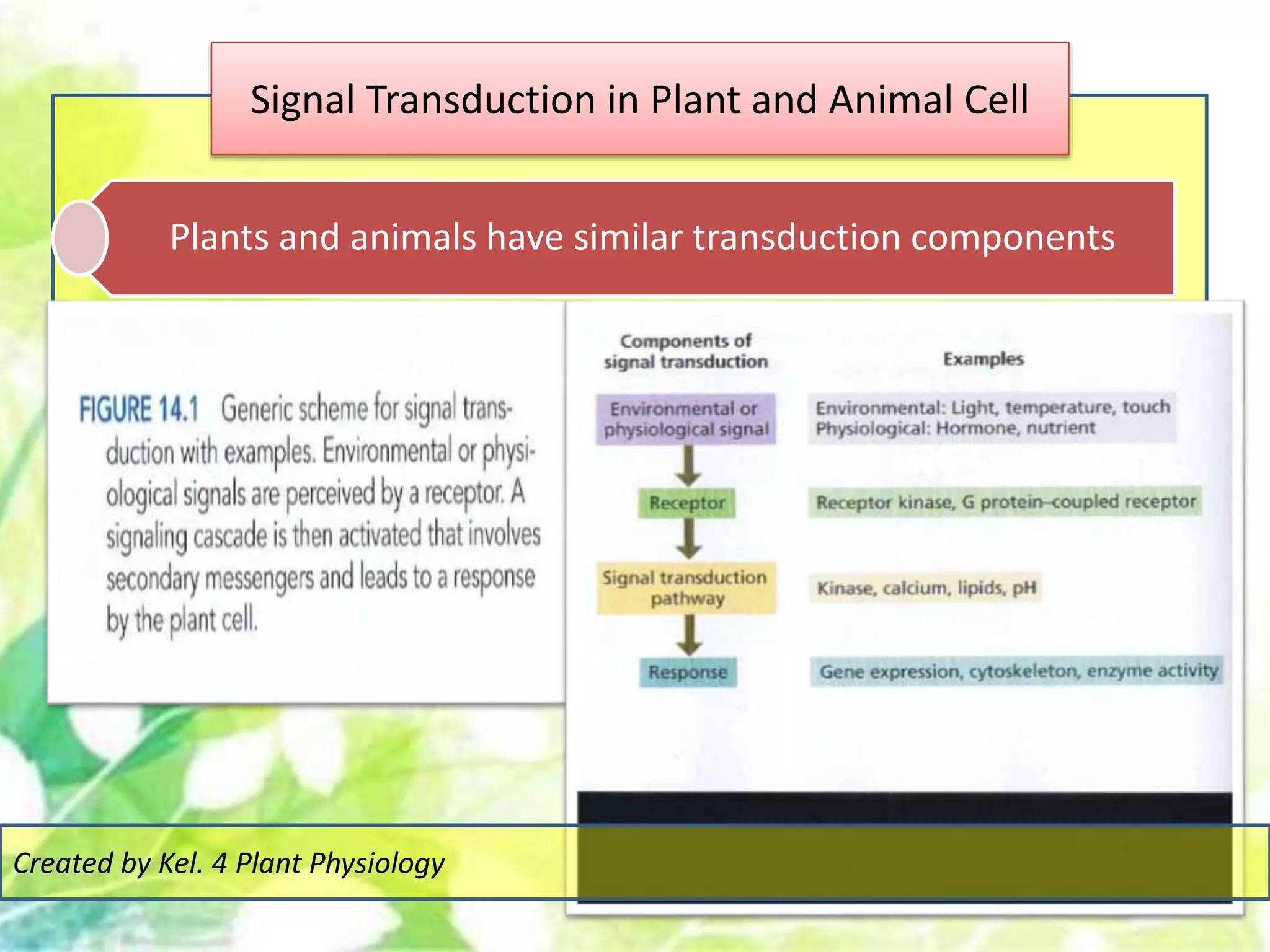
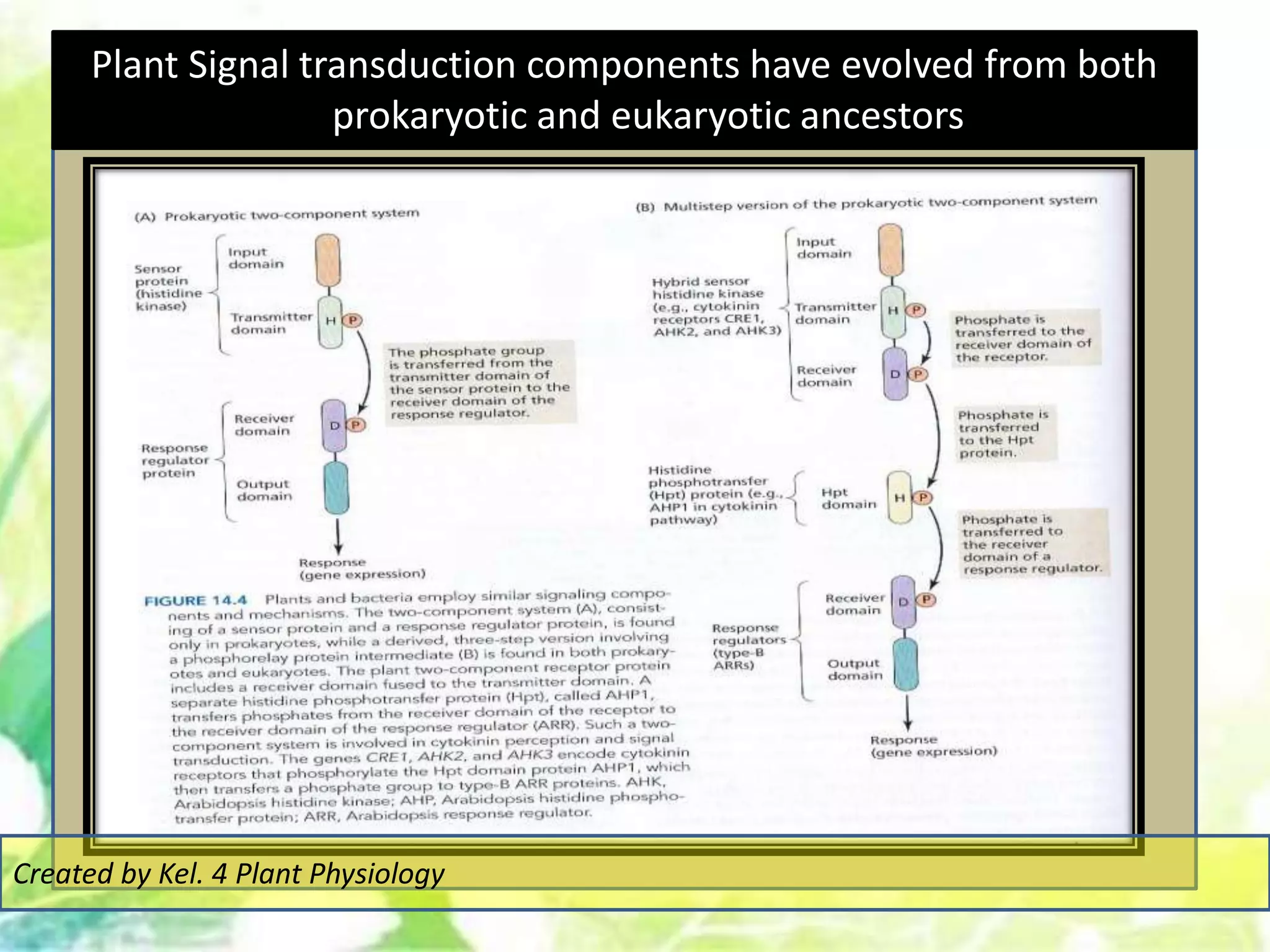
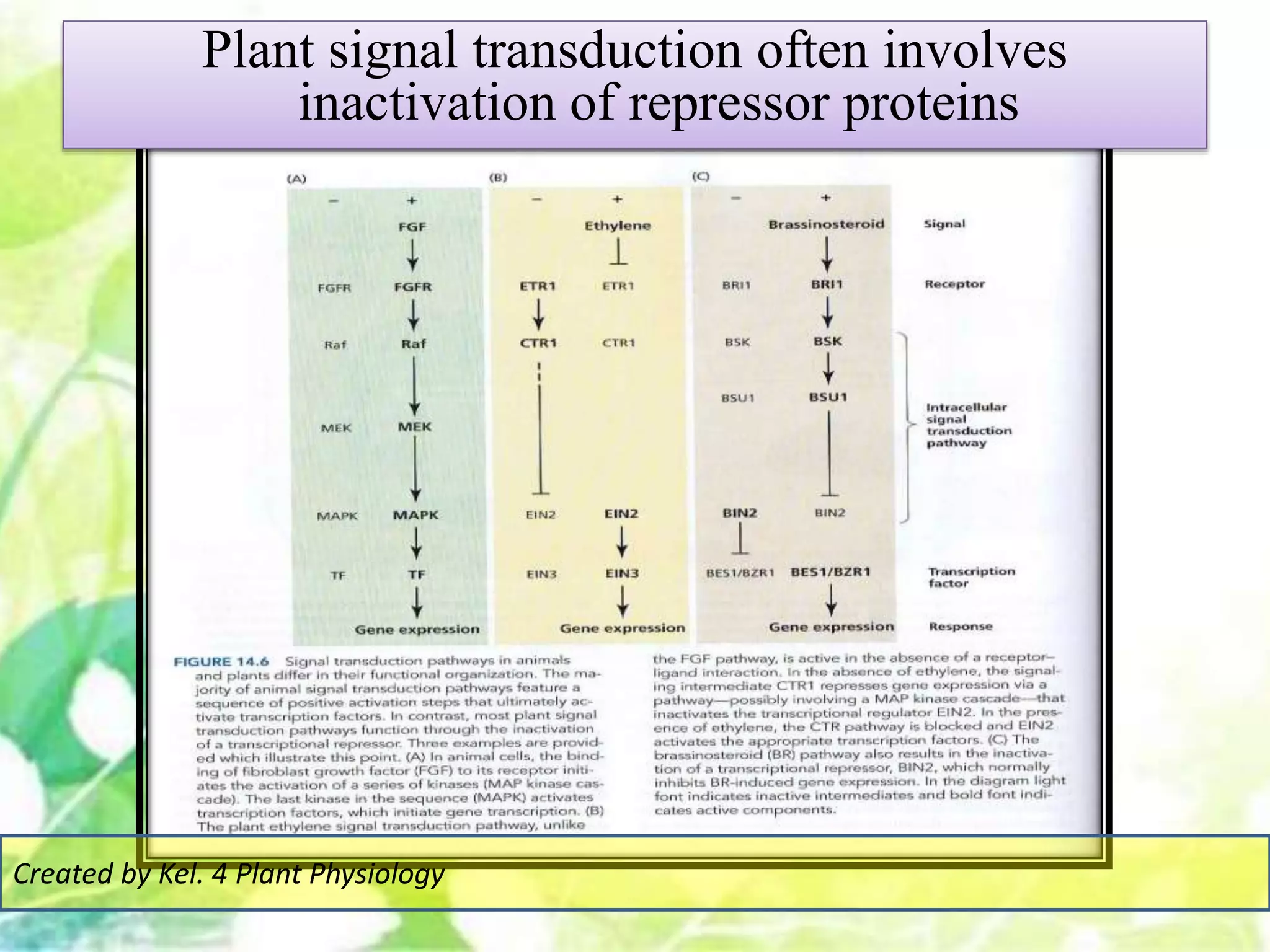
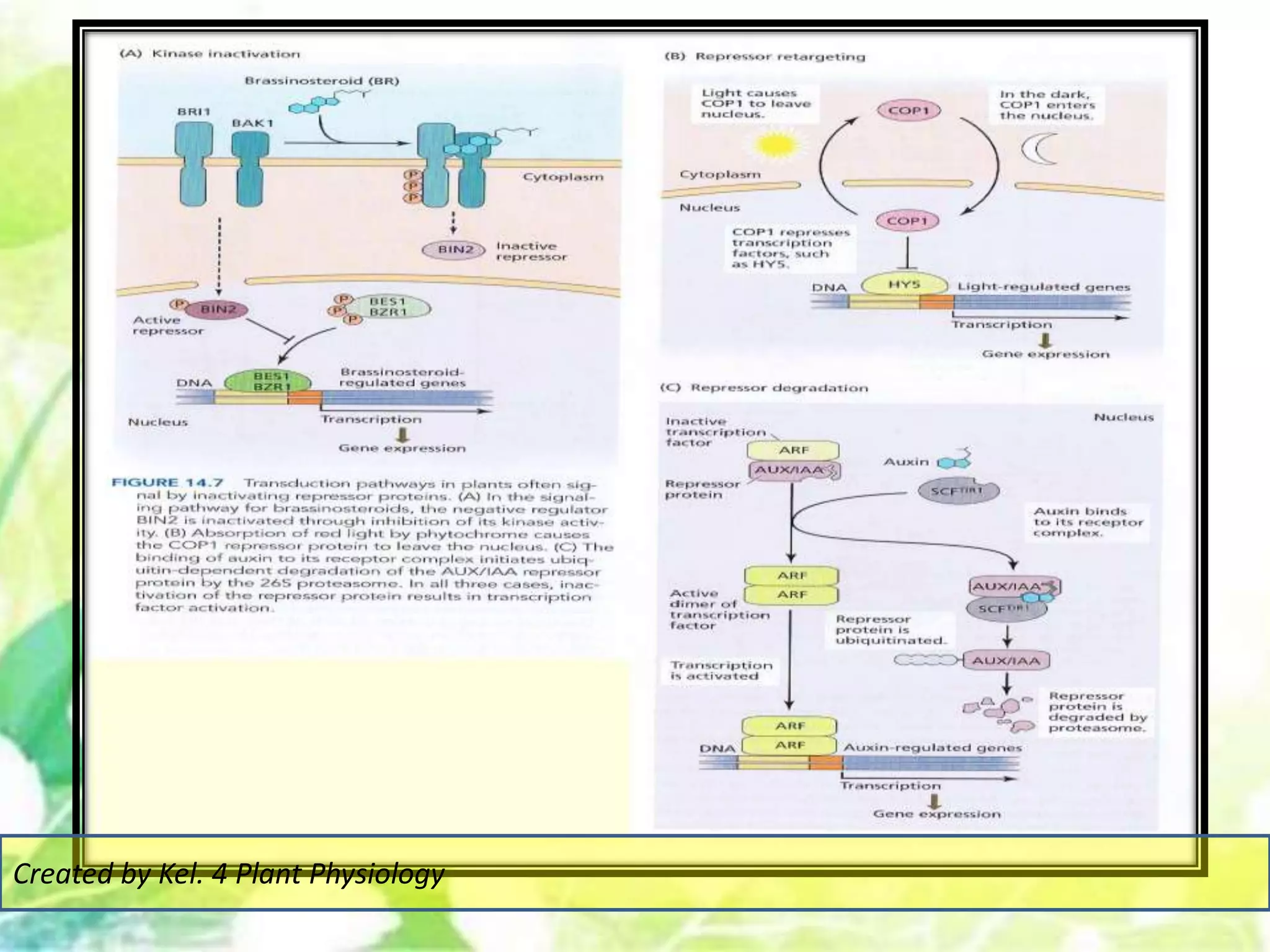
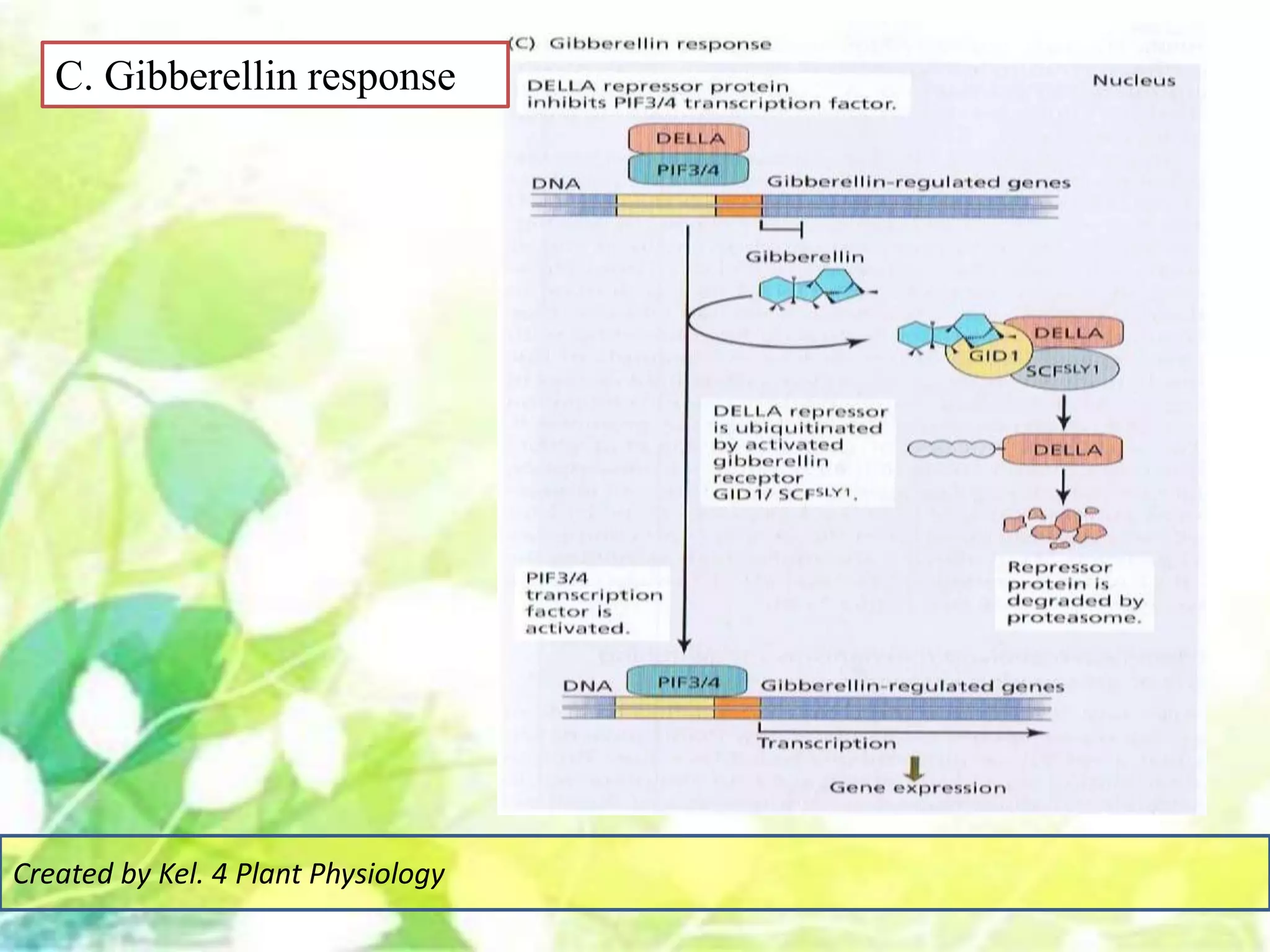
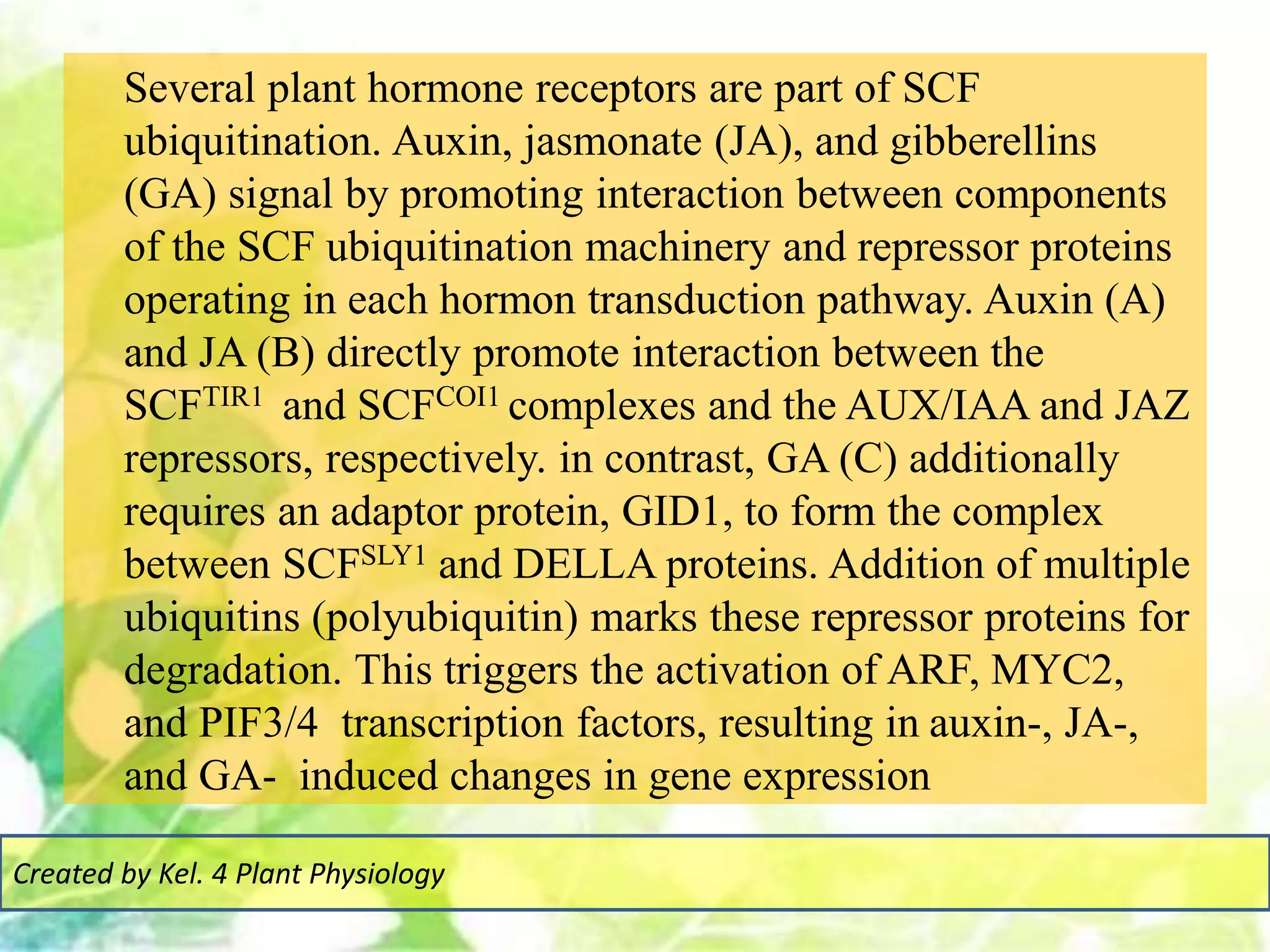
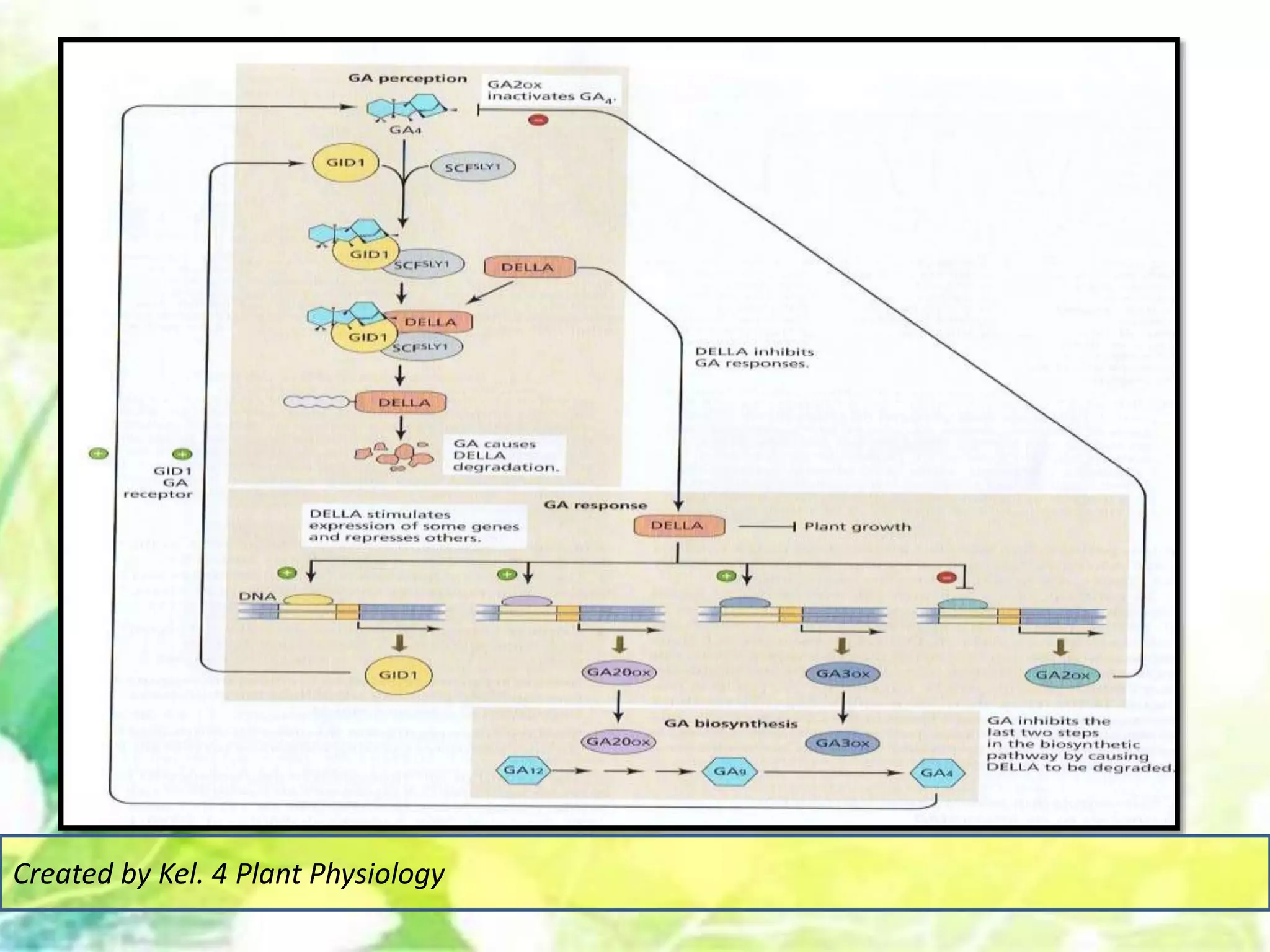
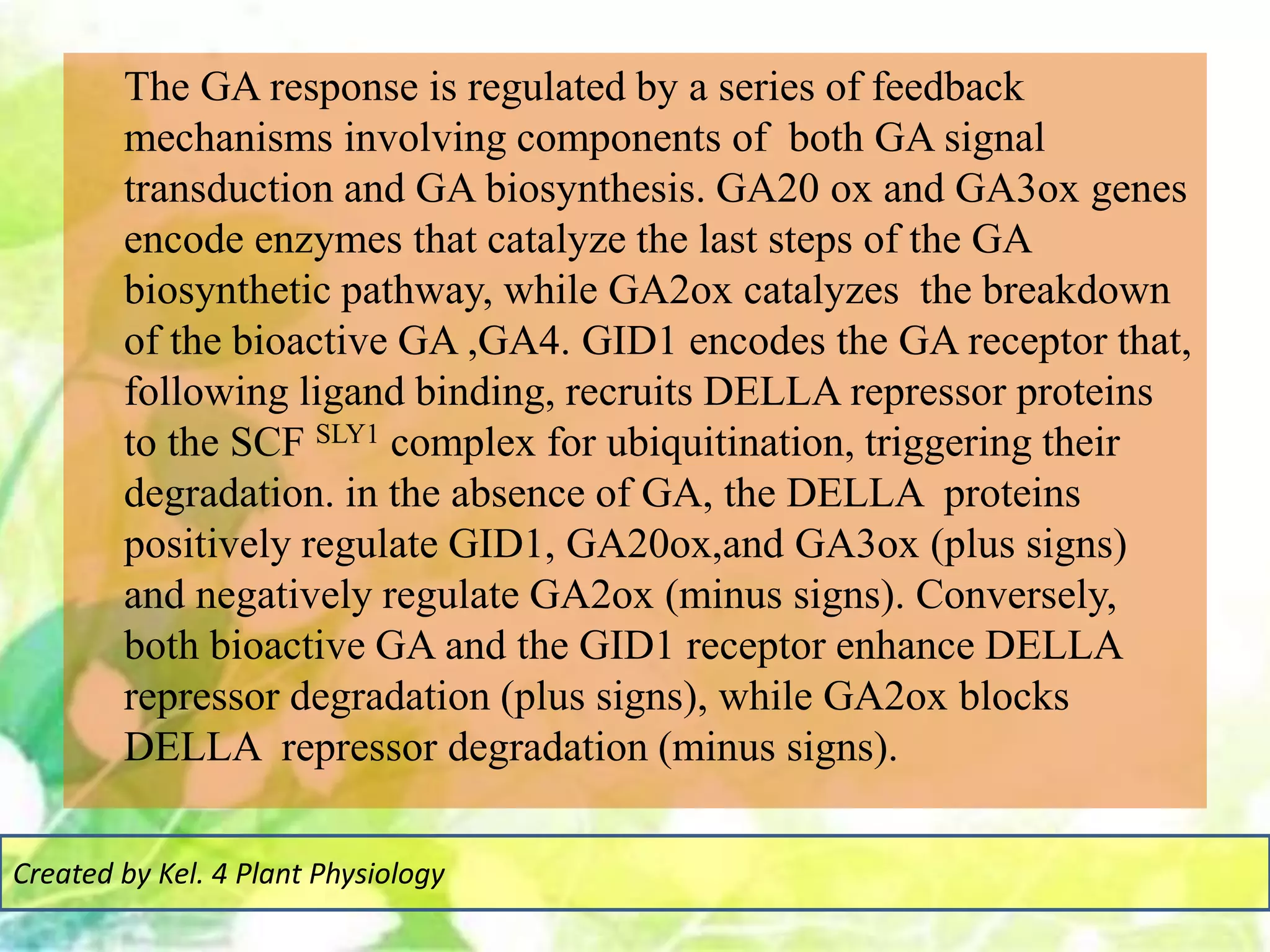
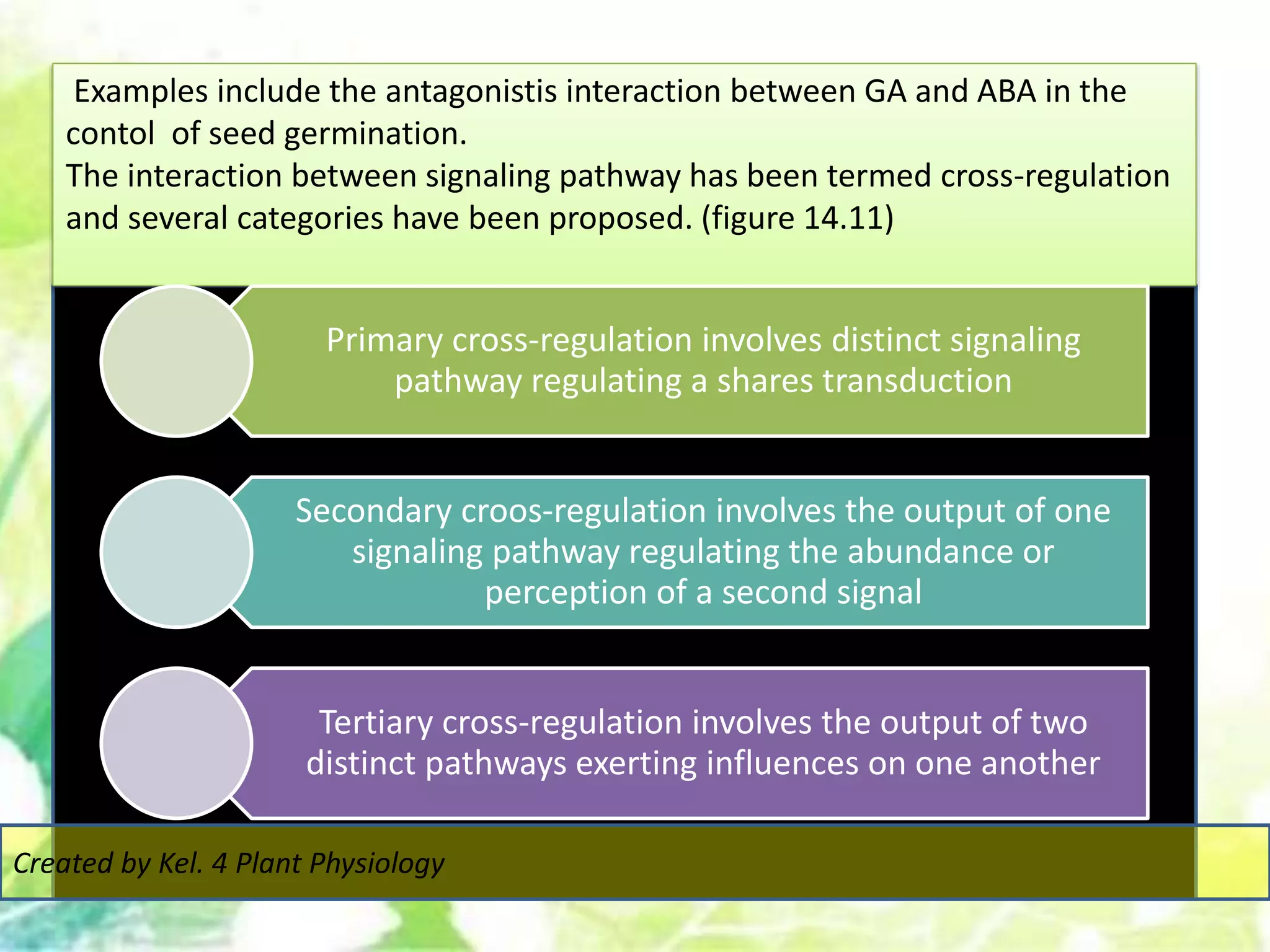
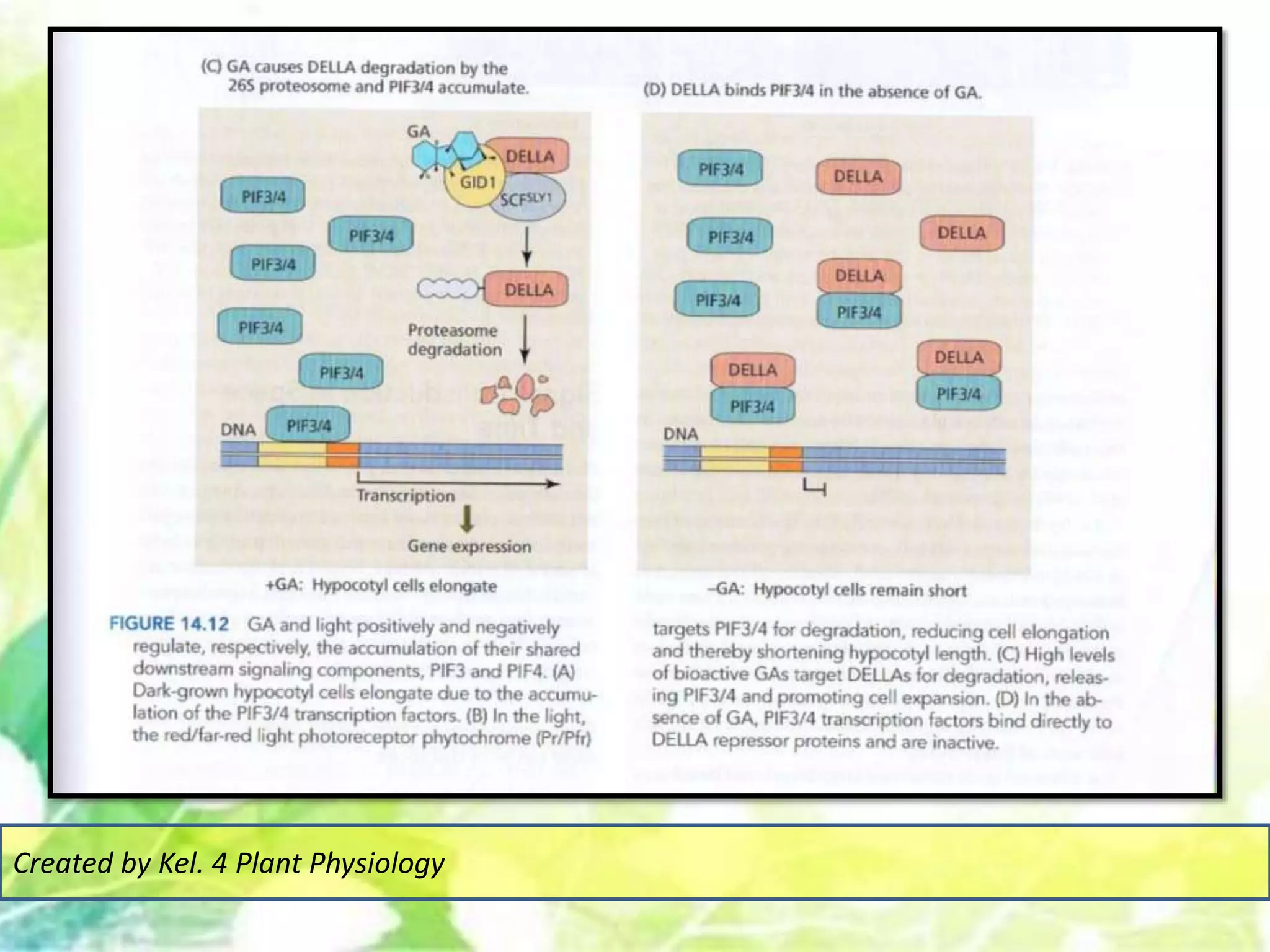
Signal transduction pathways allow plants to perceive environmental and physiological signals and fine-tune their growth and development. Key components of plant signaling include receptor kinases, protein kinases and phosphatases that activate downstream responses. Plant hormones like auxin, jasmonate, and gibberellin regulate gene expression by promoting the degradation of repressor proteins via the ubiquitin-proteasome system. Feedback loops and cross-regulation between signaling pathways allow for integration of different signals and attenuation of responses over time. Long-distance signal transduction within the plant is facilitated by movement of proteins between cells.