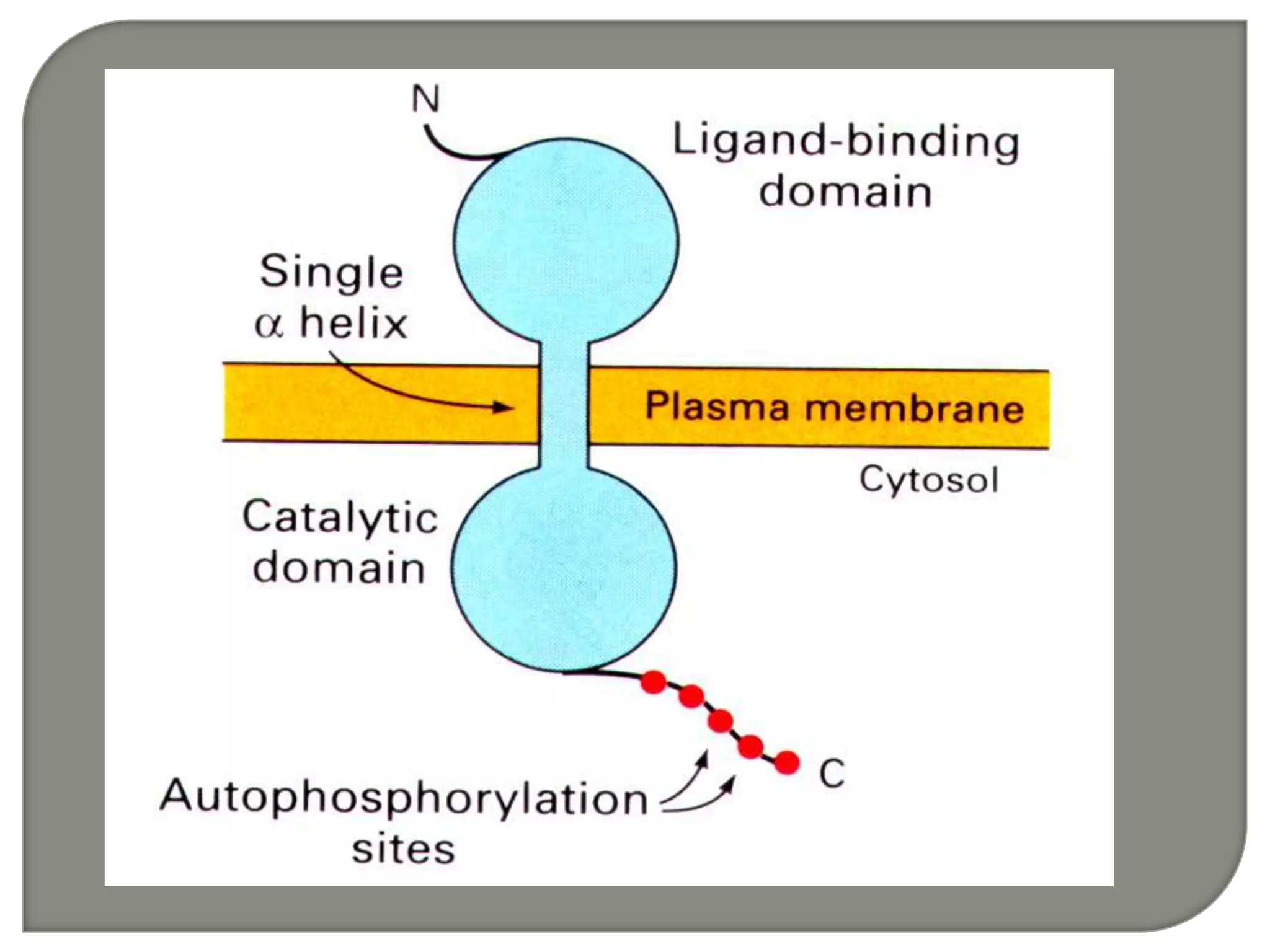
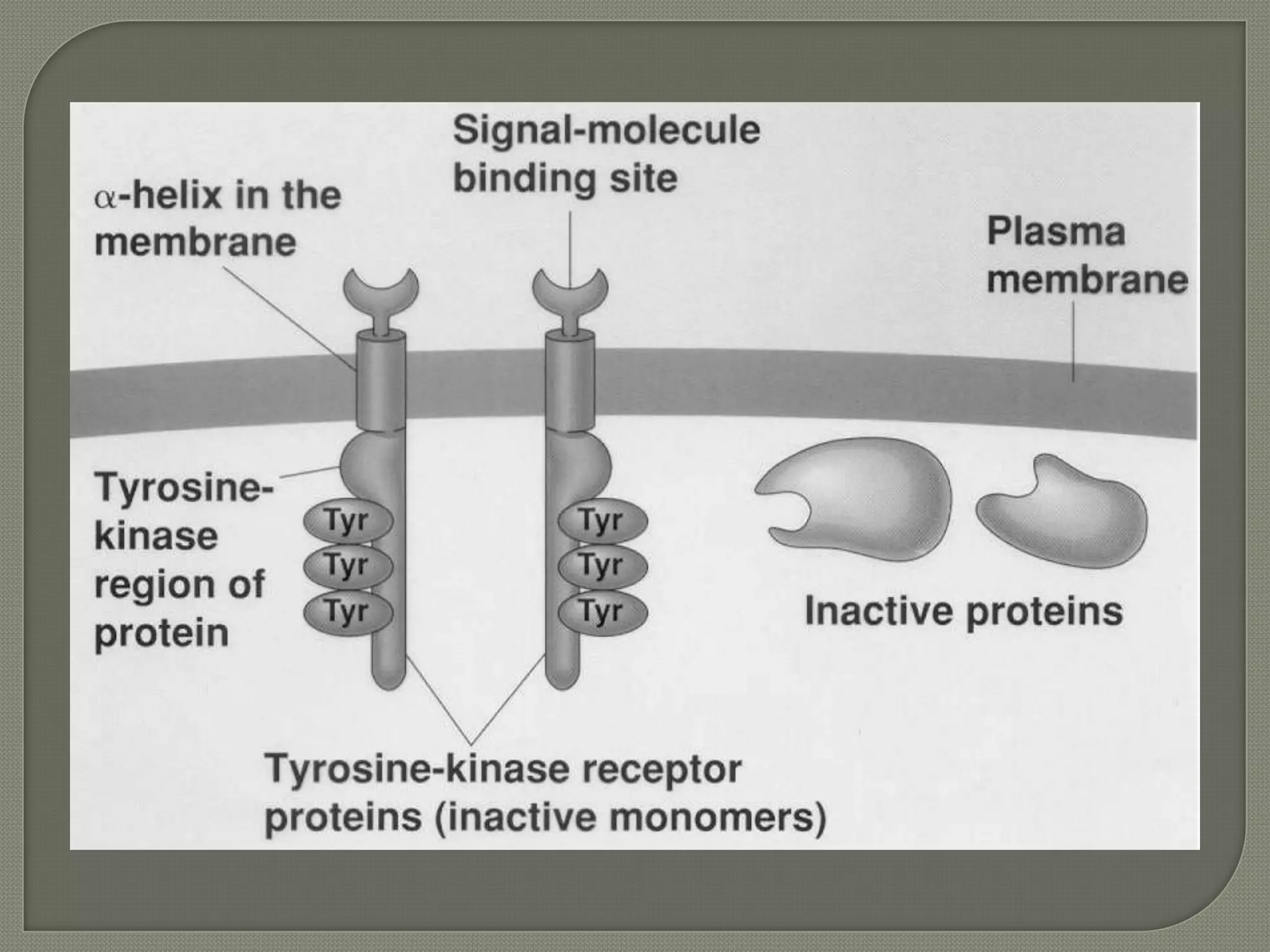
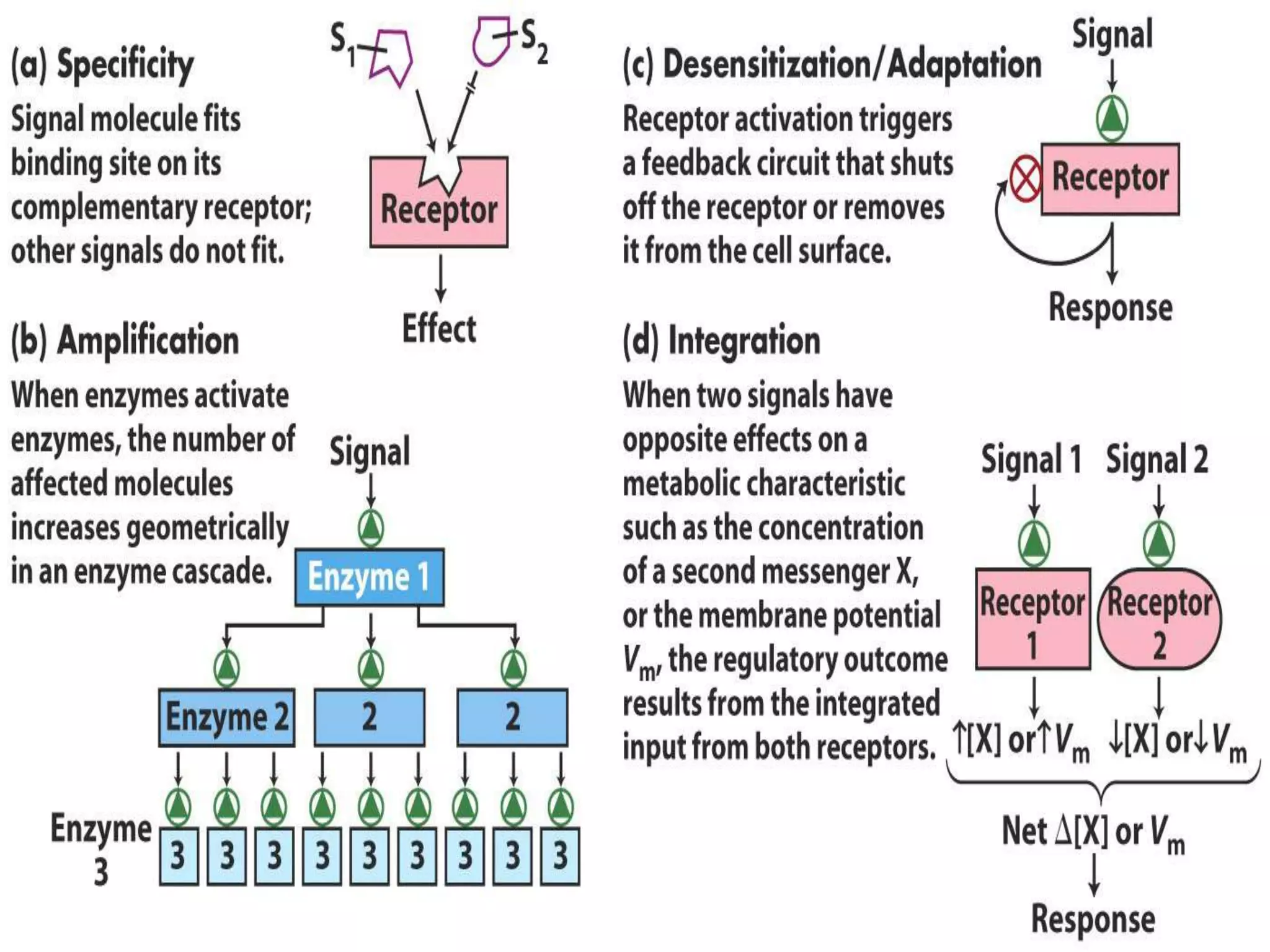
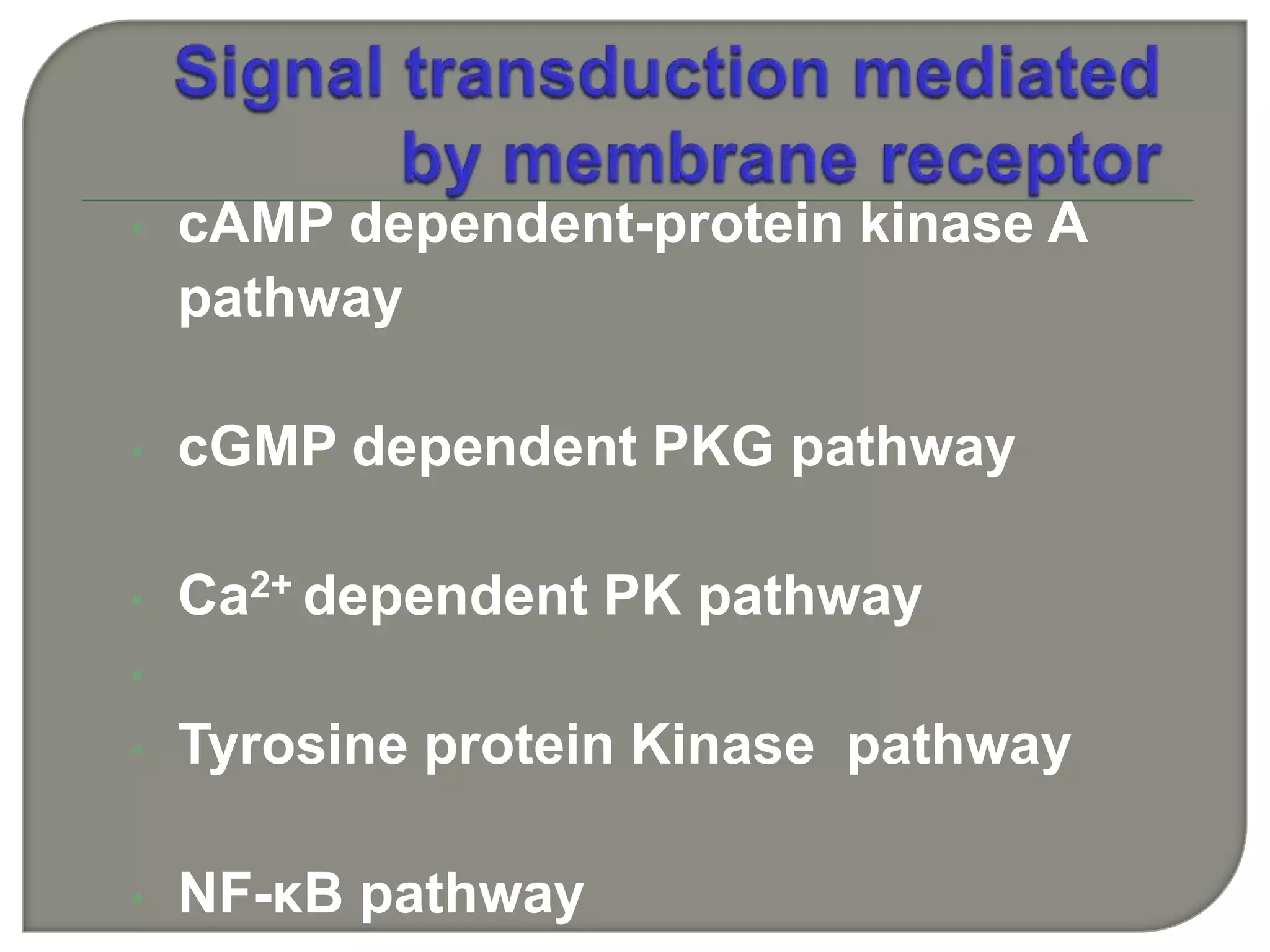
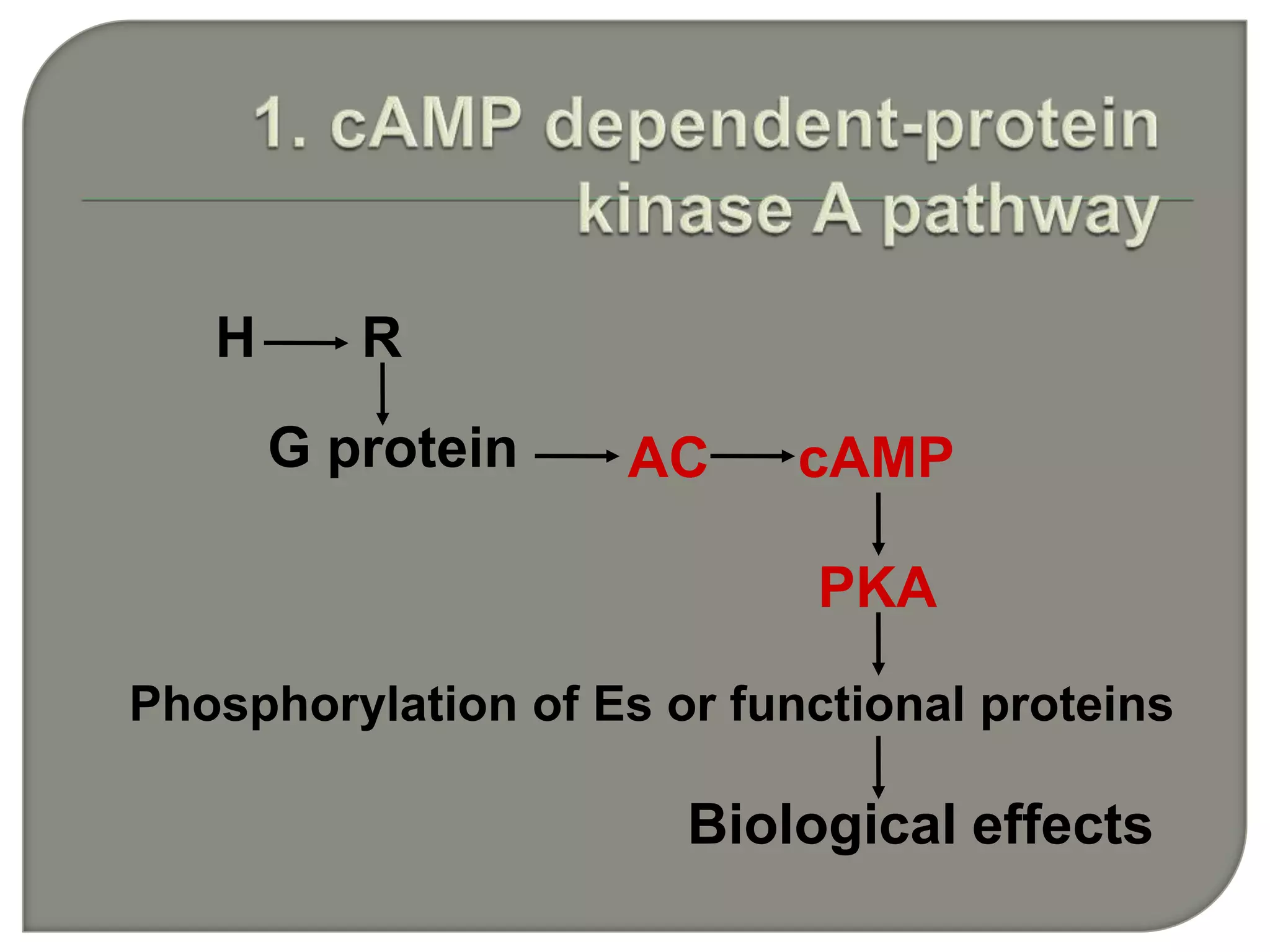
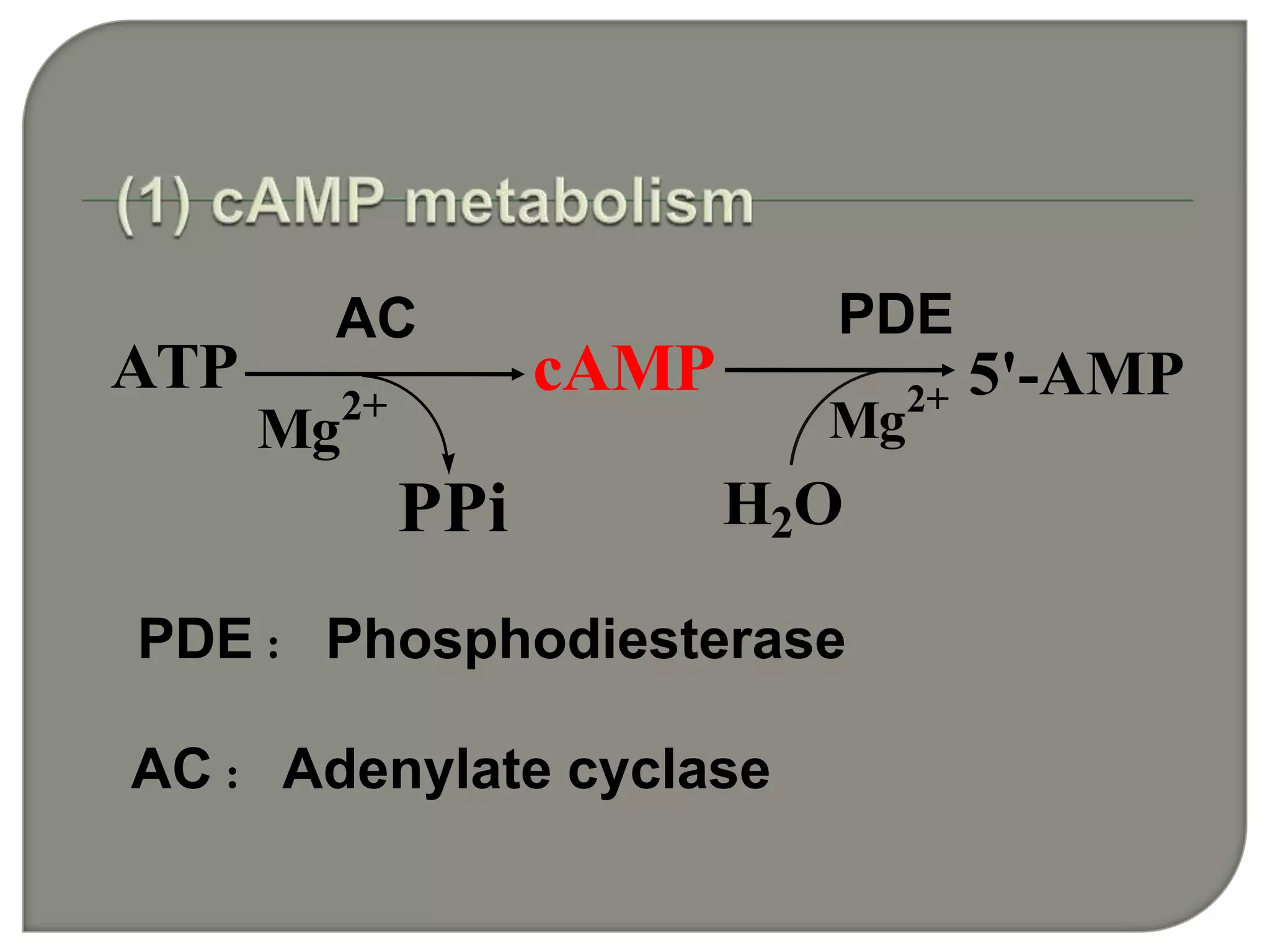
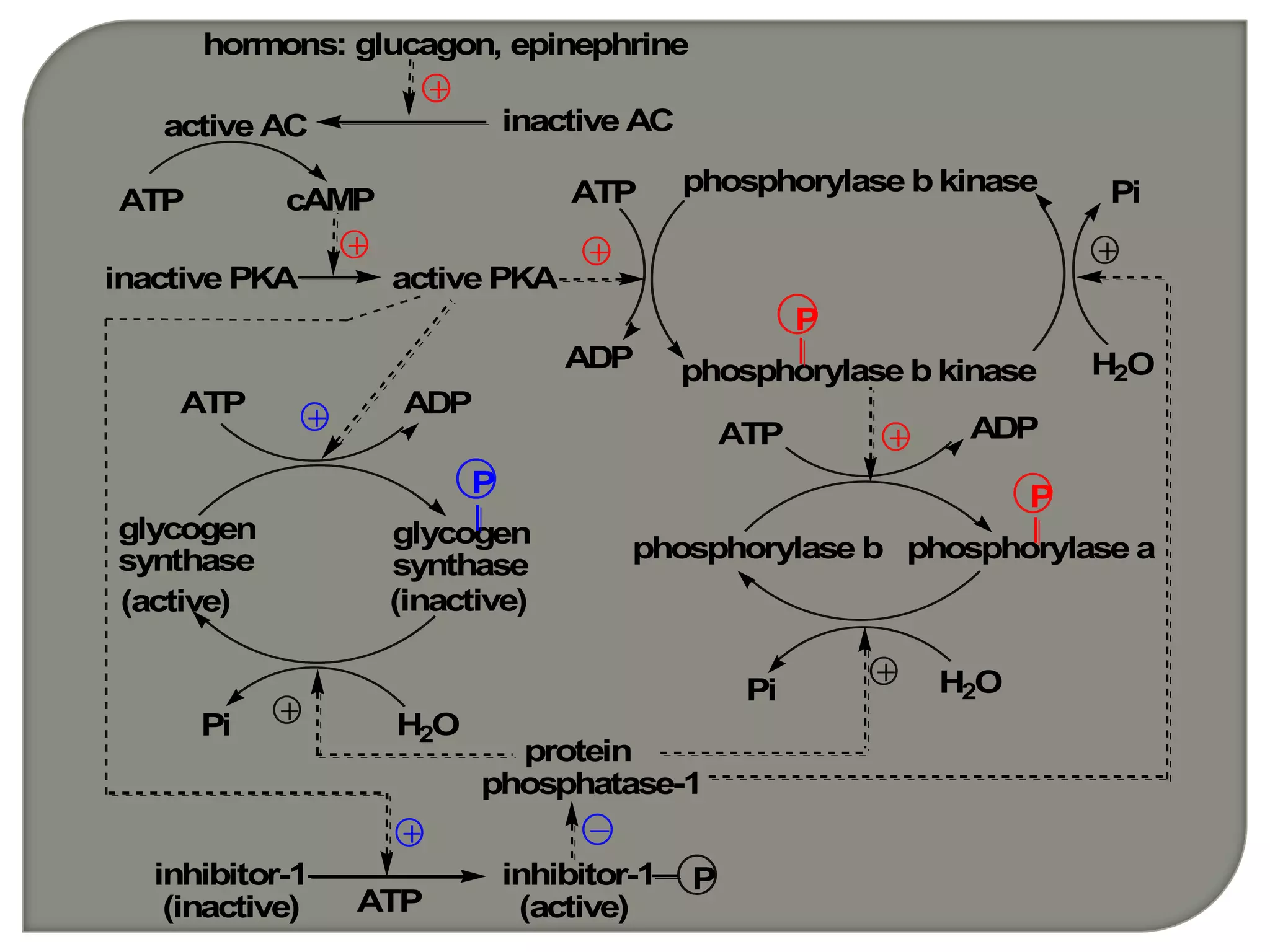
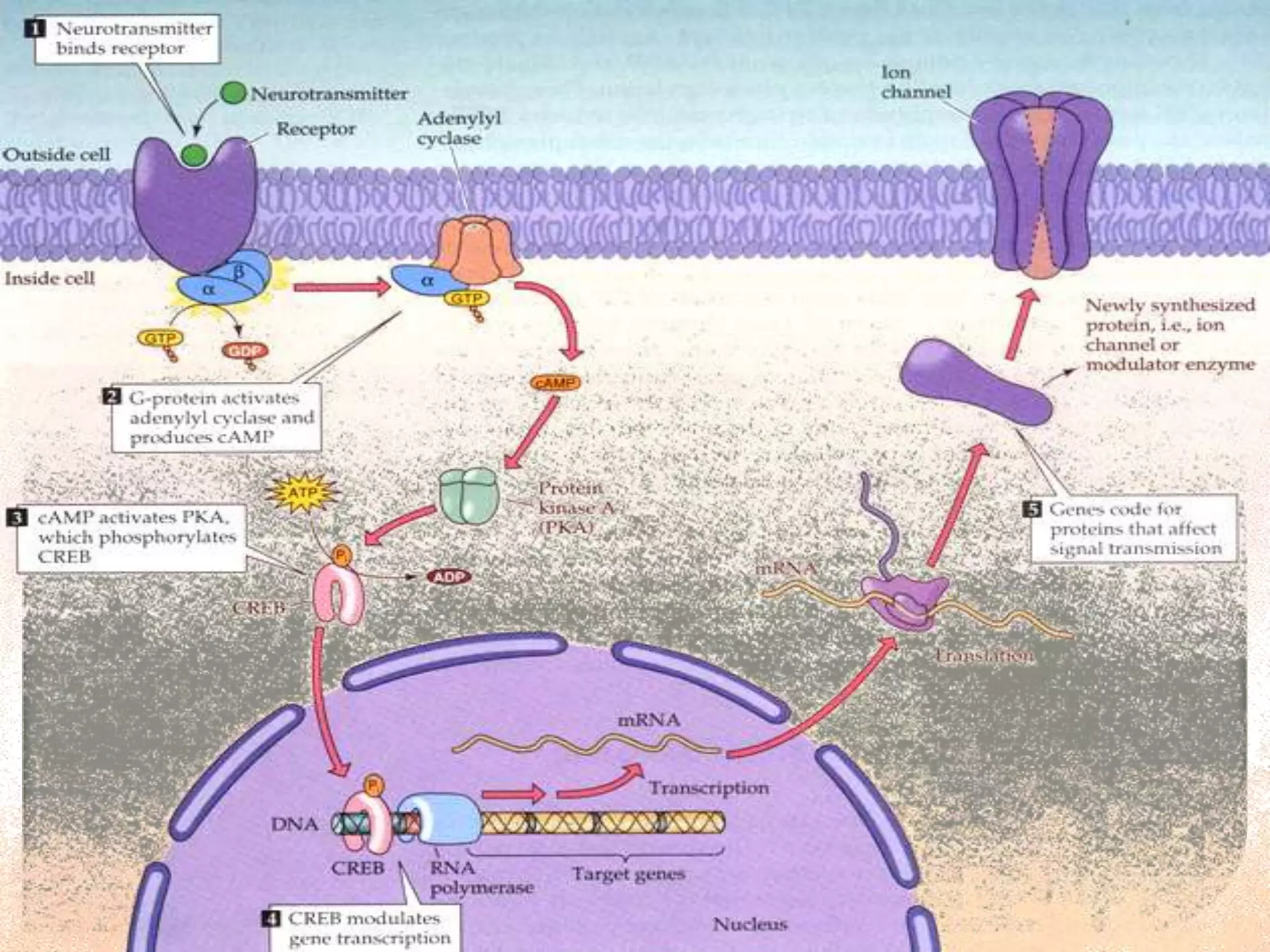
Cellular signal transduction involves signaling molecules activating receptors on target cells to initiate intracellular responses. There are various types of signaling molecules including proteins/peptides, amino acid/fatty acid derivatives, and steroids. These molecules bind to membrane receptors and induce intracellular second messengers like cAMP, IP3, Ca2+ that activate pathways culminating in altered gene expression, metabolism, or other biological effects. The document provides details on different receptor types, intracellular signaling pathways, and examples of signaling molecules that activate them.













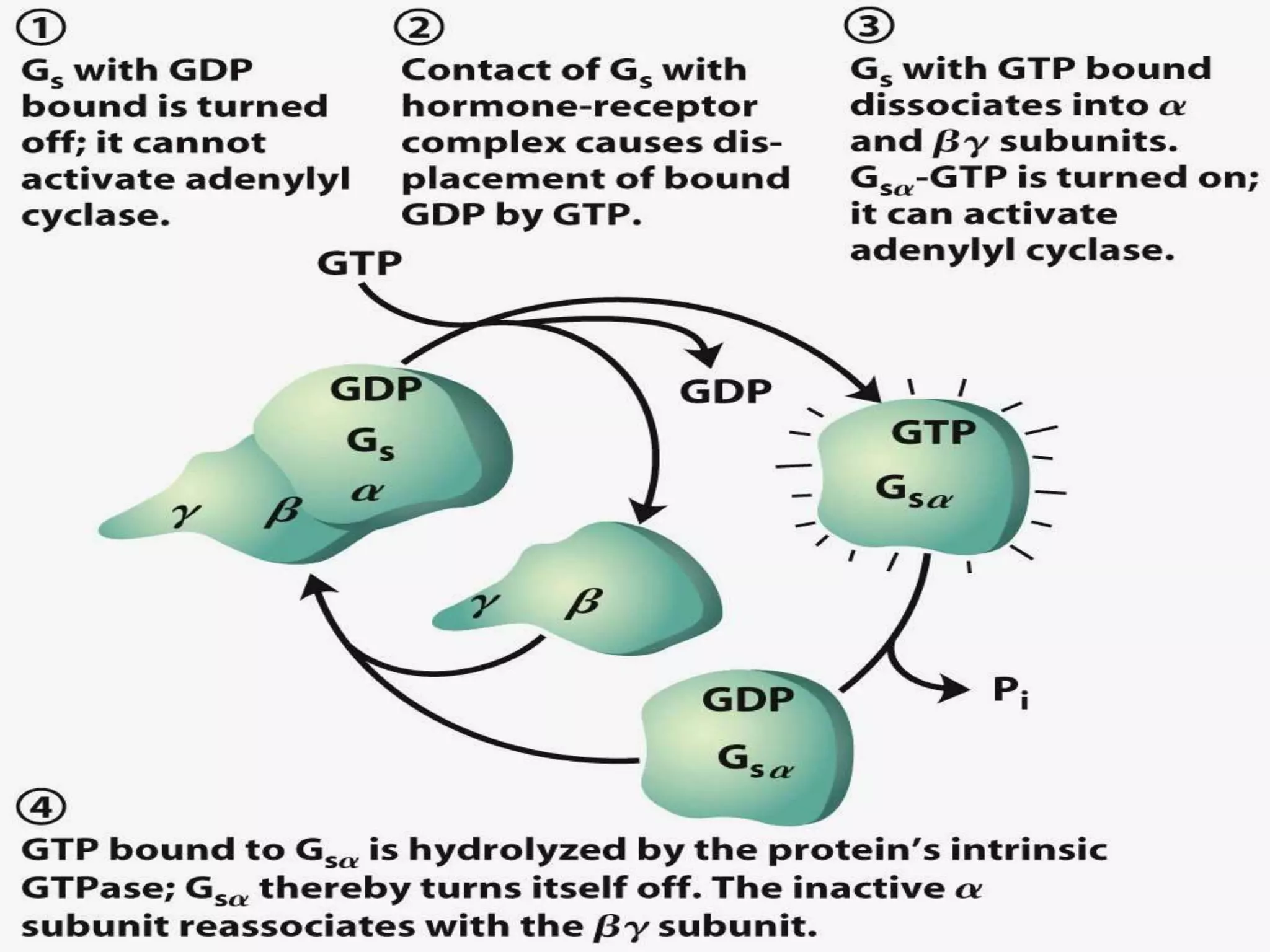
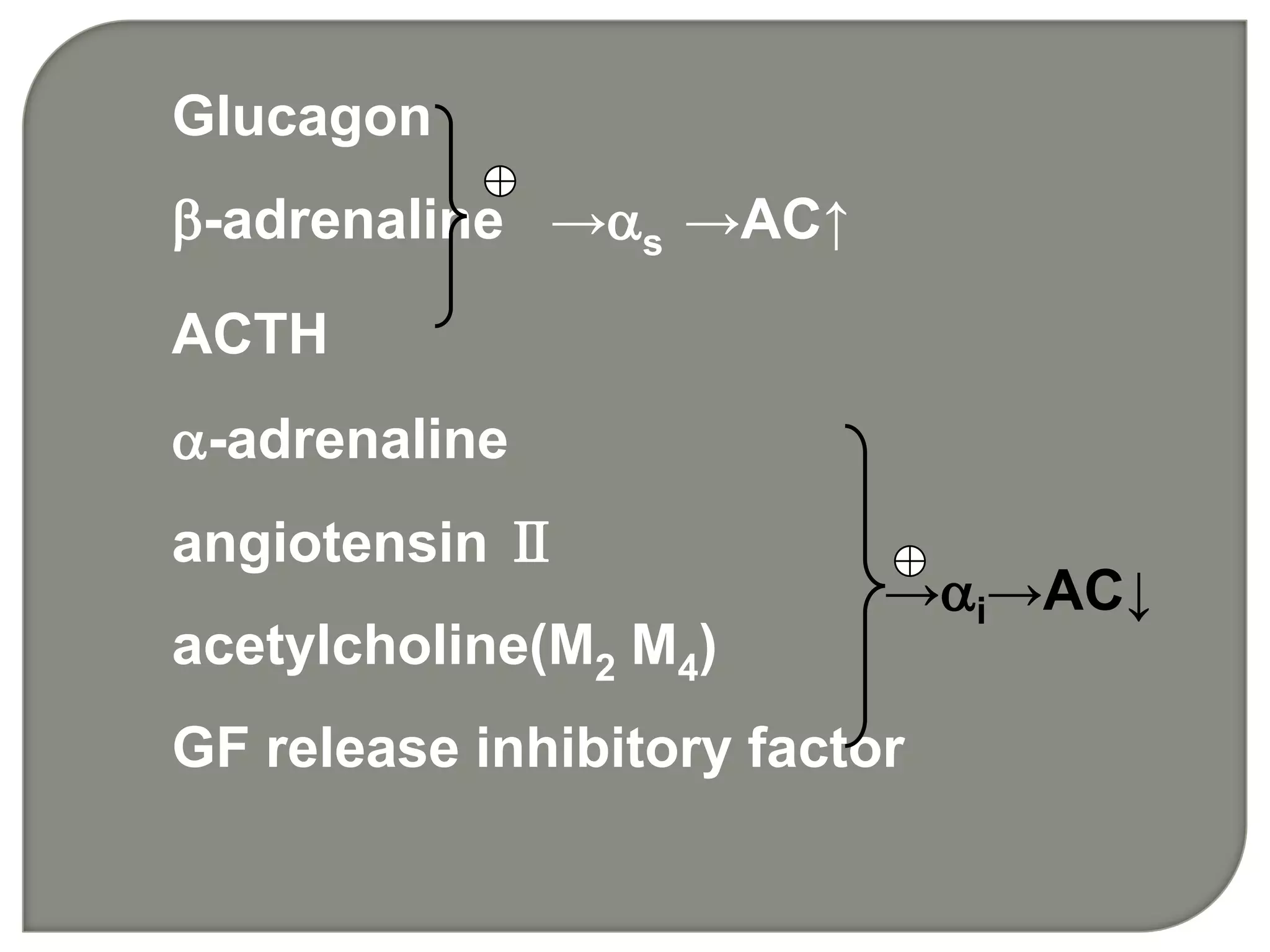
![Gs vs Gi vs Gq
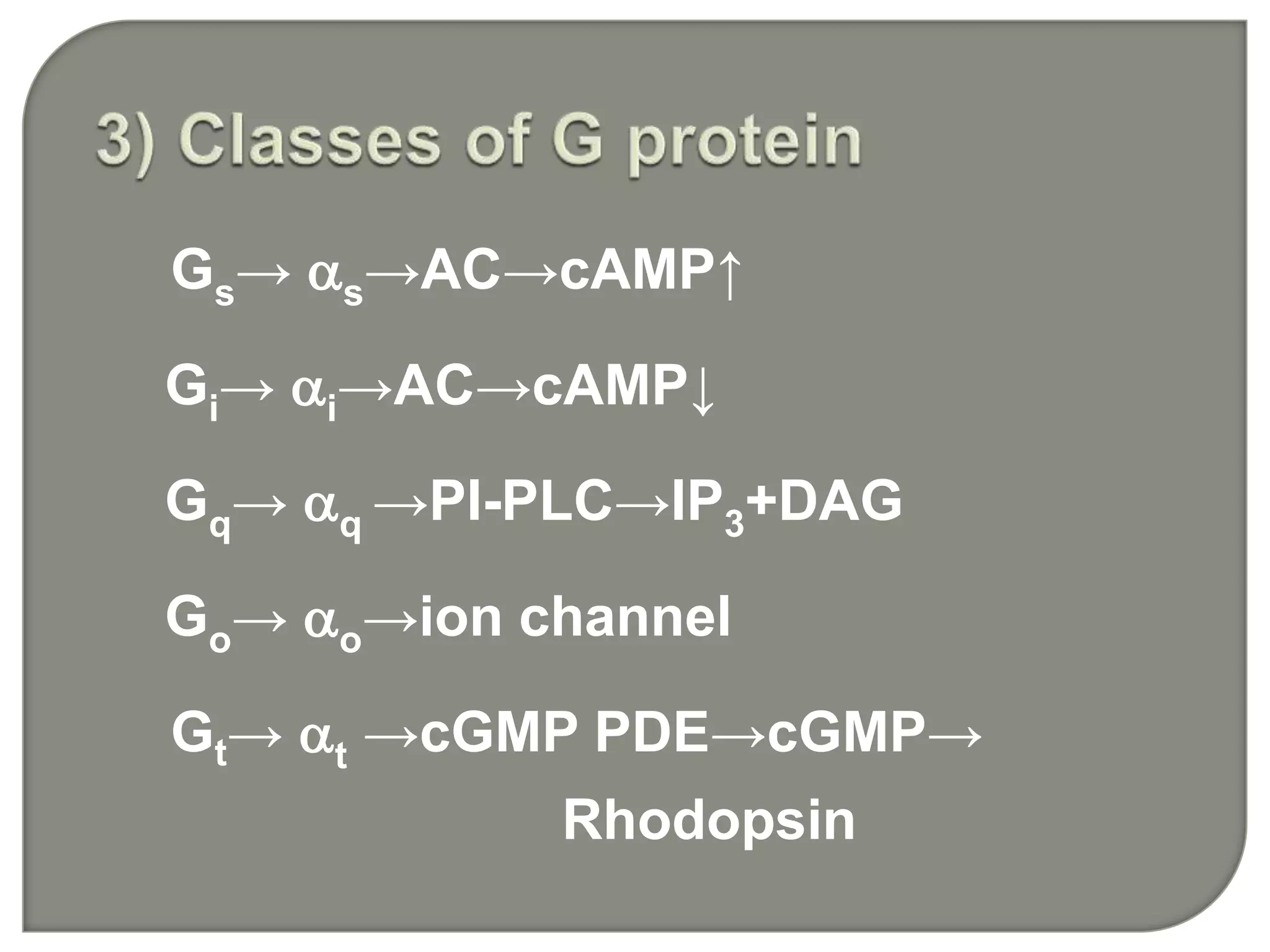
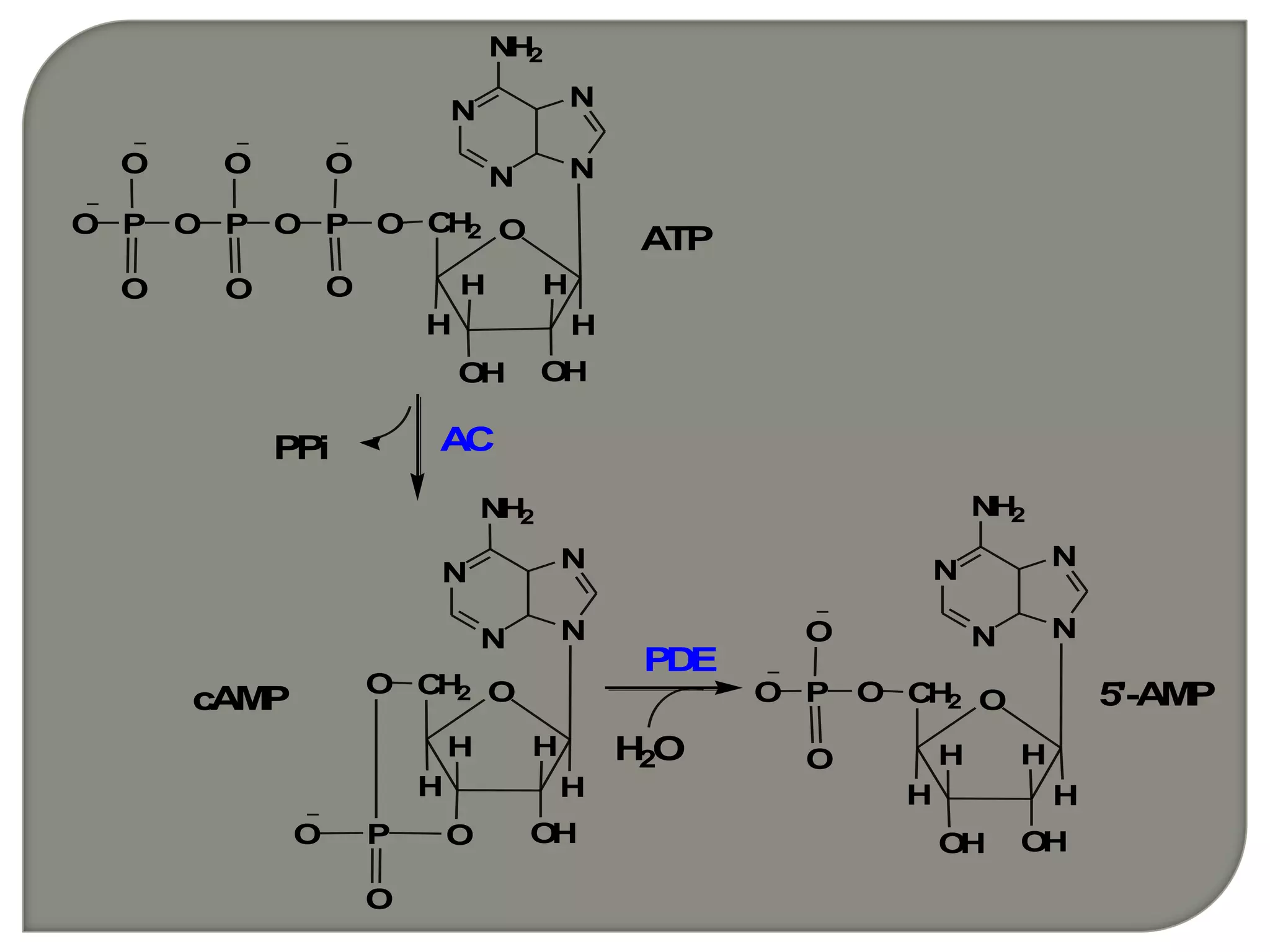
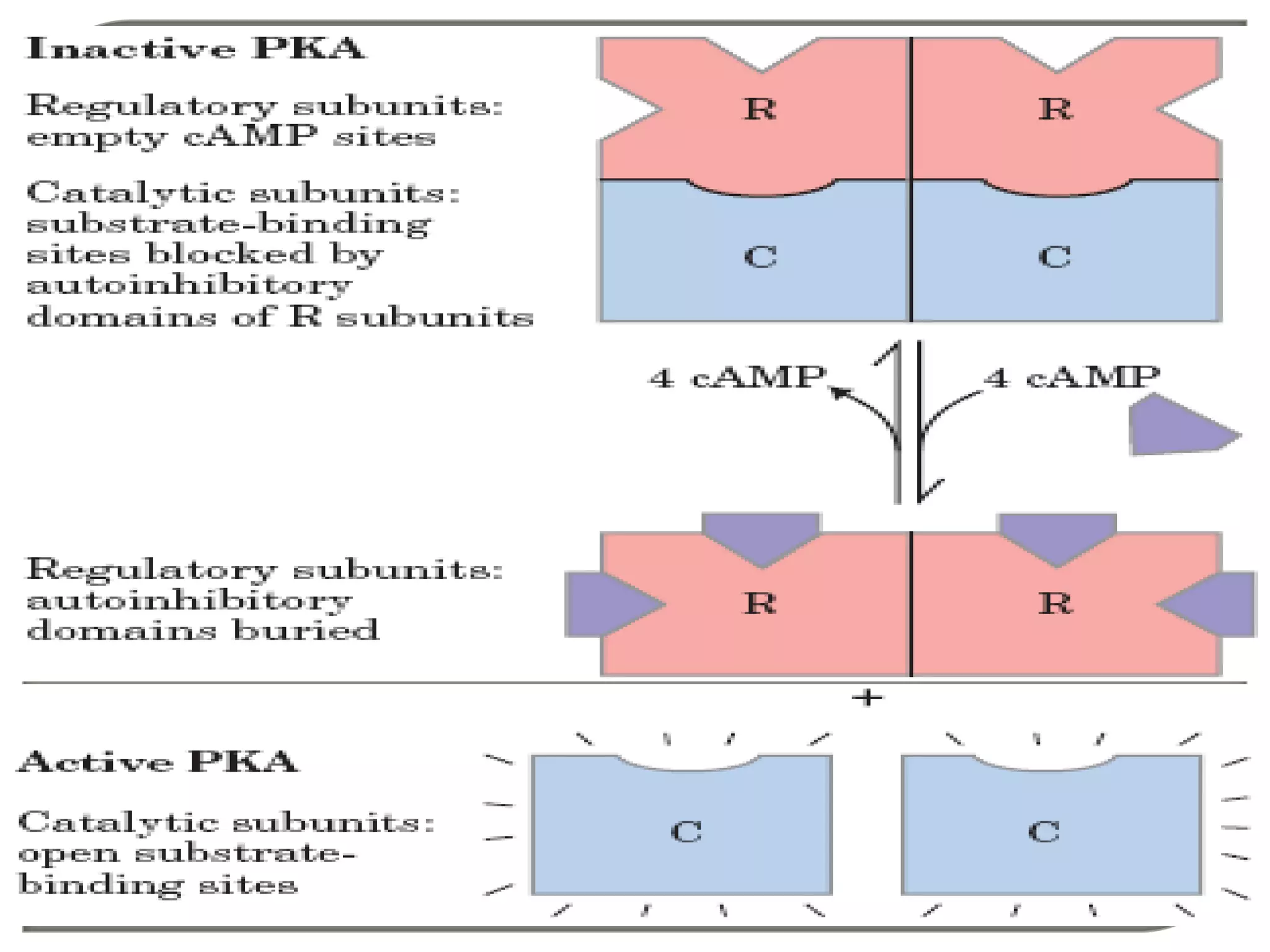
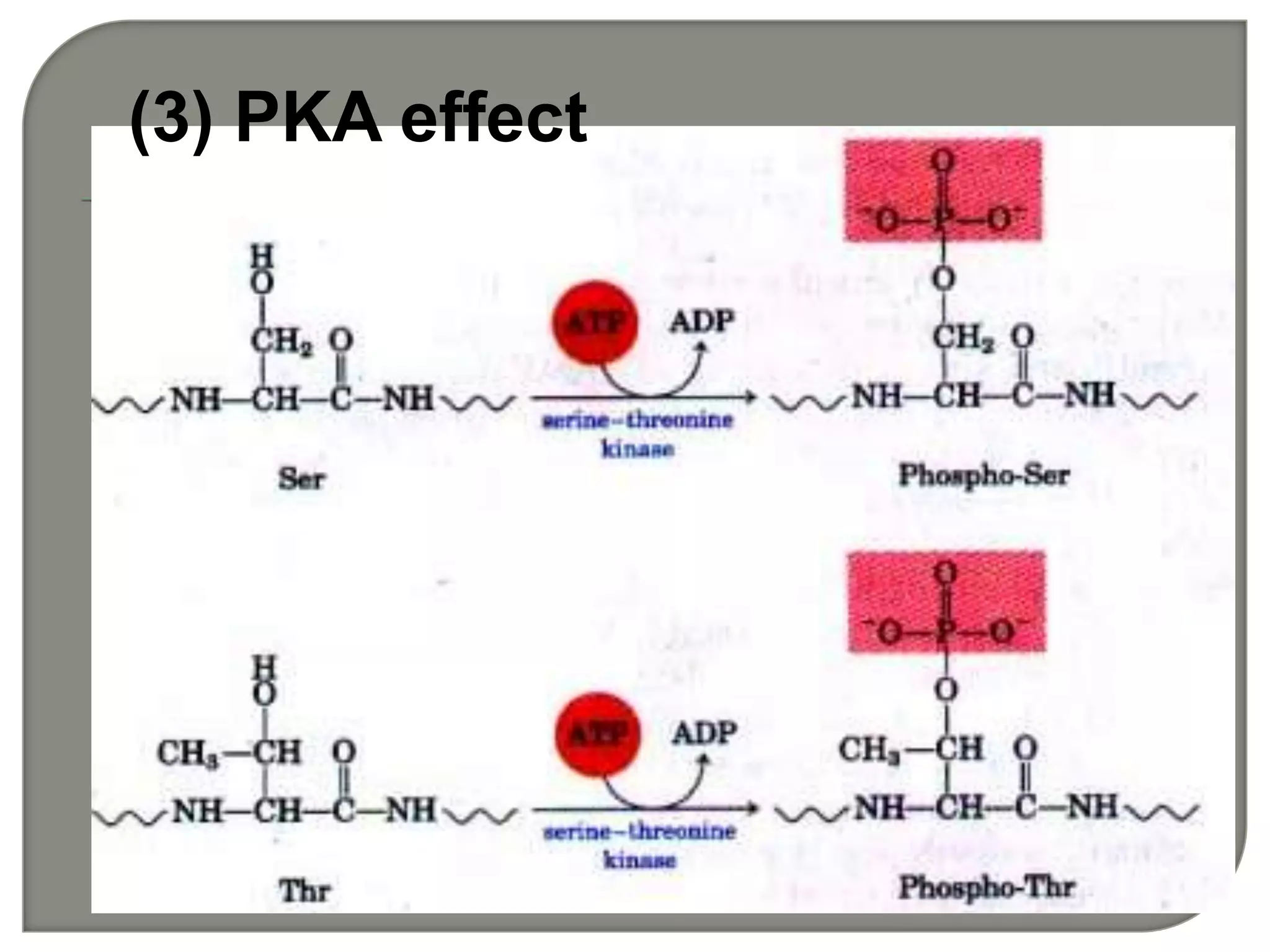
Gs and Gi coupled to adenylate cyclase [cAMP]
G q coupled to phospholipase C [Ca2+]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/signaltransduction-140330125824-phpapp01/75/Signal-transduction-30-2048.jpg)

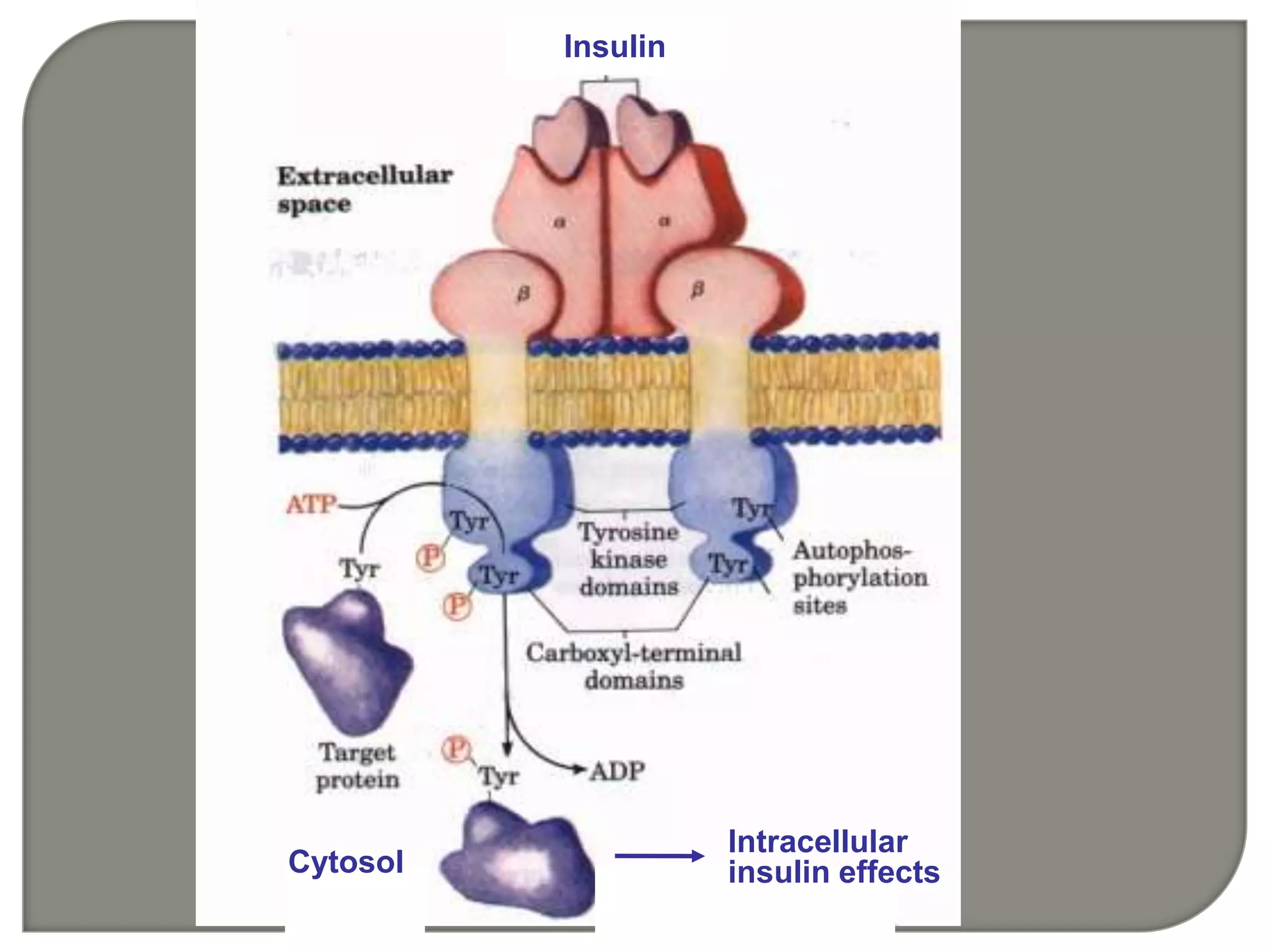
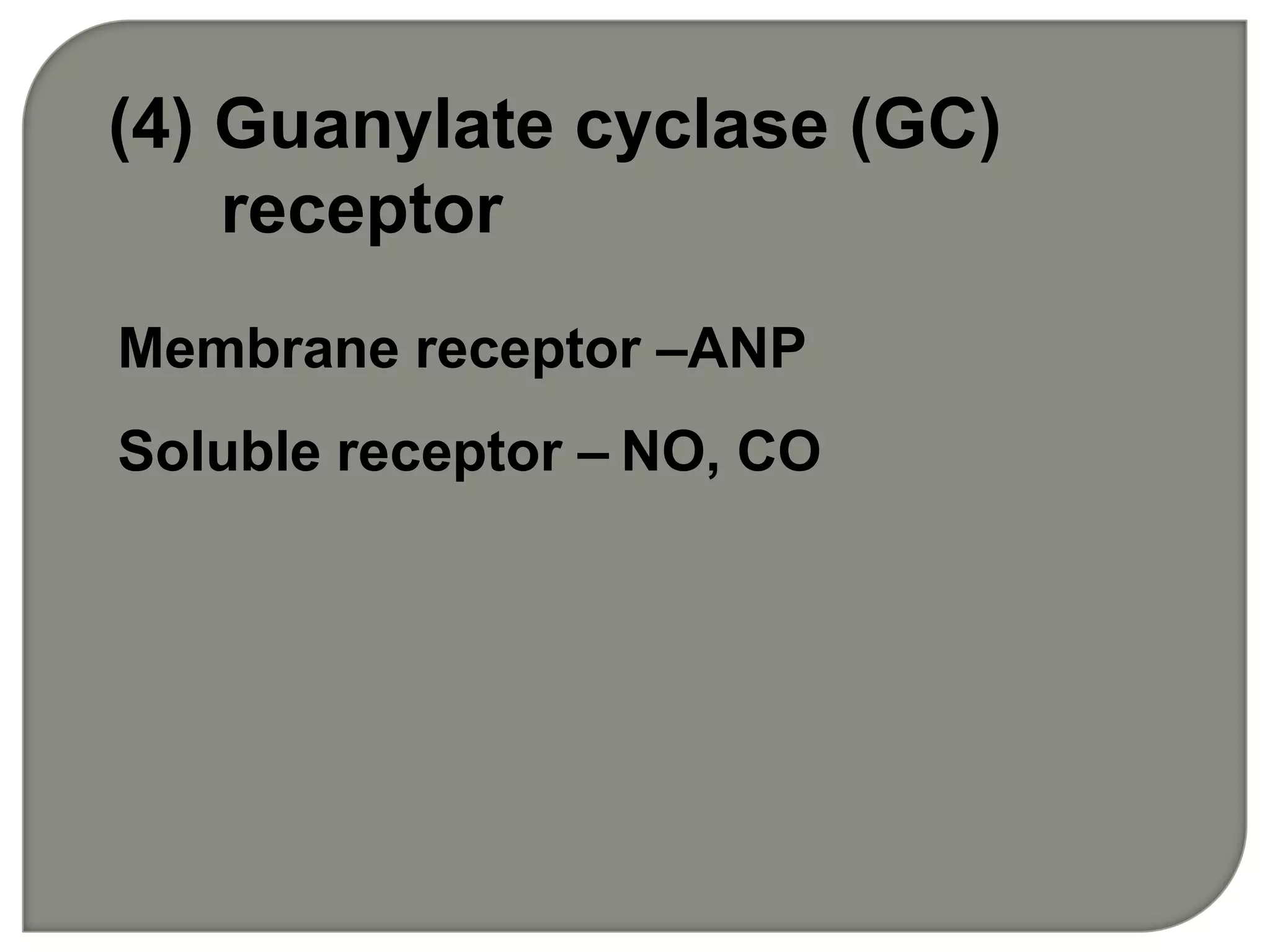
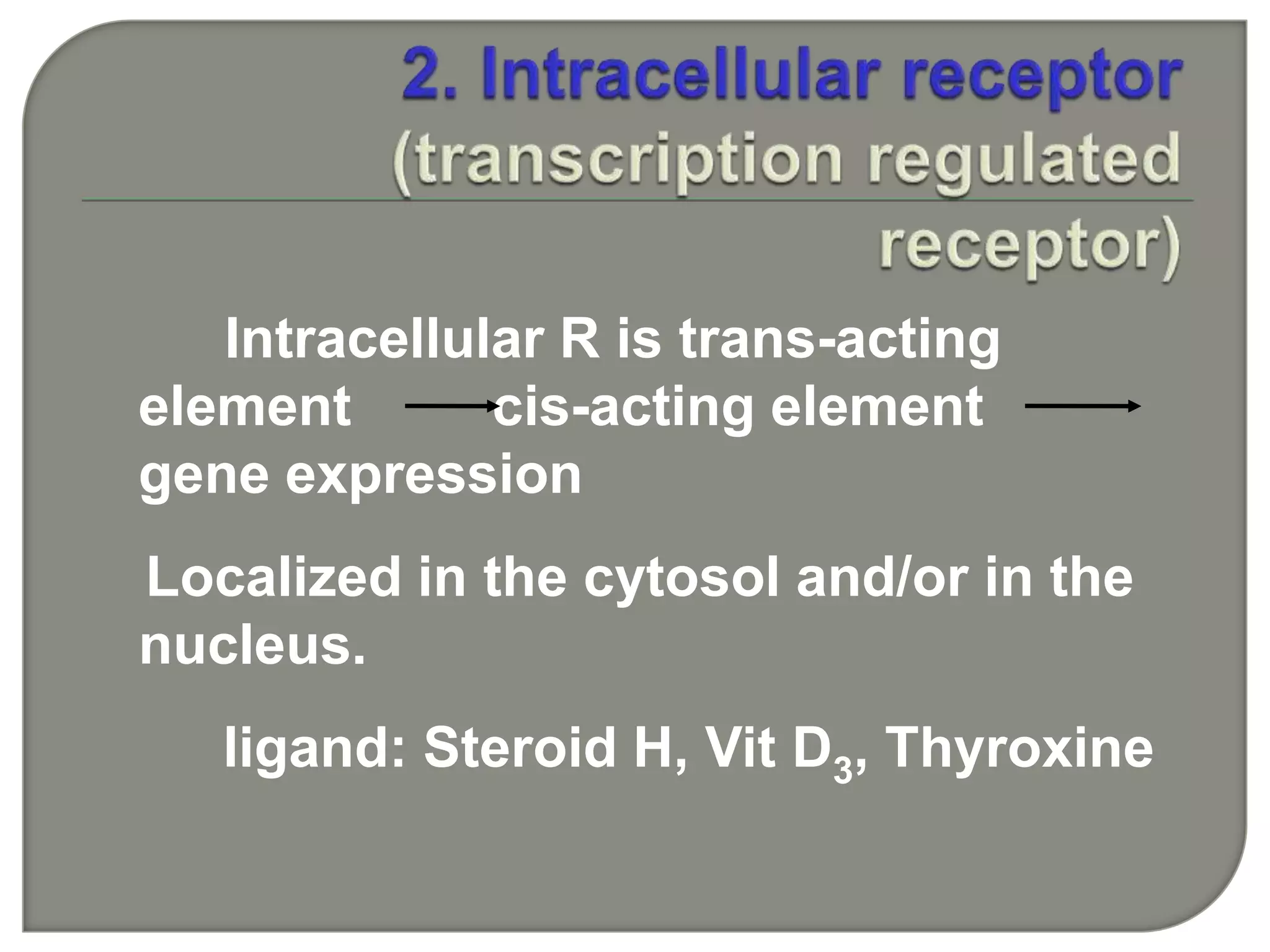
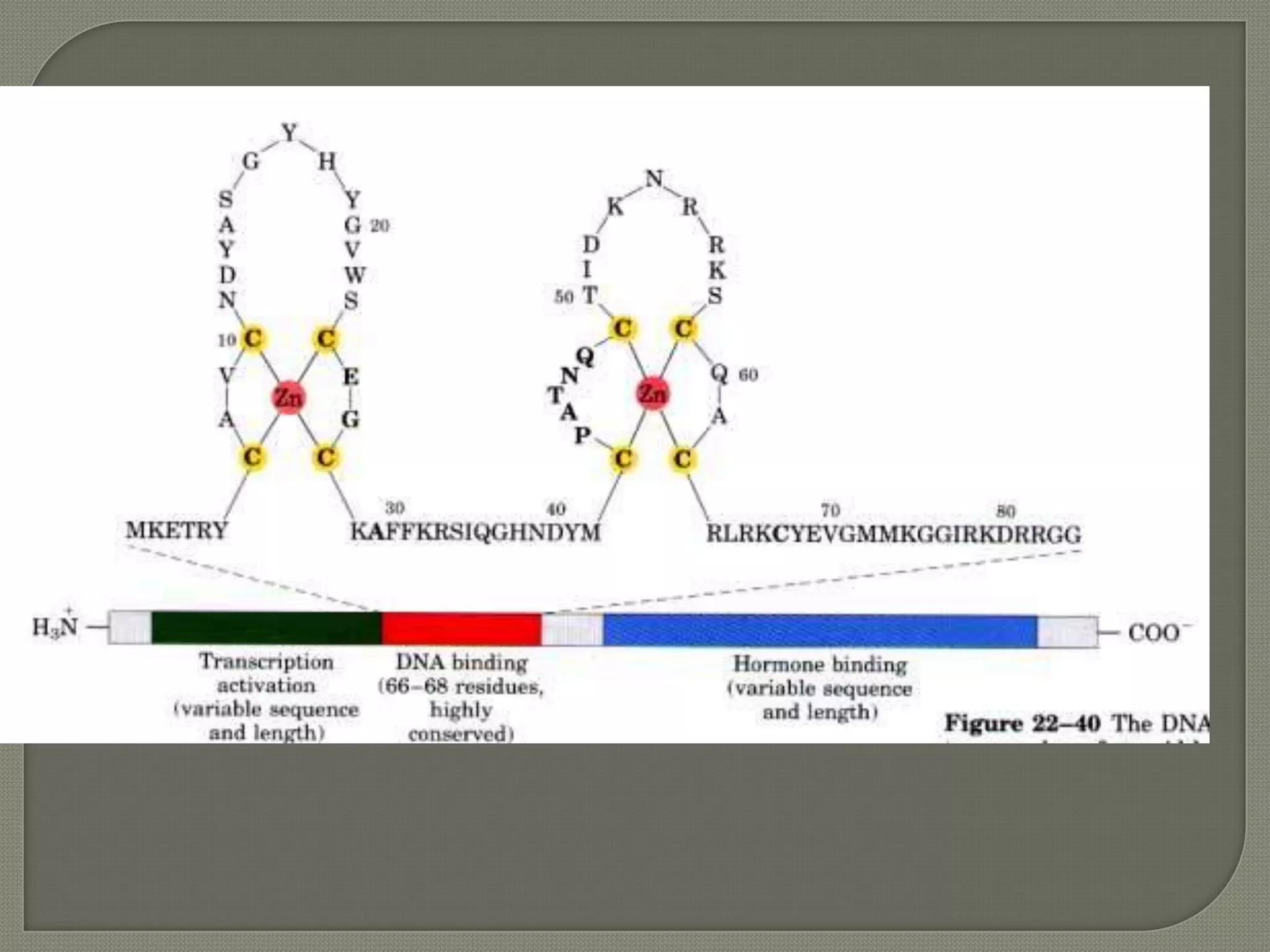


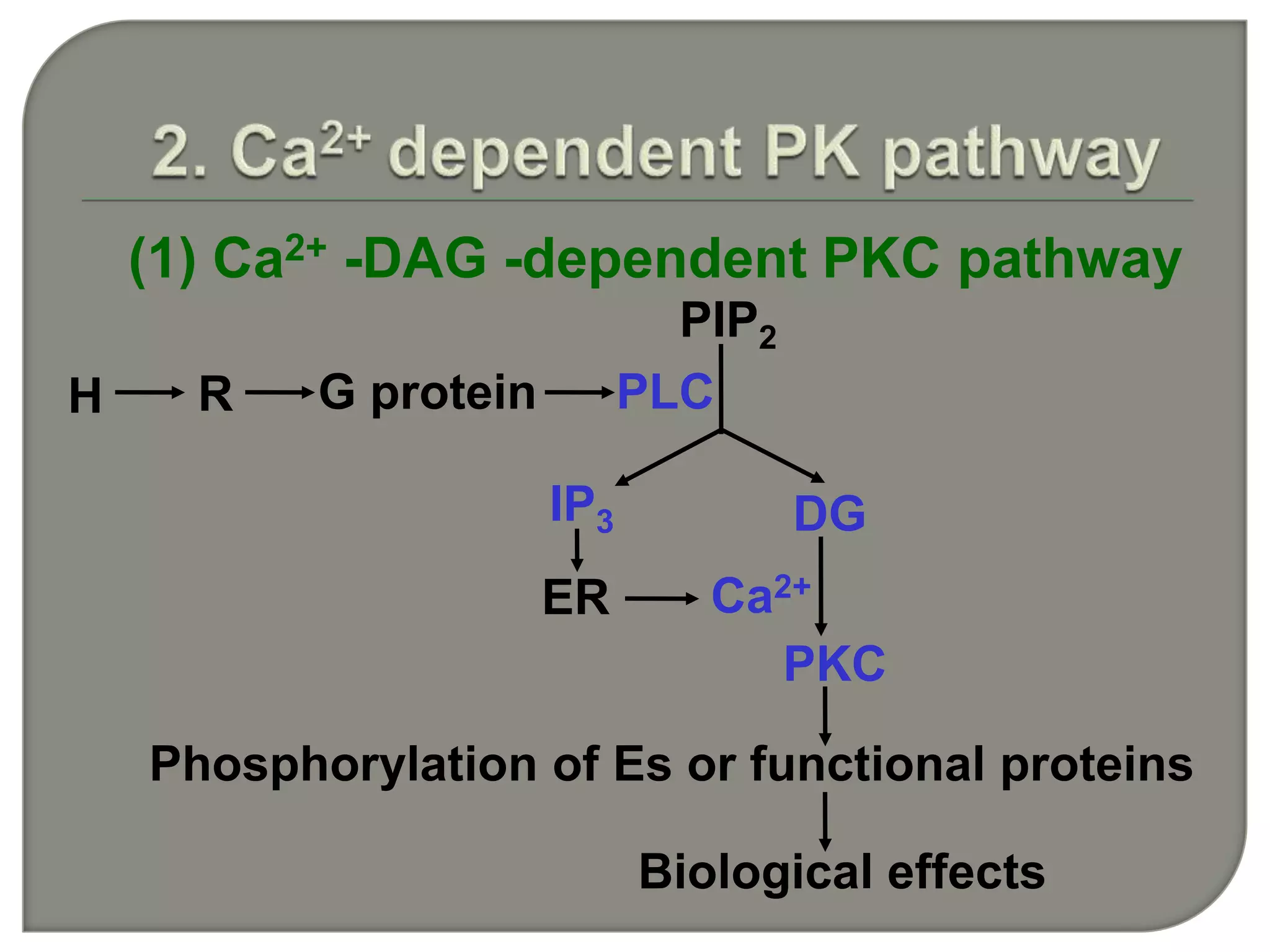
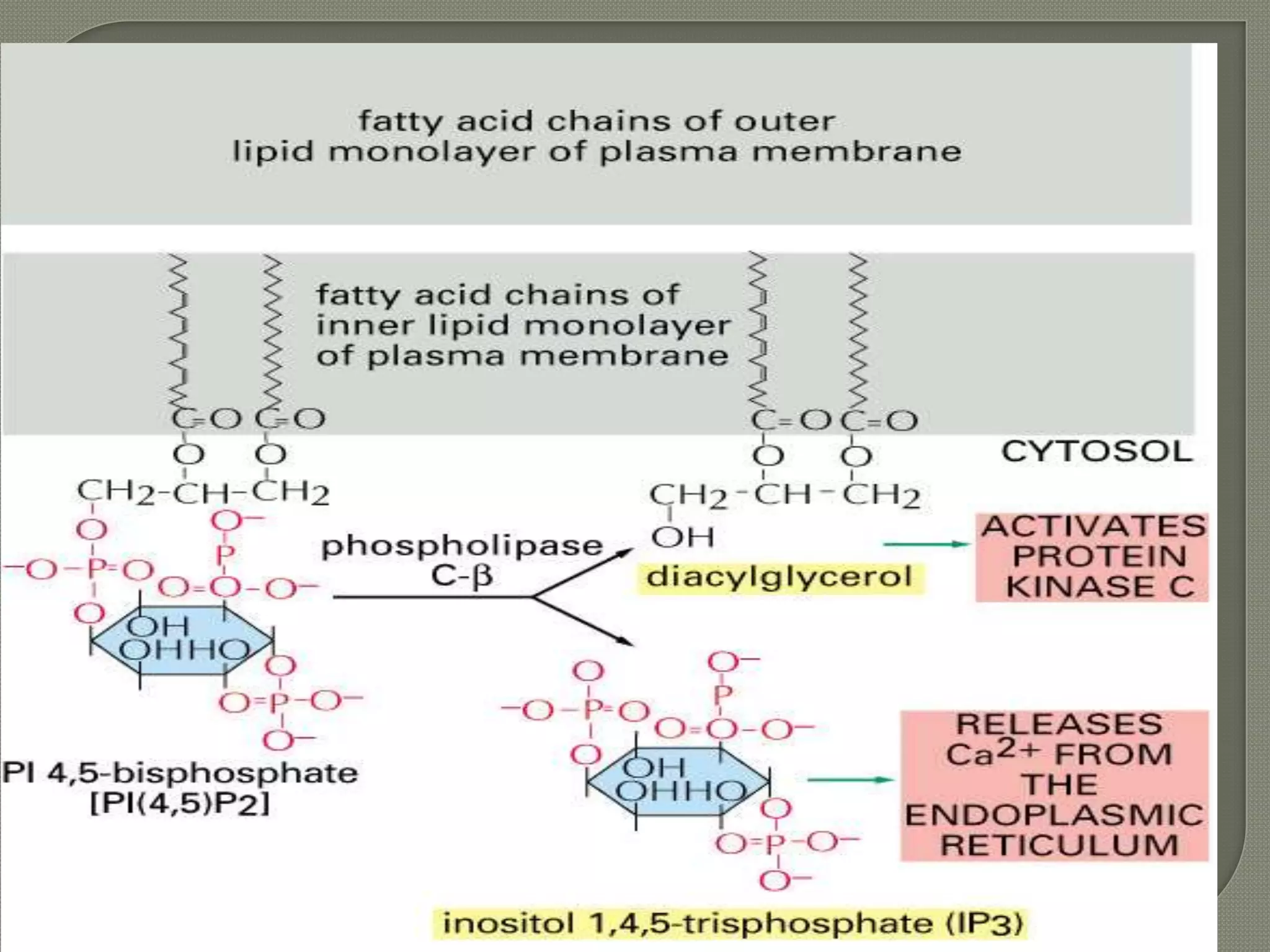
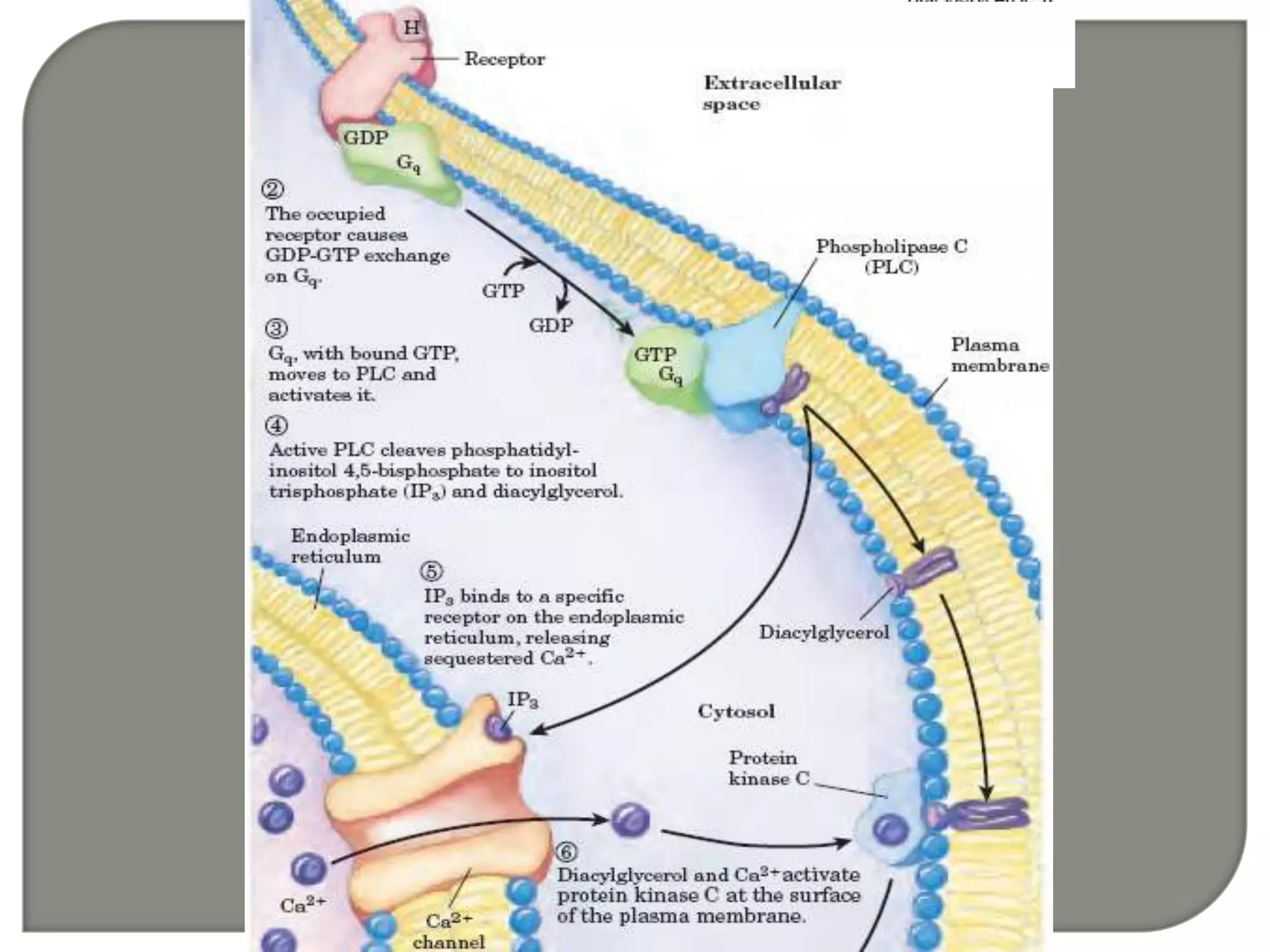
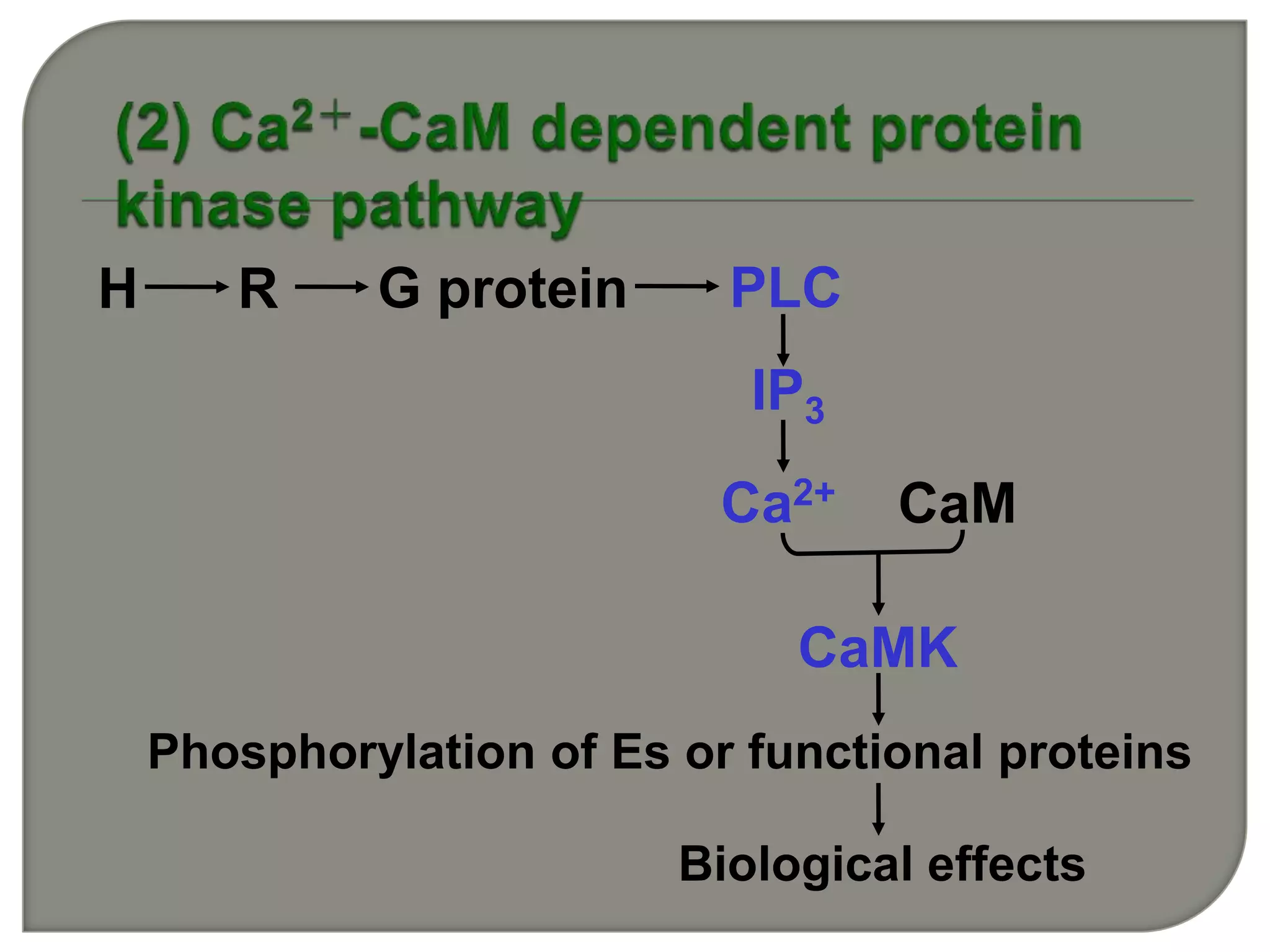
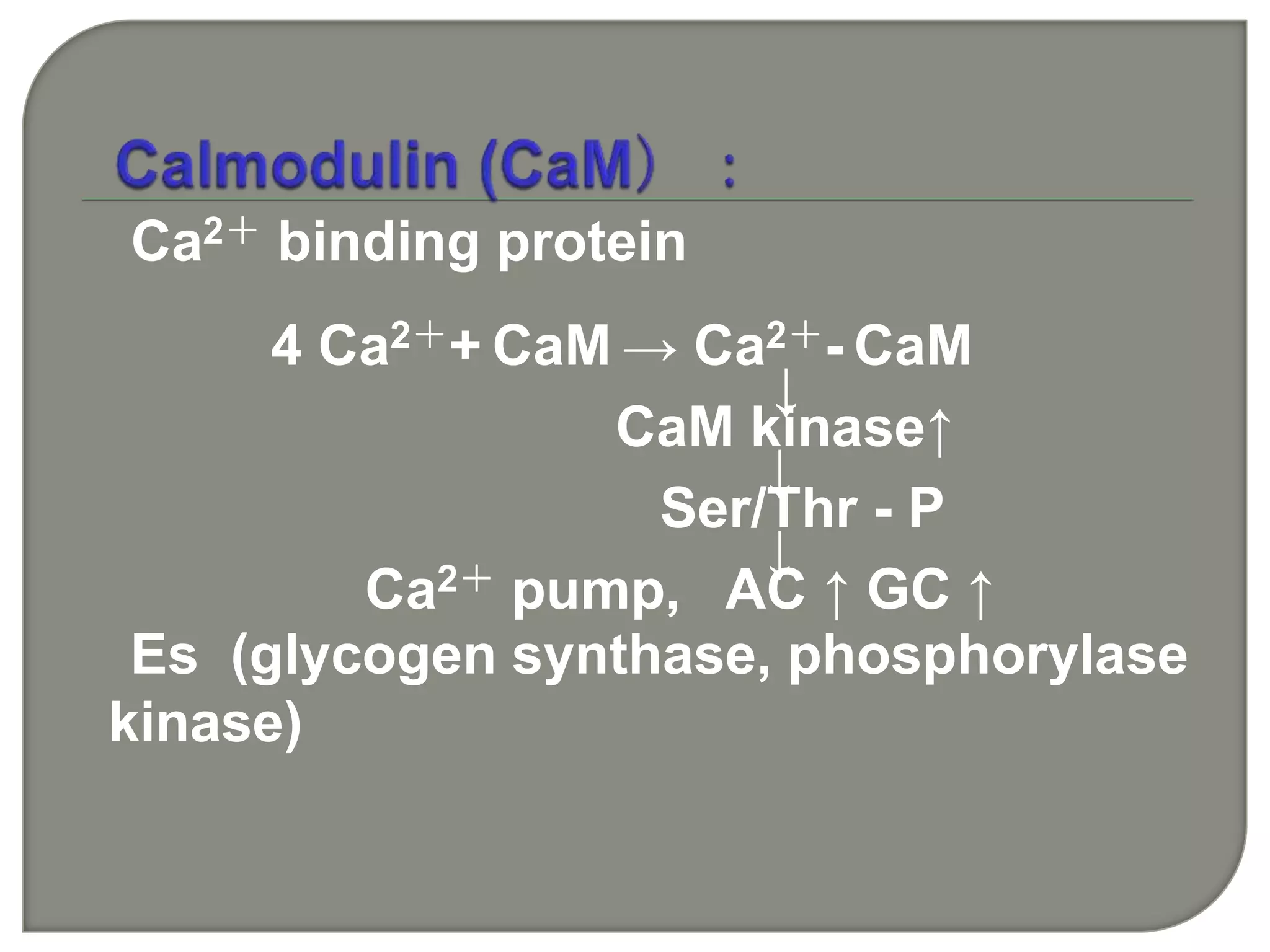
![IP3 + R→open of Ca2+
channel →[Ca2+]↑ from ER
[Ca 2+]i 0.01-1 mol/L(10-7 mol/L )
[Ca 2+]o 2.5mmol/L(10-3 mol/L )
5000~10000×
Ca2+
DG PKC ↑](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/signaltransduction-140330125824-phpapp01/75/Signal-transduction-55-2048.jpg)